Bacillus gene scarless knockout/introduction plasmids, methods and kits
A bacillus, traceless knockout technology, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of low probability of gene knockout or knockin, low success rate, long cycle, etc., to achieve the effect of easy gene manipulation and plasmid transformation, and improve efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
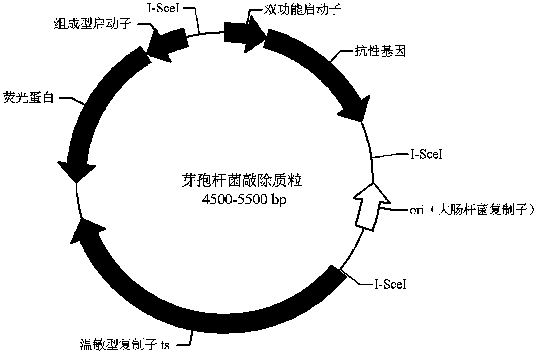
[0059] Example 1 Knockout plasmid pEBKS194-GFP+ containing I-SceI restriction site
[0060] As described in the content of the present invention, the knockout plasmid containing the I-SceI restriction site can have multiple combinations. This example uses one of the plasmid forms, pEBKS194-GFP+, to illustrate the construction process in detail. All primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0061] Construction of vector pWEBKS3
[0062] Using the expression plasmid pWEBK15 in the CN201410430501.3 patent (the antibiotic resistance gene of this plasmid is only the kanamycin resistance gene) as a template, the phosphorylated upstream and downstream primers F1 and R1 are used for full plasmid PCR amplification The amplified product was digested with restriction enzyme Dpn I overnight at 37°C and recovered, digested with Bgl II and ligated, transformed into Escherichia coli DH5α, and spread on a 50 μg / mL kanamycin resistant plate to screen positive The clones were sequenced with primer P1...
Embodiment 2
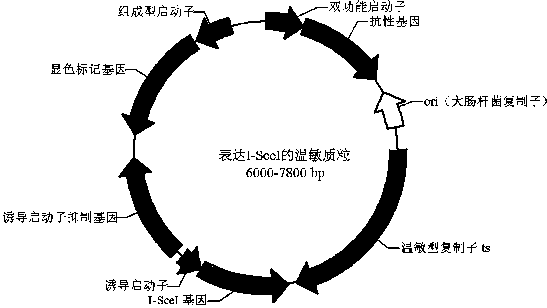
[0069] Example 2 Construction of temperature-sensitive plasmid pTISWts-RFP expressing I-Sce I enzyme
[0070] As described in the summary of the present invention, the temperature-sensitive helper plasmid expressing the I-SceI enzyme can have a variety of combinations. In this example, the construction process of one of the plasmid forms, pEBTWts-RFP, is described in detail. All primer sequences are shown in Table 1.
[0071] (1) Construction of vector pHYWVts
[0072] Using pHY300PLK vector (the plasmid contains antibiotic resistance genes including tetracycline resistance gene and ampicillin resistance) as a template, primers F8 and R8 are used to amplify the vector fragment; a synthetic temperature-sensitive replicon DNA fragment (SEQ ID NO. 16) As a template, use primers F9 and R9 to amplify the temperature-sensitive replicon WVts gene fragment. The amplified products of the gene fragment and vector fragment are digested with Dpn I enzyme overnight (37°C) and recovered, using th...
Embodiment 3
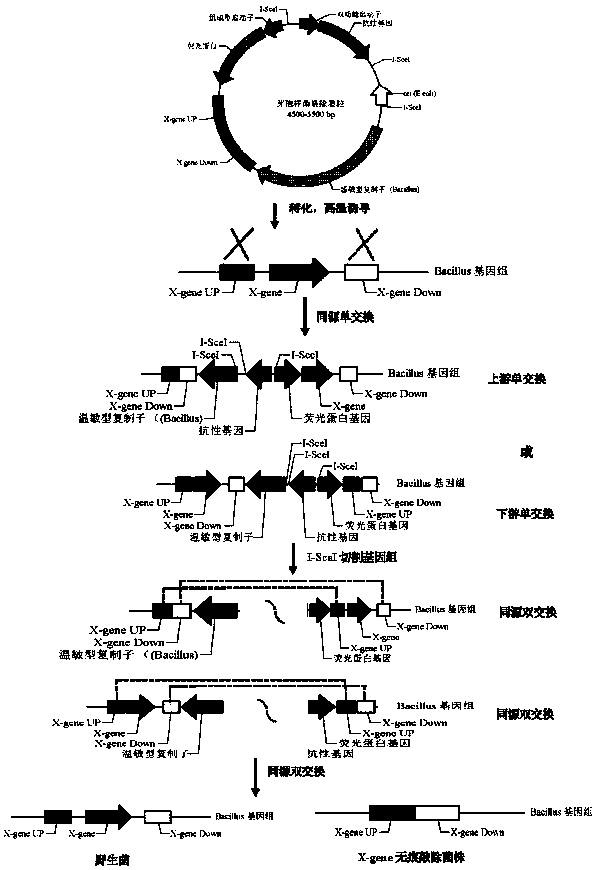
[0077] Example 3 Knockout of aprE gene in Bacillus subtilis CICC10073 strain
[0078] (1) Construction of knockout vector pKS194GFP-aprEUD
[0079] The CTAB (hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide) method was used to extract the genomic DNA of Bacillus as a template for gene amplification (reference: Acta Microbiology, 2006, 46 (1): 7-12.); with subtilis spores Bacillus CICC10073 genomic DNA was used as a template, primers F14 and R14 were used as primers to amplify the upstream homology arm aprE-UP of aprE gene, and primers F15 and R15 were used as primers to amplify the downstream homology arm aprE-down of aprE gene; GFP+ plasmid was used as a template to amplify the vector fragment with primers F4 and R6. The amplified product of the vector fragment was digested with Dpn I overnight at 37°C and recovered. The operating instructions of the seamless cloning kit were used for the vector fragment and two gene fragments. After ligation, Escherichia coli DH5α was transformed and spread o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com