Control device for an asynchronous machine and method for driving an asynchronous machine
A control device and motor controller technology, which is applied in the direction of controlling electromechanical brakes, controlling electromechanical transmission devices, controlling generators, etc., can solve the problems of inability to control asynchronous machines in a field-oriented manner, and achieve the effect of improving functional reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
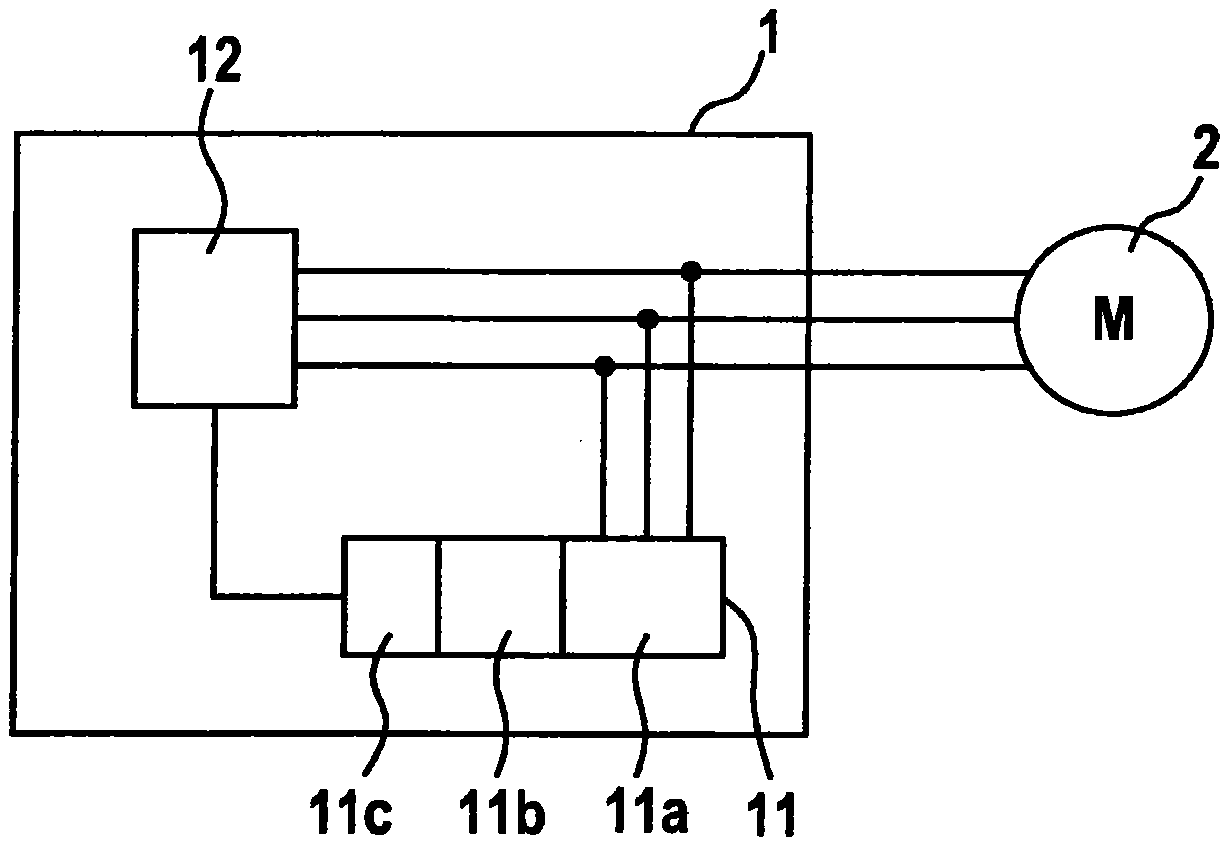
[0024] figure 1 Shown is a schematic diagram of a control device 1 for an asynchronous machine 2 , for example, according to an embodiment of the invention. The asynchronous machine 2 can here be any asynchronous machine, in particular an asynchronous machine with a squirrel-cage rotor. The asynchronous machine is preferably a three-phase AC asynchronous machine. Such an asynchronous machine comprises internally a rotatably mounted rotor and externally a stationary stator. In this case, a plurality of stator strands that are equally spaced apart from one another are introduced into the stator. These stator strands are, for example, winding wires.
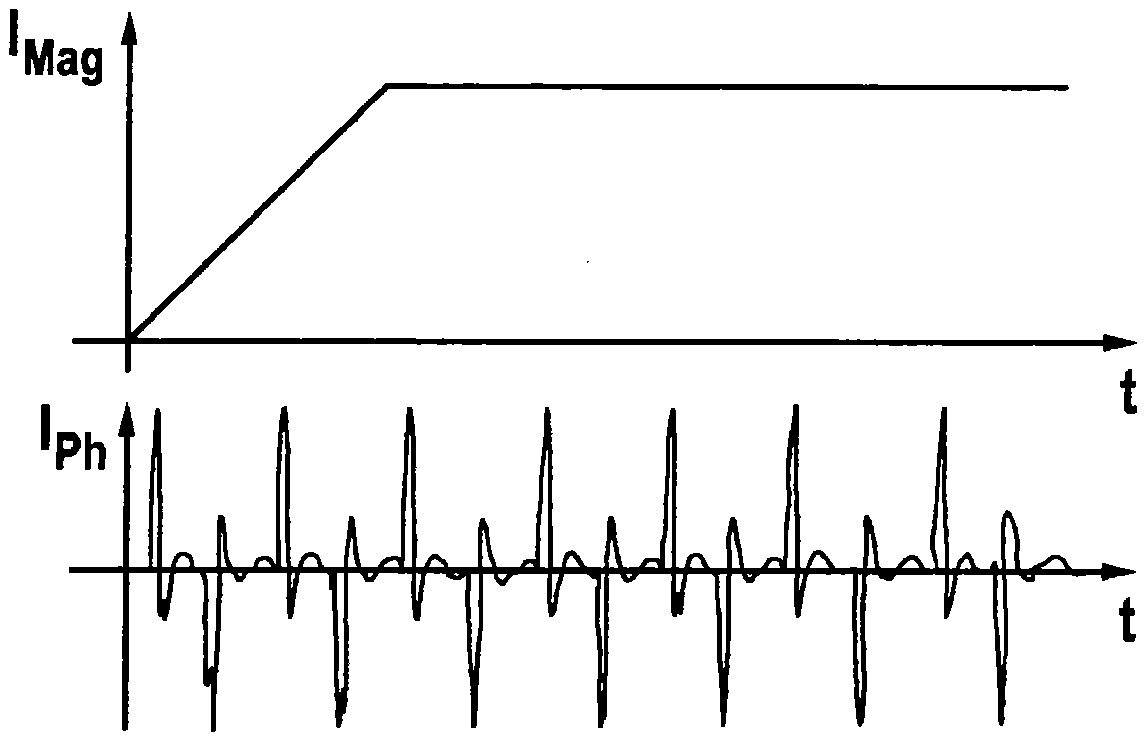
[0025] Since the asynchronous motor induces the rotor voltage through the stator magnetic field, the asynchronous motor does not initially have a rotor field when it is not powered. The rotor field must only be established during the magnetization phase. It is therefore initially not possible to determine the rotor field angle ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com