Hybrid braking excitation structure for maglev train
A magnetic levitation train, hybrid technology, applied in the direction of permanent magnet clutch/brake, asynchronous inductive clutch/brake, electric braking system, etc., can solve the problems of lack of fail-safe guidance, affecting braking effect, heating of excitation coil, etc. , to achieve the effect of energy saving and thermal management, improve reliability and safety, and reduce power loss
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing.
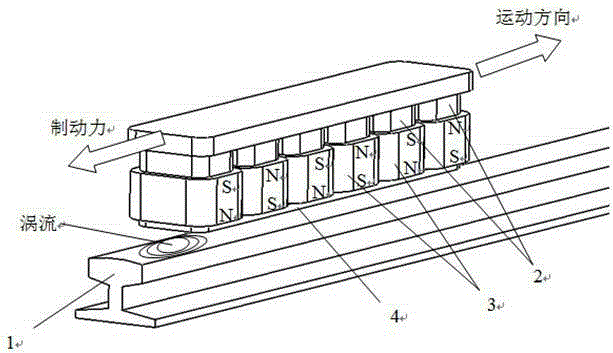
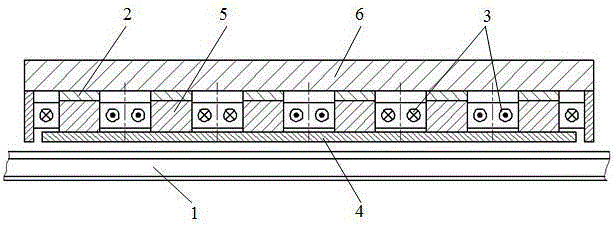
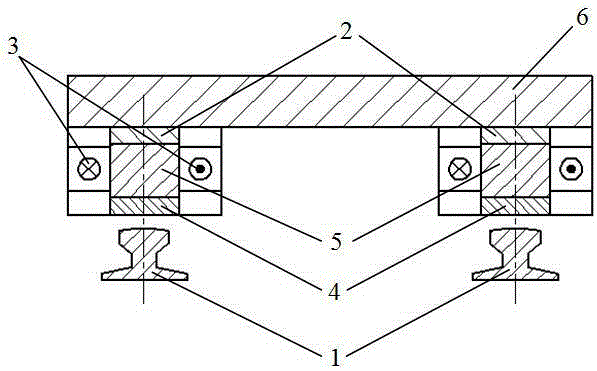
[0031] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention mainly arranges a plurality of magnetic poles composed of electromagnets and permanent magnets in the direction of the rails, and is installed at the bottom of the train directly above the rails: the magnetic poles include iron core 5, armature coil 3 and permanent magnets 2. The magnetic field direction of the permanent magnet 2 is perpendicular to the horizontal plane, and the iron cores 5 are arranged at intervals in the direction of the rail. The armature coil 3 with the excitation current is wound around each iron core 5 horizontally, and the permanent magnet 2 is installed on the top of the iron core 5. Thereby forming magnetic poles; the upper end of each permanent magnet 2 is equipped with a yoke 6 in the direction of the rail, and the lower end of each iron core 5 is equipped with a wear plate 4 .
[0032] Su...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com