Method of synchronously degrading excess sludge and treating hexavalent chromium wastewater
A technology for excess sludge and hexavalent chromium, applied in biological sludge treatment, water/sludge/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problem of high treatment cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
[0011] Specific embodiments: a method for synchronously degrading excess sludge and treating hexavalent chromium wastewater according to the present embodiment is carried out in the following steps:
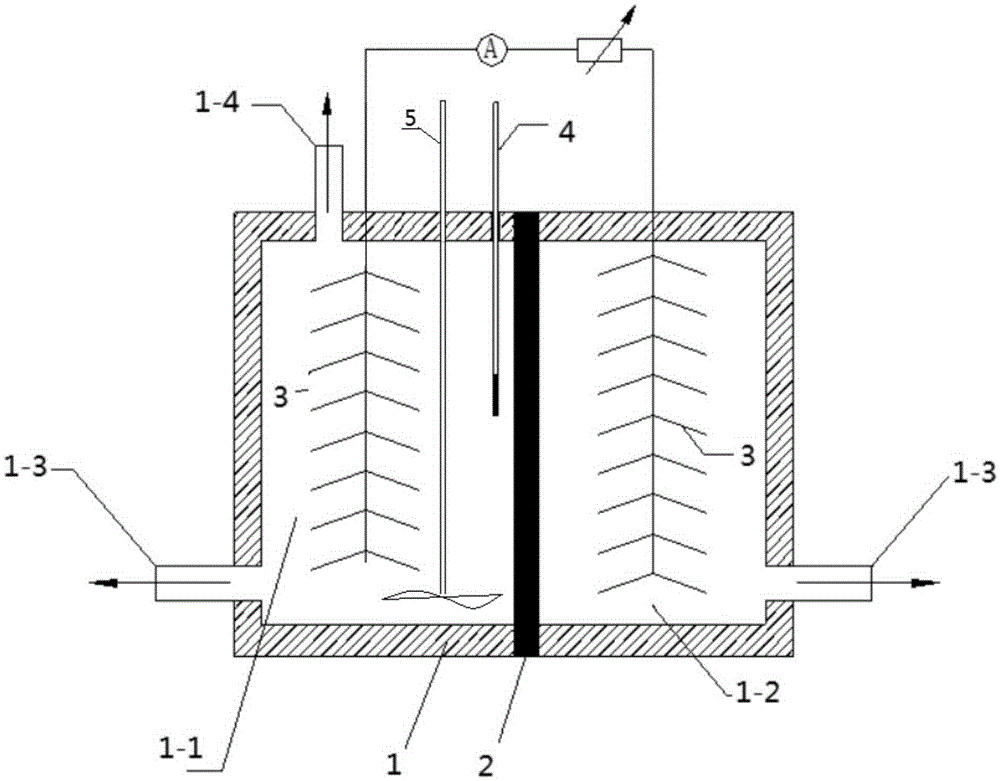
[0012] 1. Build a double-cell structure reactor: the double-cell structure reactor is composed of a shell 1, a cation exchange membrane 2, a carbon fiber brush 3, a reference electrode 4 and a stirrer 5, and the cation exchange membrane 2 is set in the shell 1. Housing 1 is divided into anode chamber 1-1 and cathode chamber 1-2, the carbon fiber brush 3 that is arranged in the anode chamber 1-1 is an anode, the carbon fiber brush 3 that is arranged in the cathode chamber 1-2 is a cathode, in the anode chamber 1-1 and the bottom of the cathode chamber 1-2 are respectively provided with a sampling tube 1-3, and the top of the anode chamber is provided with a gas collector 1-4; the anode and the cathode are connected through an external circuit; the reference electrode 4 penetrates i...
specific Embodiment approach 2
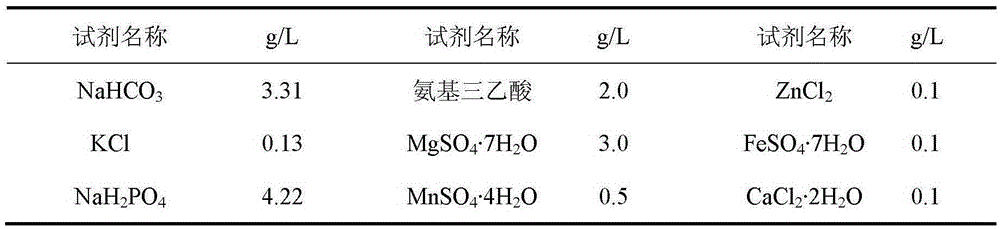
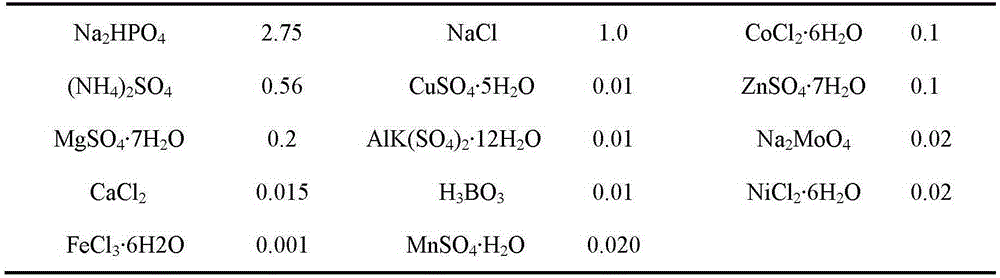
[0015] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is that the composition and proportioning ratio of the nutrient solution in step two are as shown in Table 1:
[0016] The composition and proportioning ratio of table 1 nutrient solution
[0017]
[0018]
[0019] Others are the same as the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0020] Specific embodiment three: what this embodiment is different from specific embodiment one or two is that potassium ferricyanide catholyte is according to potassium ferricyanide (K 3 [Fe(CN) 6 ] concentration of 30 ~ 35g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH 2 PO 4 ) with a concentration of 25-30 g / L, which is prepared by adding potassium ferricyanide and potassium dihydrogen phosphate into water; the others are the same as those in Embodiment 1 or 2.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com