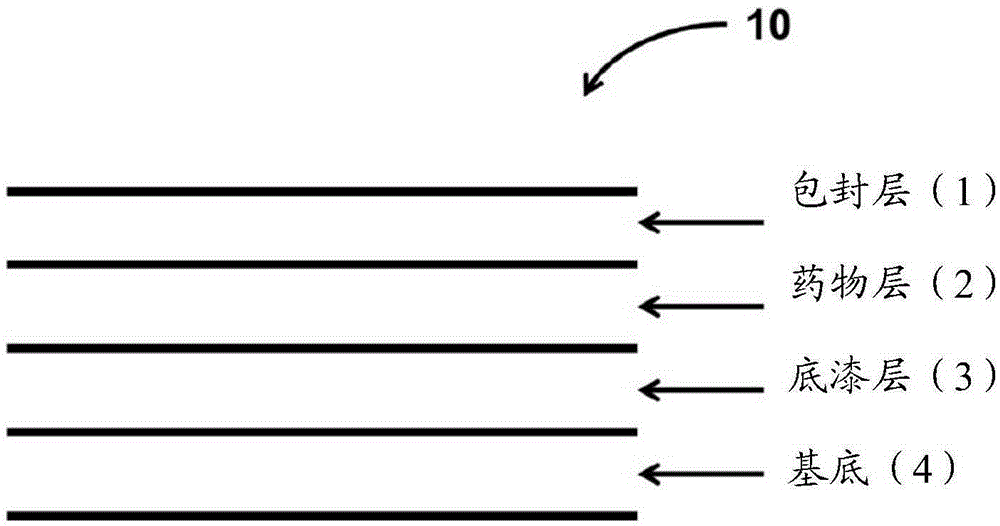
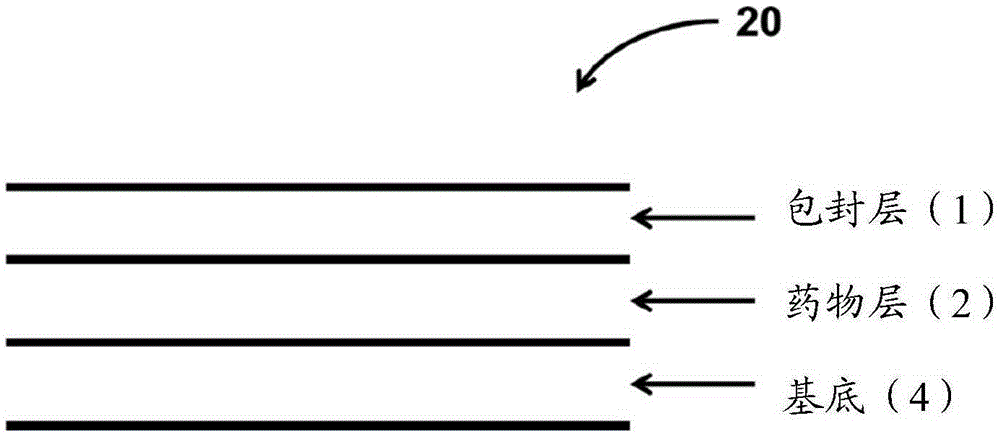
Coatings for controlled release of highly water soluble drugs
A technology for water-soluble drugs and drugs, applied in drug delivery, antibacterial drugs, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to design stable interception or enveloping coatings, ruptures, abrasions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0108] Example 1. General Coating Procedure
[0109] A. Primer layer:
[0110] Silicone catheters (0.5 mm outer diameter) were dip-coated with a 30 mg / ml Photo-POMAS solution in isopropanol. Initially, clean the silicone rubber by rubbing it with isopropyl alcohol six times with a lint-free cloth. Then, the catheter was inserted into the coating solution at a rate of 2 cm / sec, left in the solution for 30 seconds, and withdrawn from the coating solution at 0.5 cm / sec. The primer coat was air dried at room temperature for 10 minutes and then UV irradiated with 254 nm light (40 mW / cm2) for one minute.
[0111] B. Silver nitrate layer:
[0112] An aqueous solution of silver nitrate was prepared by dissolving 20 grams of silver nitrate (USP grade, 99.8-100.2%, Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) in 10 ml of distilled water. This silver nitrate solution was sprayed onto the primer coated piece with a low volume, low pressure EFD7856-46SS spray head (Nordson EFD, East Providence, RI) w...
example 2
[0115] Example 2. Slow Elution of Silver Nitrate
[0116] An eluting solution was prepared by adding 20 ml of ionic strength modifier (sodium nitrate solution, Orion 940011, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) to 1 liter of distilled water followed by 0.03 g of sodium bicarbonate. A catheter coated with 89.9 mg of total silver nitrate as described in Example 1 was placed in 150 ml of this elution solution in a capped 500 ml Erlenmeyer flask at 37°C with rotary shaking at 50 rpm. The elution solution was changed daily, and the silver content of each elution change was measured using a silver ion selective electrode (OrionIonPlus silver / sulfide electrode, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA) and an instrument (OrionStar214 pH / ISE meter, ThermoFisher Scientific, Waltham, MA). ). Table 1 shows the resulting silver content in mg / L silver ion.
[0117] Table 1.
[0118]
example 3
[0119] Example 3. Silver nitrate loading
[0120] Primer-coated pieces coated as in Example 1 were weighed in triplicate and then coated with silver nitrate as described in Example 1 with varying nozzle stroke capacities. After drying overnight, catheters were reweighed in triplicate. Table 2 contains weights showing different application of silver nitrate depending on nozzle width. A second coat of silver nitrate can be applied, repeating the conditions in Example 1B. The weight after drying overnight at room temperature is also shown in Table 2.
[0121] Table 2.
[0122]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com