Tobacco specific nitrosamine reduction in plants
A plant and plant cell technology, applied in the fields of tobacco, plant peptides, tobacco treatment, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
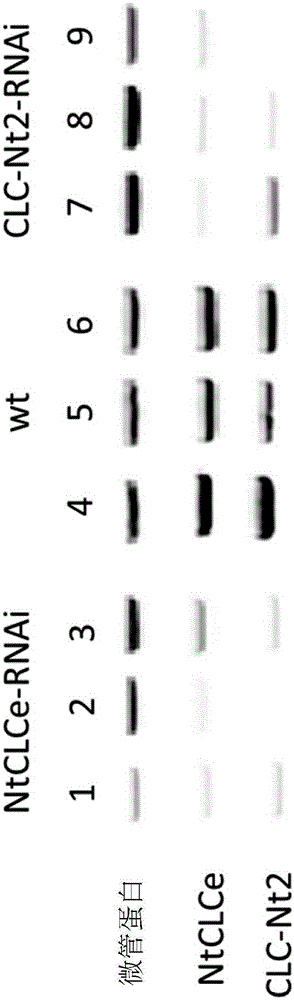
[0261] Example 1: Identification of NtCLCe-s sequence
[0262] To identify NtCLCe-s, the associated transcript (NtCLCe-s: NCBI_43350-v4ctg-in) was detected in common tobacco leaves by RT-PCR analysis and the presence of potentially matching EST contigs. Data from an Affymetrix custom-made tobacco exon array (sequence probes from NtPMIa1g22230e1-st) were used to confirm that NtCLCe-s are equally expressed in roots, green leaves and senescent leaves of Nicotiana vulgaris. In addition, it was found that cold stress and strong cadmium stress did not affect the expression level of NtCLCe-s, thus suggesting that NtCLCe-s is constitutively expressed in tobacco root and leaf organs. Constitutive NtCLCe expression may be linked to the maintenance of its essential cellular role in plastids, which are putatively linked to the nitrogen assimilation pathway. According to the WoLFPSORT software, NtCLCe-s are highly predicted to be plastid membrane proteins. RNAseq studies confirm the pr...
example 2
[0263] Example 2: Identification of NtCLCe-t sequence
[0264] To identify NtCLCe-t, associated transcripts were detected in common tobacco leaves by RT-PCR analysis and the presence of corresponding EST contigs. RNAseq studies confirm the presence of transcripts in its progenitor Nicotiana tomentosa, thus suggesting that expression of NtCLCe-t copies may be lost in N. Row.
example 3
[0265] Example 3: Expression of NtCLCe-s or NtCLCe-t in Common Tobacco Leaves
[0266] Both CLC-Nt2-s and CLC-Nt2-t genes are expressed in common tobacco leaves, as indicated by the presence of both transcripts in common tobacco leaves (customized tobacco exon array study validated by RT-PCR ) and corresponding EST contigs (CLC-Nt2-s: MIRA_20760-v4ctg-in; CLC-Nt2-t: NCBI_56794-v4ctg-in). In addition, RNAseq studies confirmed the presence of corresponding transcripts in two ancestral species, N. americanum and N. tomentosa.
[0267] When looking more closely at the transcriptome data from the tobacco exon array using the probes NtPMIa1g19904e2-st and NtPMIa1g50210e2-st specific for CLC-Nt2-t and CLC-Nt2-s, respectively , it can be seen that the two copies are differentially expressed in common tobacco. CLC-Nt2-s is weakly expressed in Burley root (TN90), and CLC-Nt2-t is sensitive to circadian rhythm. Both genes were expressed in smoked tobacco roots and leaves and were in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com