Preparation method of sheet-shaped alpha-Fe2O3/ZnO composite photocatalyst
A technology of -fe2o3 and compound light, which is applied in the field of preparation of sheet-shaped α-Fe2O3/ZnO composite photocatalyst, can solve the problems of secondary preparation and high cost, and achieve the effect of improving utilization rate, mild reaction conditions and low energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
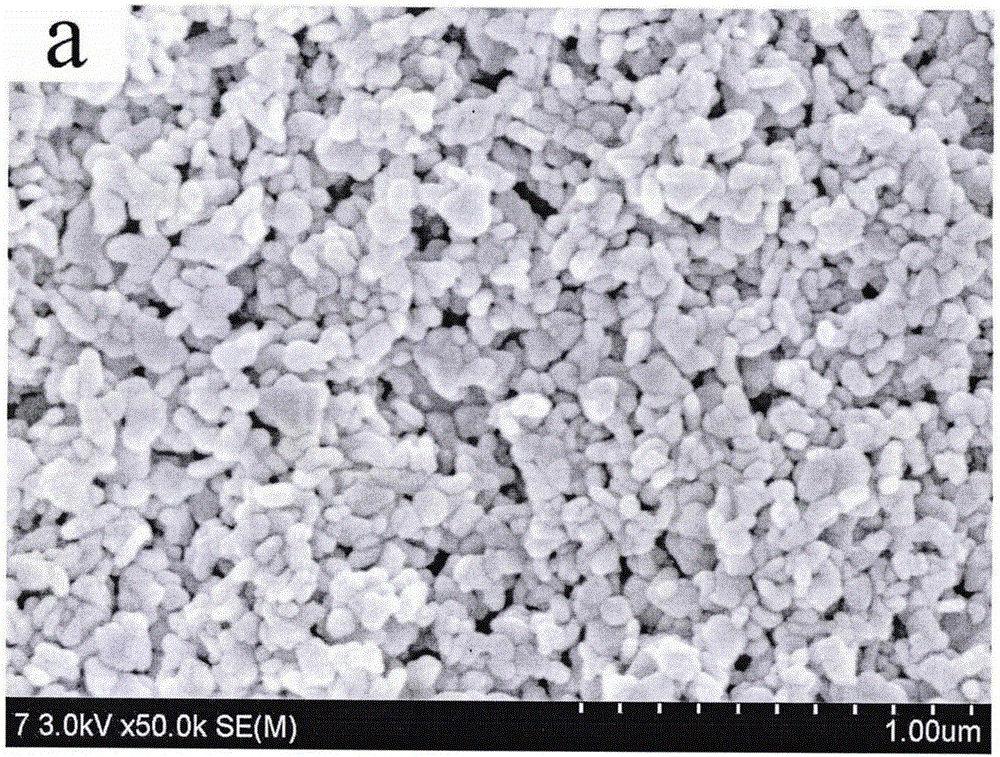
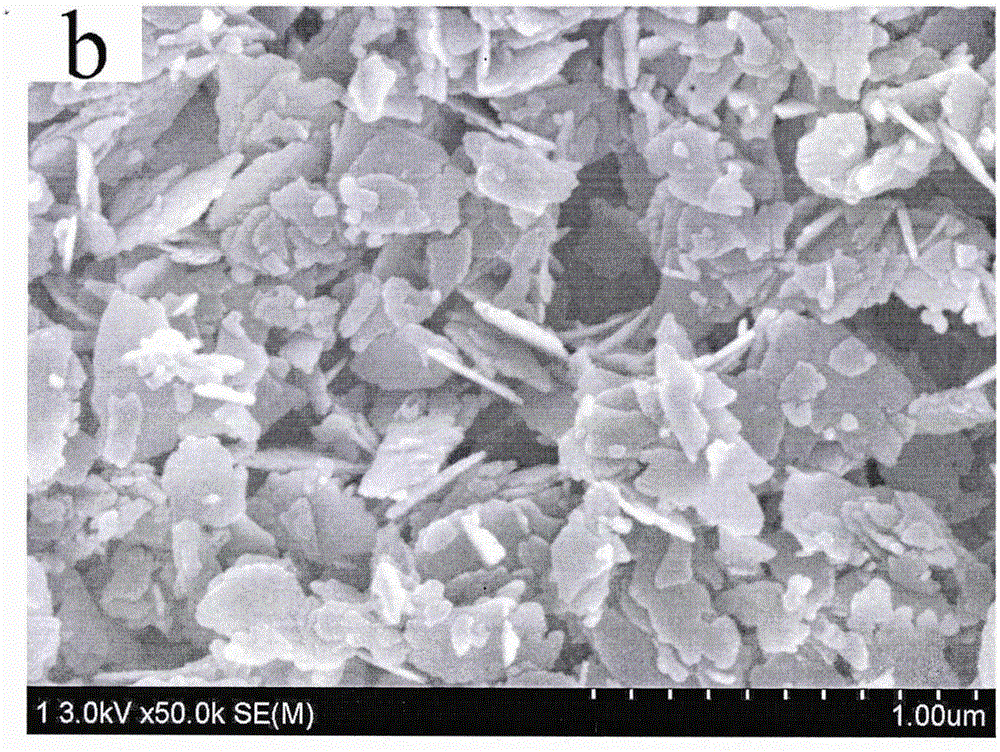
[0033] Take 1mol·L -1 Put 2mL of ferric nitrate aqueous solution in a beaker, under magnetic stirring, first add 4mol·L -1 Sodium hydroxide aqueous solution 45mL, then add 1mol·L dropwise -1 Zinc nitrate aqueous solution 20mL (the molar ratio of ferric nitrate, sodium hydroxide and zinc nitrate is 1:90:10). After the dropwise addition was completed, stirring was continued for 1 h. The reaction precursor solution was transferred to a Erlenmeyer flask with a ground stopper, immersed in a water bath previously heated to 80° C., and aged for 5 h. Finally, after suction filtration, washing with distilled water for 2-3 times, and drying naturally, α-Fe 2 o 3 / ZnO composite catalyst.
Embodiment 2~6
[0034] Embodiment 2~6 and comparative example
[0035] Embodiments 2 to 6 and the comparative example have the same operating steps as in Example 1, the only difference being the type, concentration, ratio and aging temperature of the ferric salt, alkali and zinc salt used, as shown in Table 1. .
[0036] Table 1 Embodiment 2~6 and comparative example
[0037]
[0038] The aging temperature in Table 1 refers to the temperature of the water bath set when the reaction precursor solution is transferred to a conical flask with a ground stopper and immersed in a pre-heated water bath for aging. At a higher aging temperature, the reaction is relatively fast, so the required aging time is correspondingly shorter; at a lower aging temperature, the reaction is relatively slow, so the required aging time is correspondingly longer. When the aging temperature is limited to 80-99°C, the reaction is more thorough and takes a shorter time, and the purity of the prepared composite cataly...
experiment example 1
[0039] Experimental example 1: XRD characterization of photocatalyst
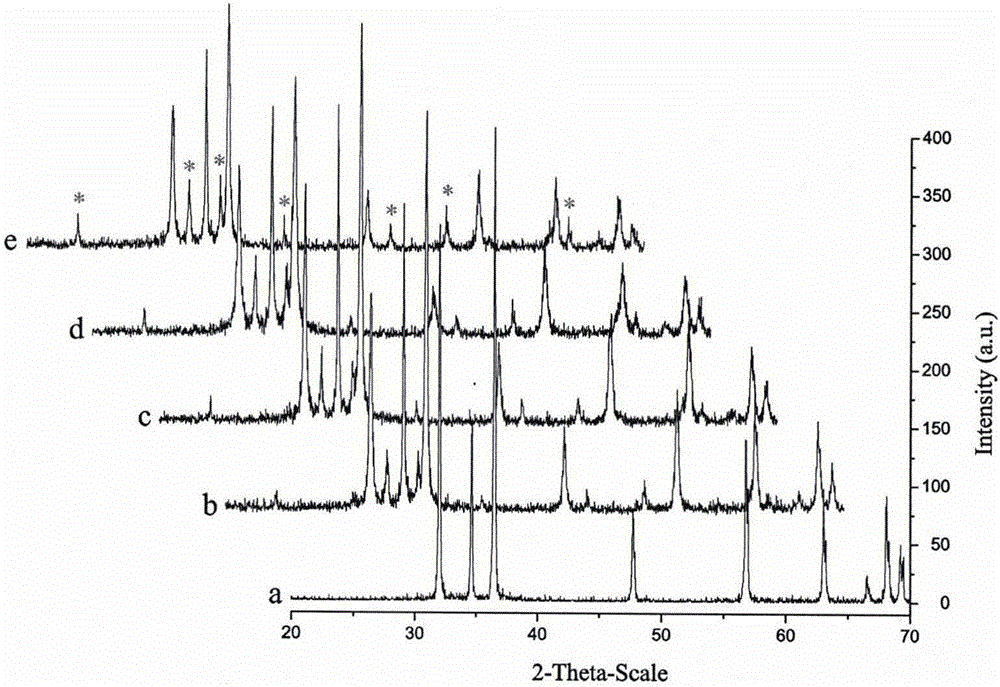
[0040] figure 1 For the pure ZnO photocatalyst prepared by comparative example and the α-Fe prepared by Examples 1~4 2 o 3 XRD characterization pattern of / ZnO composite photocatalyst. It can be seen that the diffraction peaks at 2θ=24.1°, 33.1°, 35.6°, 40.8°, 49.4°, 54.0°, and 63.9° belong to α-Fe 2 o 3 (JCPDSNo.33-0664), other diffraction peaks belong to ZnO (JCPDSNo.36-1451). With the increase of the amount of ferric salt used, the α-Fe in the product 2 o 3 The intensity of the characteristic diffraction peaks increases gradually. No other impurity peaks were found, indicating that the product was of high purity.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com