Zero Voltage Switching Quasi-Resonant High Gain DC Boost Converter
A zero-voltage switching, DC boost technology, applied in the field of boost converters, can solve the problems of reduced circuit efficiency, increased voltage or current stress of switching devices, and increased switching loss of devices, and achieves simple circuit topology and switching loss. Reduction and switching noise reduction effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
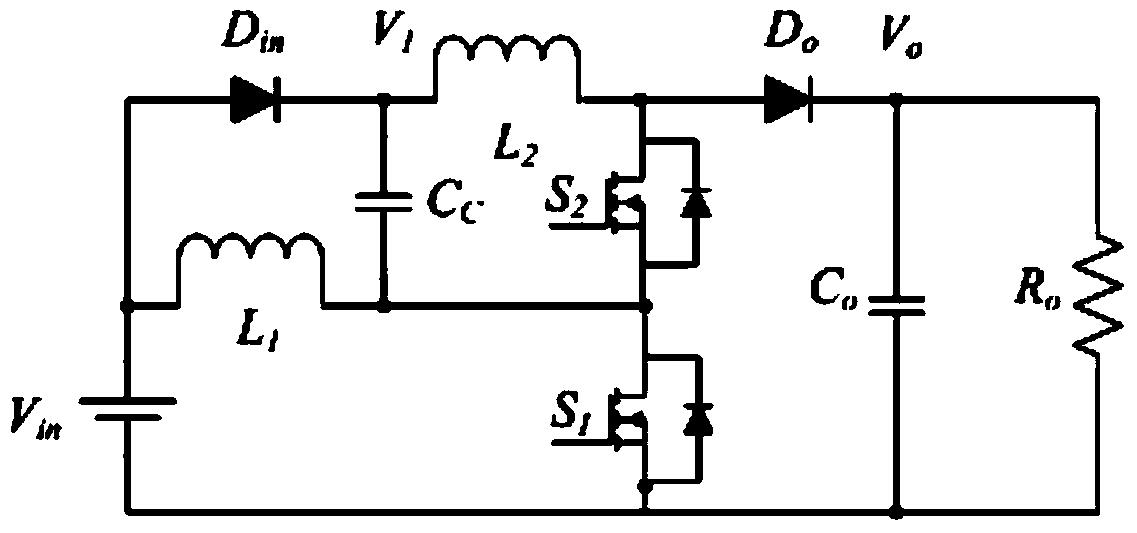
[0018] As shown in Figure 1, the topological example diagram of the high-gain DC boost converter under hard switching in the prior art, the converter input voltage V in The positive output is divided into two channels and respectively connected to the inductor L 1 One end and the diode D in Positive terminal, diode D in negative terminal and the inductor L 1 The other end is respectively connected to the charge pump capacitor C c across the charge pump capacitor C c Inductor L connected in series at both ends 2 and the main switch MOSFET S 2 , the charge pump capacitor C c with the main switching MOSFET S 2 connection point through the main switch MOSFET S 1 Connect to the converter input voltage V in Negative pole, inductance L 2 and the main switch MOSFET S 2 connection point through the freewheeling diode D o Connect to filter capacitor C o , filter capacitor C o Parallel load R at both ends o .
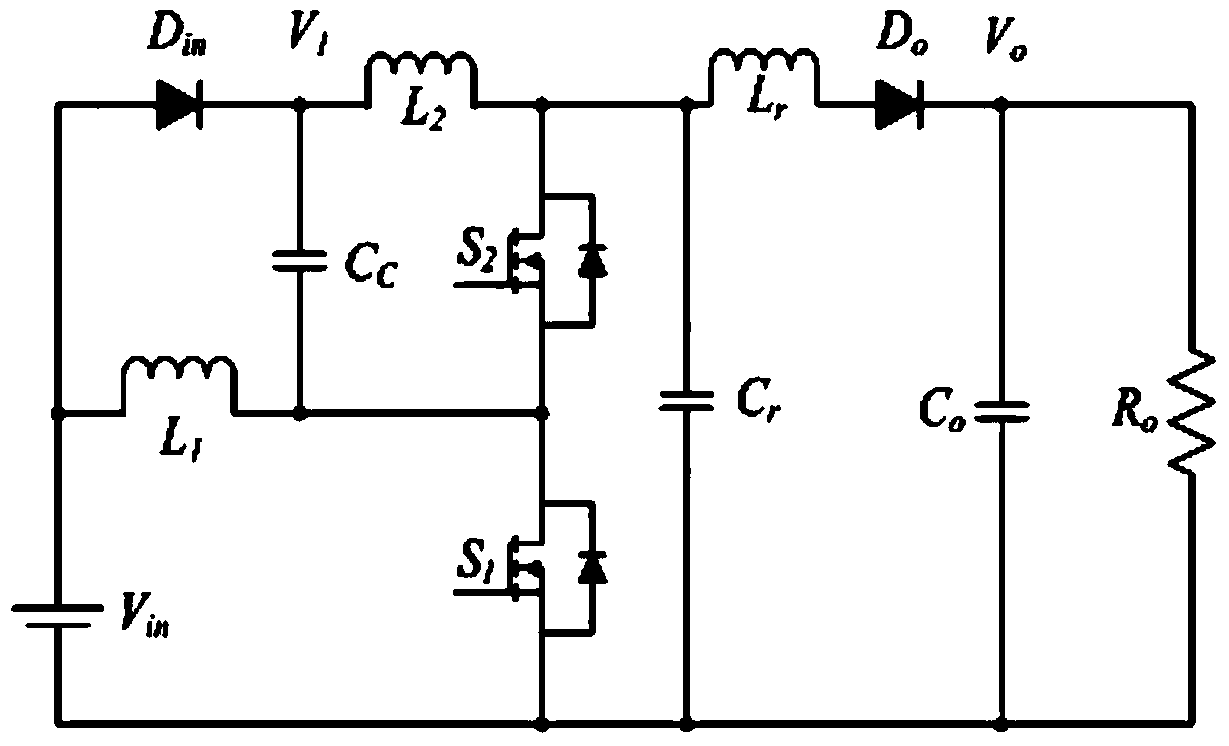
[0019] Such as figure 2 The topology example diagram of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com