A promoter for regulating gene expression in non-secretory glandular hairs and its application
A non-secreting glandular hair and gene regulation technology, applied in the field of promoters, can solve the problems of normal growth burden of plants, excessive consumption of cell material and energy, and regulation of target genes in time and space.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
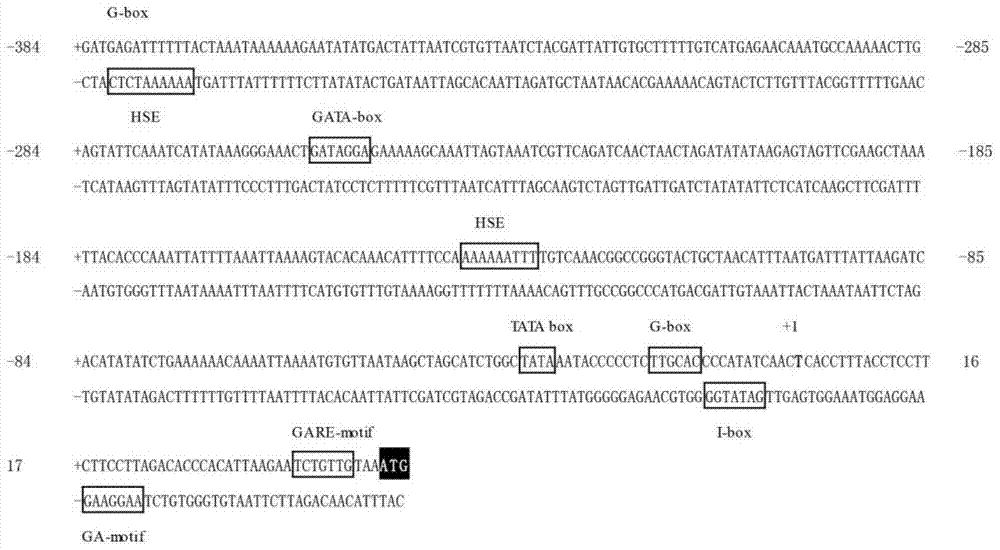
[0038] This embodiment relates to obtaining the AaPDS1 gene promoter, which specifically includes the following steps:
[0039] Step 1: Cultivate sterile seedlings of Artemisia annua
[0040] The seeds of Artemisia annua were soaked in 75% ethanol by volume for 1 minute, and then soaked in 20% (w / v) NaClO for 20 minutes, rinsed with sterile water for 3 to 4 times, and dried with sterile absorbent paper for inoculation Cultivate it on a hormone-free MS solid medium at 25°C, 16h / 8h (light / dark) light, and you can get sterile A. annua seedlings after 14 days;
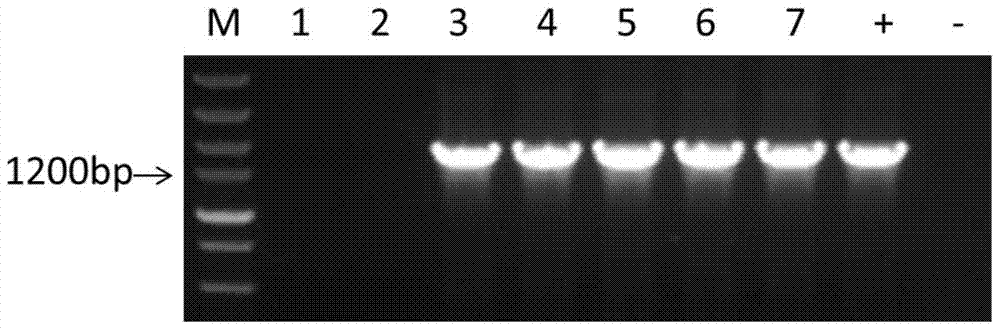
[0041] Step 2: Cloning of the promoter sequence in genomic DNA
[0042] 1. Extraction of genomic DNA
[0043] Put a piece of Artemisia annua leaf (1cm) in a 1.5mL centrifuge tube 2 Left and right size, use ice box to hold), add 2 steel balls. Add 300μL TPS buffer (operated in a fume hood, TPS contains mercaptoethanol), shake for 90 seconds at 55-60 Hz. Then add 300μL TPS buffer (fume hood). Water bath at 65℃ for 1h (shaking ever...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com