Cellulase producing bacteria and application thereof
A cellulase and bacteria-producing technology, applied in the field of biochemistry, can solve the problems of high animal feeding costs, environmental pollution, incomplete degradation of cellulose components, etc., and achieve shortened production cycle, broad application prospects, and pH applicable range. wide effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] Example 1 Isolation, screening and identification of Bacillus megaterium SMY0001
[0023] Primary screening of bacterial strains: Collect 6 parts of the hindgut content of healthy grass carp, weigh 0.5g samples respectively, add 4.5mL sterile water to prepare a suspension, kill non-spore vegetative bodies in a water bath at 80°C, and then spread on carboxyl carp On the sodium methylcellulose screening plate, cultivate at 37°C for 48 hours, and obtain 18 strains of bacteria.
Embodiment 218
[0024] The identification of embodiment 218 cellulolytic bacteria:
[0025] After collecting the culture fluid of 18 cellulolytic bacteria, the genomic DNA was extracted and used as a template for PCR to amplify the full-length 16S of the bacteria. After the PCR products were recovered and cloned, they were sequenced, and the sequencing results were recorded in the GenBank database using BLAST (BasicLocalAlignmentSearchTool) software. Perform a sequence similarity search to determine the strain information. The results showed that 12 of the 18 bacterial strains were Bacillus.
Embodiment 3
[0026] Embodiment 3, screening the bacterial classification SMY0001 with the highest enzymatic activity:
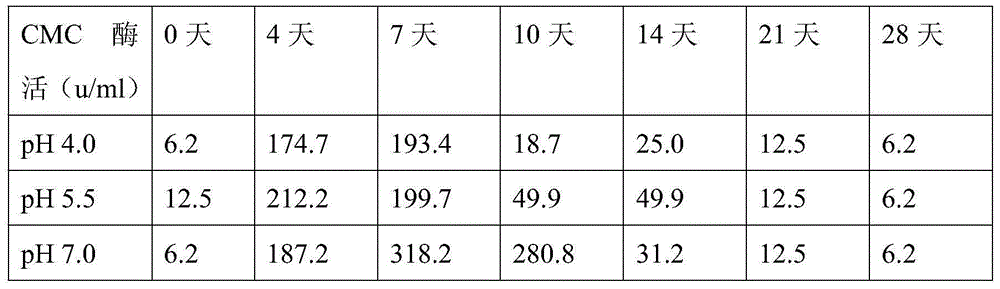
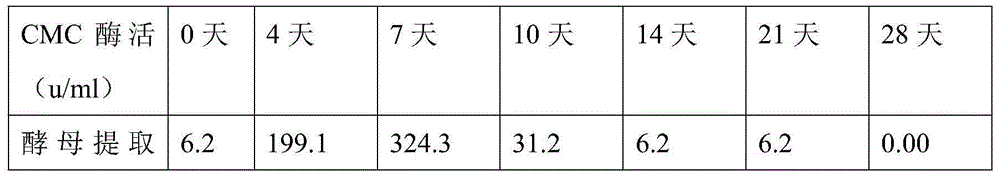
[0027] Preparation of crude enzyme liquid: Inoculate 12 strains of bacillus into carboxymethylcellulose medium (composition: 1% sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 1% yeast extract, 1.5% inorganic salt, 96.5% water, pH7 .0), cultured at 55°C for 7 days, and centrifuged at 8000r / min for 20min to obtain crude enzyme solution.
[0028] Determination of CMC enzyme activity: use 1% sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) as the substrate, add enzyme solution with appropriate dilution factor, react at 50°C, 80r / min, pH4-10 for 30 minutes, and measure the enzyme produced by enzymolysis Glucose volume. A unit of CMC enzyme activity is defined as: the amount of enzyme that produces one milligram of glucose per milliliter of enzyme solution per hour under standard reaction conditions, expressed in u / ml. From the test results, the Bacillus megaterium strain SMY0001, which highly expresses c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com