All-fiber wind measurement laser radar apparatus baed on asymmetric M-Z interferometer and method
A wind-measuring lidar and fiber laser technology, which is used in measurement devices, instruments, fluid velocity measurement, etc., can solve the problems of demanding stability of lasers and M-Z interferometers, increasing the dynamic range of frequency shift measurement, and increasing M-Z interferometers. , to achieve the effects of insensitivity to laser energy fluctuations, large dynamic range of wind speed measurement, and compact structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
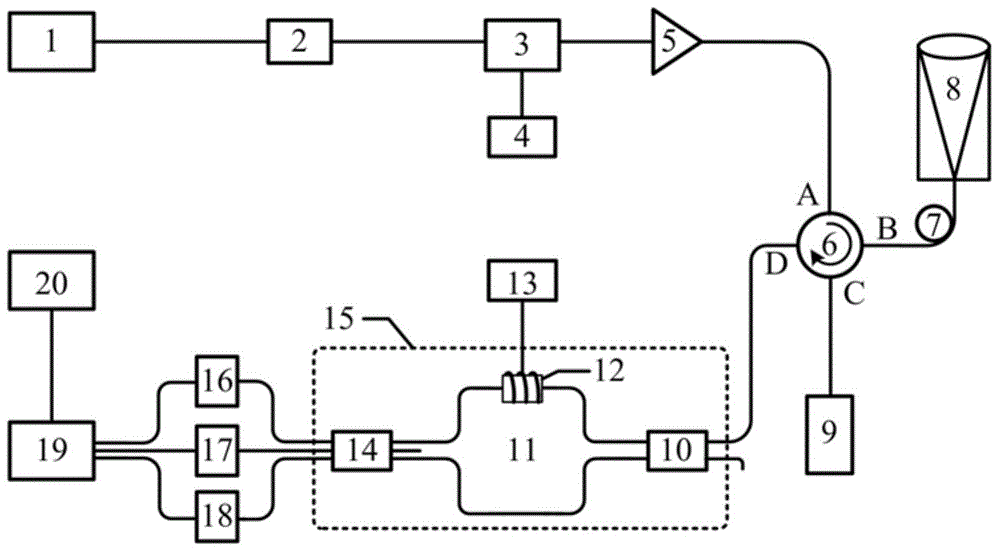
[0030] figure 1 A schematic structural diagram of an all-fiber wind-measuring lidar based on an asymmetric M-Z interferometer provided in Embodiment 1 of the present invention; figure 1 As shown, it mainly includes:
[0031] Continuous fiber laser 1, fiber isolator 2, EOM 3 (intensity modulator), arbitrary function generator 4, EDFA 5 (fiber amplifier), fiber circulator 6, time-delay fiber 7, optical transceiver and scanning system 8, fiber Bragg Grating 9, 2×2 fiber coupler 10, fiber M-Z interferometer 11, piezoelectric ceramic 12, piezoelectric ceramic driver 13, 3×3 fiber coupler 14, first detector 16, second detector 17, third Detector 18, acquisition card 19 and computer 20; Wherein:
[0032]The output end of the continuous fiber laser 1 is connected to the input end of the fiber isolator 2, the output end of the fiber isolator 2 is connected to the input end of the EOM 3, the output end of the EOM 3 is connected to the input end of the EDFA 5, and the arbitrary functio...
Embodiment 2
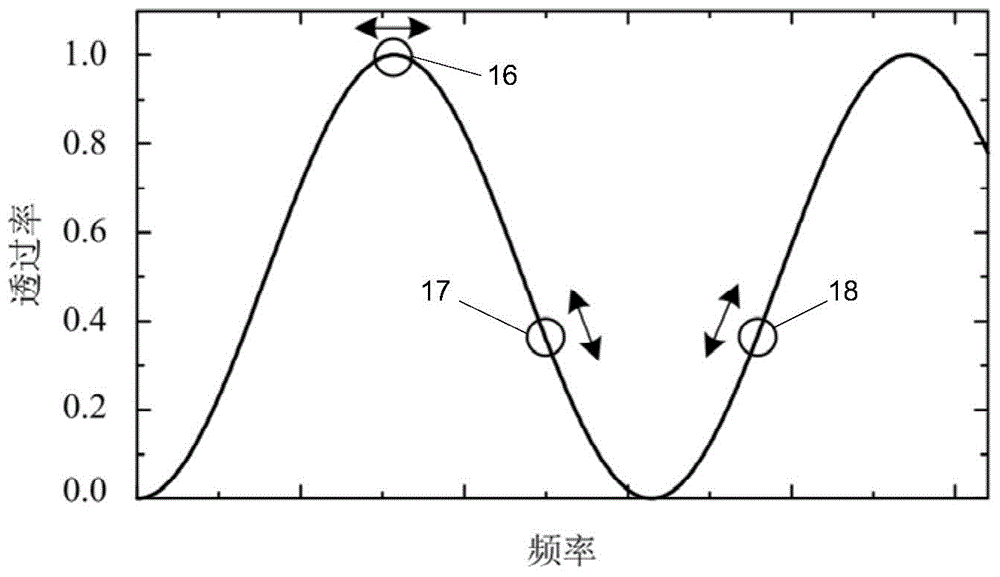
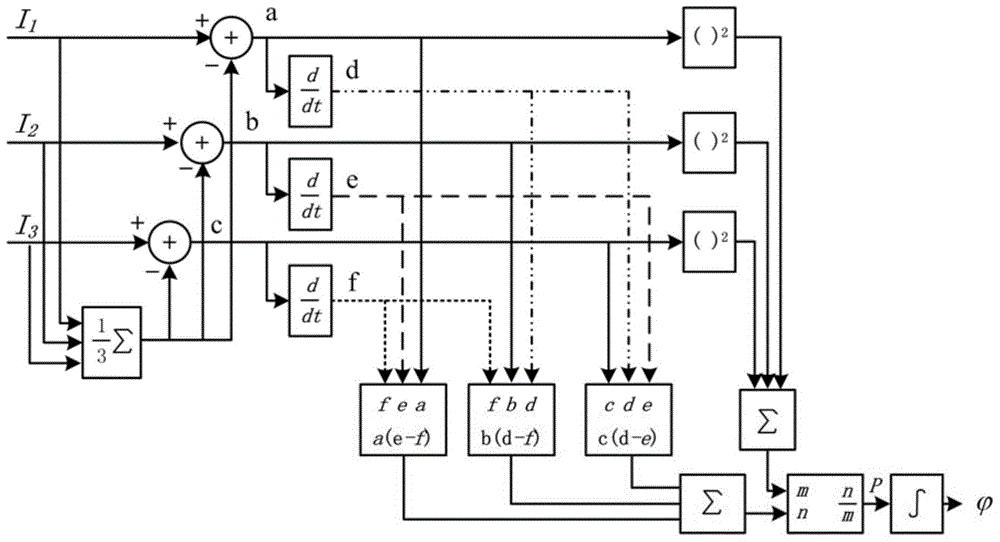
[0080] An embodiment of the present invention provides an all-fiber wind detection lidar wind measurement method based on an asymmetric M-Z interferometer. The asymmetric M-Z interferometer formed by the fiber coupler is used as the frequency discriminator of the wind lidar; the differential-cross multiplication demodulation method is used to extract the Doppler frequency shift information; the method of changing the arm length of the piezoelectric ceramic is used to realize the M-Z interference of the fiber The self-calibration of the instrument; the time-division multiplexing method is used to determine the laser emission frequency by collecting the backscattering cursor of the time-delayed optical fiber. The invention has compact structure, strong anti-interference ability, does not need to lock the relative position of M-Z interferometer and laser frequency, is insensitive to laser energy fluctuation, has high energy utilization rate, and has a large dynamic range of wind s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com