High-viscosity and low-melting-point metal conductive paste and preparation method and application thereof
A low melting point metal, conductive paste technology, applied in metal/alloy conductors, cable/conductor manufacturing, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of large air gap, limited electrical conductivity, low feasibility, etc., to improve electrical conductivity, electrical conductivity Adjustable, easy-to-use effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 shows a typical application of a high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste of the present invention.
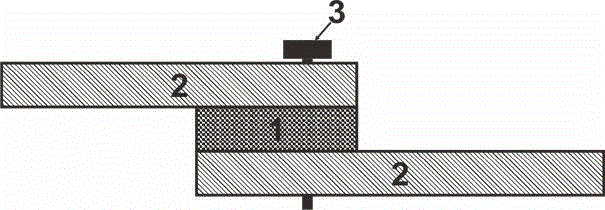
[0028] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a high-conductivity low-melting-point metal conductive paste applied to electronic components in Example 1. Among them: 1 is conductive paste, 2 is electronic components, and 3 is fastening screws.
[0029] In the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste of this embodiment, the low-melting-point metal is gallium-indium-tin-zinc alloy (alloy mass fraction: Ga 61%, In 25%, Sn 13%, Zn 1%), and the melting point is 8°C. The metal powder is copper powder, the mass fraction accounts for 50% of the mass of the conductive paste, and the particle size is 1 μm.
[0030] When using, first apply the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste evenly between the electronic components; then fix it tightly with screws. The conductivity and viscosity of the high-viscosity and ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a high-conductivity low-melting-point metal conductive paste applied to electronic components in Example 1. Among them: 1 is conductive paste, 2 is electronic components, and 3 is fastening screws.
[0034] In the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste of this embodiment, the low-melting-point metal is gallium-indium-tin-zinc alloy (alloy mass fraction: Ga 61%, In 25%, Sn 13%, Zn 1%), and the melting point is 8°C. The metal powder is copper powder, the mass fraction accounts for 0.01% of the mass of the conductive paste, and the particle size is 1 mm. When using, first apply the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste evenly between the electronic components; then fix it tightly with screws. The conductivity and viscosity of the high-viscosity and low-melting-point metal conductive paste of the present invention can be adjusted according to different application occasions, that is, it ha...
Embodiment 3
[0037] figure 1 It is a structural schematic diagram of a high-conductivity low-melting-point metal conductive paste applied to electronic components in Example 1. Among them: 1 is conductive paste, 2 is electronic components, and 3 is fastening screws.
[0038] In the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste of this embodiment, the low-melting-point metal is gallium-indium-tin-zinc alloy (alloy mass fraction: Ga 61%, In 25%, Sn 13%, Zn 1%), and the melting point is 8°C. The metal powder is copper powder, the mass fraction accounts for 20% of the mass of the conductive paste, and the particle size is 4 μm.
[0039] When using, first apply the high-viscosity low-melting-point metal conductive paste evenly between the electronic components; then fix it tightly with screws. The conductivity and viscosity of the high-viscosity and low-melting-point metal conductive paste of the present invention can be adjusted according to different application occasions, that is...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com