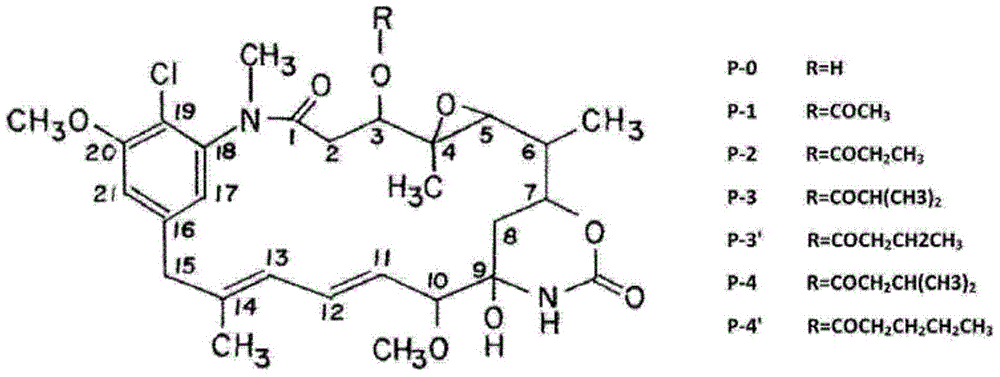
Method for preparing ansamitocin P-3 from precious orange actinosynnema pretiosum
A technology of ansesomycin and actinomycetes, which is applied in the field of biological fermentation, can solve the problems of low proportion of anseomycin P-3, difficulty in large-scale production, inability to synthesize maytansinol and the like, and achieves low cost, The effect of increasing output and saving production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0058] Embodiment 1: 50L tank fed-batch fermentation (during fermentation and cultivation, no hot-pressed bean cake powder was added, and the addition method of isobutanol was fed-batch)
[0059] (1) Spore culture: the spores of Actinomyces fasciculatus orientalis spores frozen in 20% glycerol tubes were cultured by streaking on a solid medium culture dish, and cultured upside down at 28°C for 6 days;
[0060] Solid medium formula: yeast extract 0.3%, soybean peptone 0.5%, malt extract 0.3%, glycerin 1%, agar powder 2%, natural pH;
[0061] (2) Seed culture: Add 6L liquid seed medium to a 10L fermenter, and after sterilizing at 121°C for 30 minutes, scrape the spores from the culture dish and inoculate them into the liquid seed medium; Stir at a speed of 80rpm; during the cultivation process, the dissolved oxygen is kept above 30% by adjusting the ventilation and strengthening the stirring, the maximum ventilation is 1vvm, the maximum rotation speed is 350rpm, and the seed liq...
Embodiment 2
[0067] Embodiment 2: 50L tank fed-batch fermentation (add hot-pressed bean cake powder during fermentation and cultivation, and the supplementary mode of isobutanol is fed-batch)
[0068] (1) Spore culture: as in Example 1;
[0069] (2) seed culture: as embodiment 1;
[0070] (3) Fermentation culture: as in Example 1, the difference is that the liquid fermentation medium is: cornstarch 5%, corn steep liquor dry powder 2%, hot-pressed bean cake powder 2%, glucose 0.5%, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 0.025%, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.3%, CaCO 3 0.4%, CaCl 2 0.1%, isobutanol 0.3%, CoCl 2 ·6H 2 O 0.0005%, FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.0002%, initial pH 7.2;
[0071] For 0-60 hours of fermentation culture, 22.5% glucose solution was added at a flow rate of 0.5mL / L / h. After 60 hours of fermentation, 25% glucose, 10% hot-pressed bean cake powder and 10% glucose solution were added at a rate of 1mL / L / h. % isobutanol feed solution, fermented and cultivated for 412 hours, until the expression of ansamitocin P-3...
Embodiment 3
[0073] Example 3: 50L tank fed-batch fermentation
[0074] (1) Spore culture: as in Example 1;
[0075] (2) seed culture: as embodiment 1;
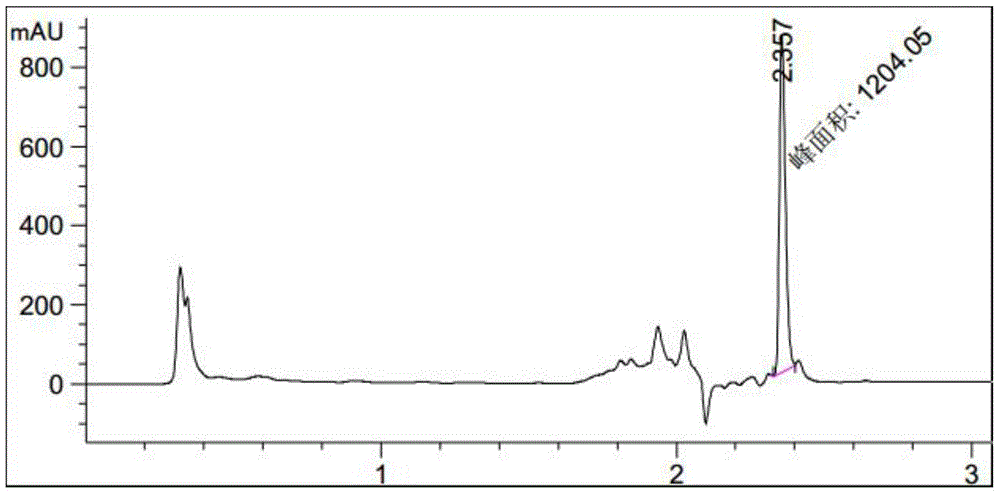
[0076] (3) Fermentation culture: as in Example 2, the difference is the feeding process, fermentation culture 0-60h, add 22.5% glucose solution with a flow rate of 0.5mL / L / h, after fermentation 60h, add 22.5% glucose solution with 1mL / L Feed solution containing 25% glucose and 10% hot-pressed bean cake powder was added at a rate of / h, and 55mL of isobutanol was added once every 24h; The expression level of is no longer increasing, the fermentation has ended, and the expression level reaches 1211mg / L (such as figure 1 shown);
[0077] (4) Sample processing and detection methods are as in Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com