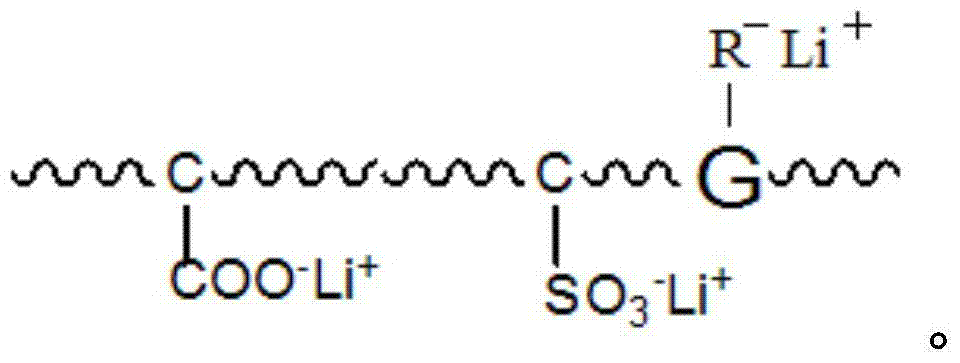Graphene polymer electrolyte and preparation method thereof
A graphene and polymer technology, applied in solid electrolytes, non-aqueous electrolytes, circuits, etc., can solve problems such as poor compatibility between organic groups and metal lithium, low conductivity of polymer electrolytes, and impact on use value, achieving Effects of high electrical conductivity, unique properties, and high mechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
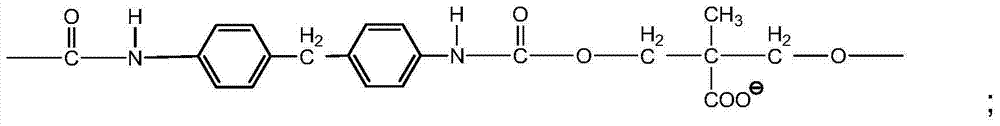
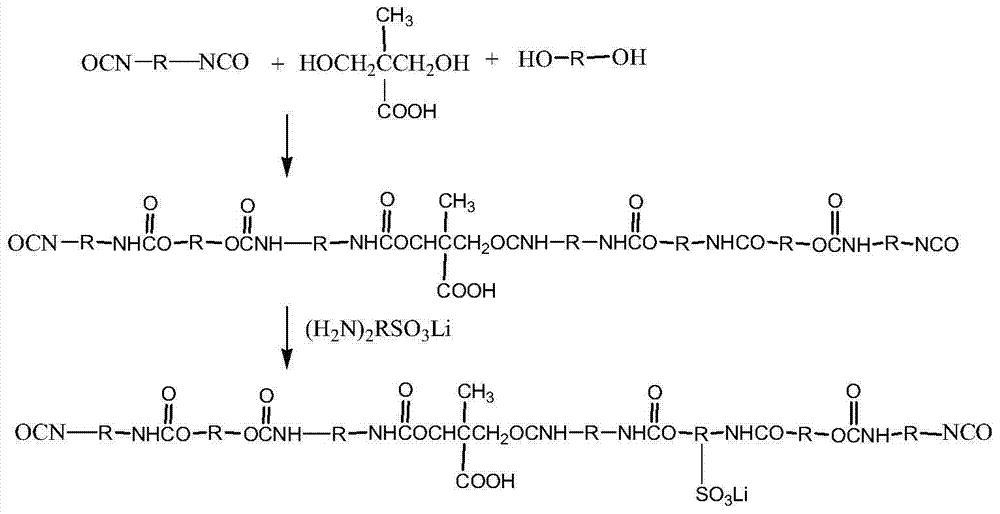
[0032] This embodiment provides a graphene polymer electrolyte, which is prepared by reacting water-based polyurethane and graphene, specifically:
[0033] S1. In a 500ml four-neck flask equipped with a stirring thermometer, reflux condenser and feeder, add PEG (2000) and PTMG (2000) with a mass ratio of 1:1 according to the ratio of NCO / OH to 1.2. Dehydration at room temperature for 2 hours, cooling to 80°C, adding DMPA with a total mass of 4% of the PEG and PTEG, vacuum dehydration for 1 hour, cooling to 60°C to obtain a prepolymer, adding 3% of the prepolymer mass to it Solvent NMP, and add IPDI of 8% by mass of the prepolymer and T-12 of 0.03% by mass of the prepolymer, slowly raise the temperature to 85°C, and continue the reaction for 3h until the NCO value reaches the theoretical value, and the NCO value It can be determined by the di-n-butylamine method to obtain an NCO-terminated water-based polyurethane prepolymer, and then add 3% lithium disulfamate to the NCO-termi...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides a graphene polymer electrolyte, which is prepared by reacting water-based polyurethane and graphene, specifically:
[0042] S1. In a 500ml four-neck flask equipped with a stirring thermometer, reflux condenser and feeder, add PEG (2000) and PTMG (2000) with a mass ratio of 2:1 according to the NCO / OH ratio of 1.4. Dehydration at room temperature for 3 hours, cooling to 85°C, adding DMPA with a total mass of 3.5% of the PEG and PTEG, vacuum dehydration for 1.5 hours, cooling to 65°C to obtain a prepolymer, adding 5% of the mass of the prepolymer to it solvent NMP, and add 10% of the prepolymer mass of IPDI and 0.05% of the prepolymer mass of T-12, slowly heat up to 90 ° C, and continue the reaction for 4 hours until the NCO value reaches the theoretical value, the NCO The value can be measured by the di-n-butylamine method, promptly obtains the water-based polyurethane prepolymer of NCO termination, then adds the lithium disulfamate of 4% of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0050] This embodiment provides a graphene polymer electrolyte, which is prepared by reacting water-based polyurethane and graphene, specifically:
[0051] S1. In a 500ml four-neck flask equipped with a stirring thermometer, reflux condenser and feeder, add PEG (2000) and PTMG (2000) with a mass ratio of 1.5:1 according to the NCO / OH ratio of 1.8, at 120°C Dehydration at room temperature for 4 hours, after cooling to 75°C, adding DMPA with a total mass of 5% of the PEG and PTEG, vacuum dehydration for 2 hours, cooling to 70°C to obtain a prepolymer, adding 7% of the mass of the prepolymer to it Solvent NMP, and add 12% of the prepolymer mass of IPDI and 0.06% of the prepolymer mass of T-12, slowly raise the temperature to 90°C, and continue the reaction for 4.5h until the NCO value reaches the theoretical value, the NCO The value can be measured by the di-n-butylamine method, promptly obtains the water-based polyurethane prepolymer of NCO termination, then adds the lithium dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com