Preparation method for fiberboard with low formaldehyde content
A fiberboard and low-formaldehyde technology, applied in the field of fiberboard, can solve the problems of secondary pollution, high cost, low bonding strength, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
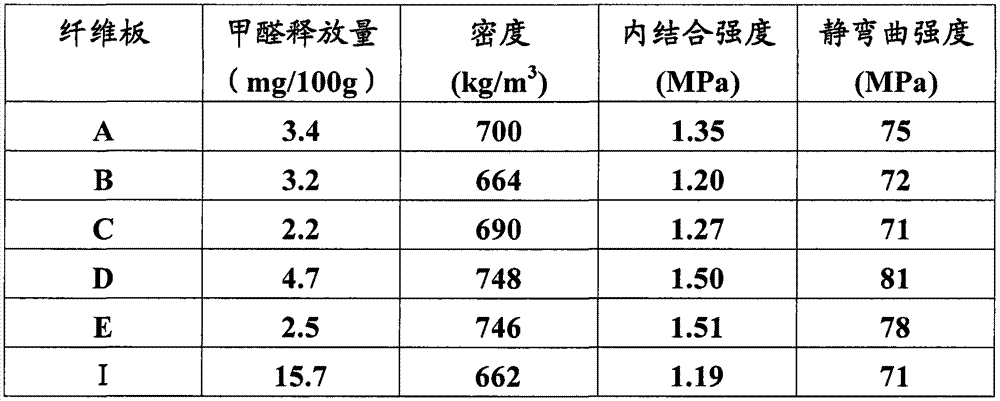
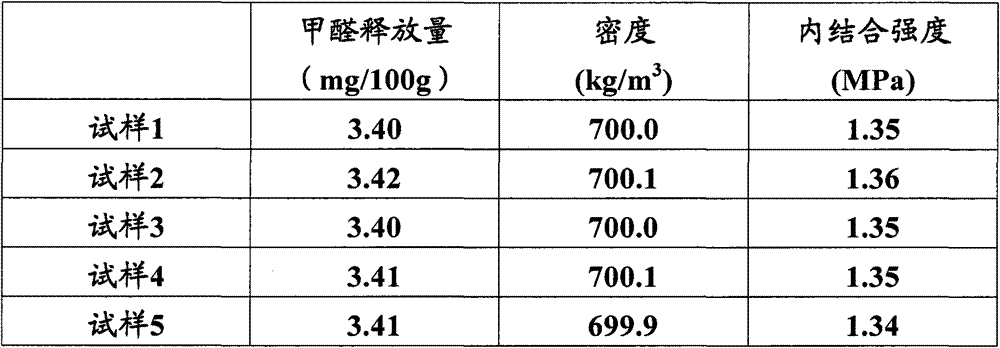
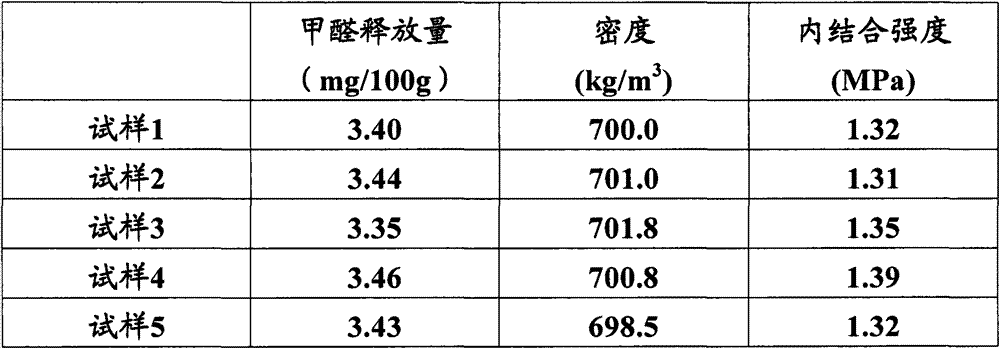
[0046] 125 parts by weight of fiber slurry, 10 parts by weight of urea-formaldehyde resin, and 6.5 parts by weight of propyl benzoate are uniformly mixed in a stirring tank, and the mixture is dried at 50-70°C until the water content is 15 wt%, to obtain a mixture. The mixture was pre-pressed at 4-5MPa for 30s to form a blank, and the blank was isostatically pressed at 8MPa and 70°C for 1min to form a slab. The slab is hot-pressed, and the hot-pressing conditions are as follows: the temperature is 150-160°C; the temperature is raised to 13.5-19MPa within 20-30s, and the pressure is maintained for 60-120s; and then the pressure is reduced to 3.5-5.5MPa within 10-15s. Hold the pressure for 65-135s; then rise to 6-8.5MPa within 10-15s, hold the pressure for 50-75s; finally depressurize evenly to 0MPa within 30-45s. The hot-pressed sheet was cooled to room temperature, tempered and sanded to obtain a fiberboard A with a thickness of 25 mm.
Embodiment 2
[0048] 167 parts by weight of fiber slurry, 20 parts by weight of urea-formaldehyde resin, and 11 parts by weight of propyl benzoate are uniformly mixed in a stirring tank, and the mixture is dried at 60-70°C until the water content is 10 wt%, to obtain a mixture. The mixture was pre-pressed at 4-5MPa for 40s to form a blank, and the blank was isostatically pressed at 7MPa and 70°C for 50s to form a slab. The slab is hot-pressed, and the hot-pressing conditions are as follows: the temperature is 150-160°C; the temperature is raised to 13.5-19MPa within 20-30s, and the pressure is maintained for 60-120s; and then the pressure is reduced to 3.5-5.5MPa within 10-15s. Hold the pressure for 65-135s; then rise to 6-8.5MPa within 10-15s, hold the pressure for 50-75s; finally depressurize evenly to 0MPa within 30-45s. The hot-pressed sheet was cooled to room temperature, tempered and sanded to obtain a fiberboard B with a thickness of 25 mm.
Embodiment 3
[0050] 140 parts by weight of fiber slurry, 15 parts by weight of modified urea-formaldehyde resin, and 4.5 parts by weight of propyl benzoate were uniformly mixed in a stirring tank, and the mixture was dried at 80° C. until the moisture content was 10 wt % to obtain a mixture. The mixture is pre-pressed at 4-5MPa for 1min to form a blank, and the blank is isostatically pressed at 7-8MPa and 60-70°C for 50s to form a slab. The slab is hot-pressed, and the hot-pressing conditions are as follows: the temperature is 150-160°C; the temperature is raised to 13.5-19MPa within 20-30s, and the pressure is maintained for 60-120s; and then the pressure is reduced to 3.5-5.5MPa within 10-15s. Hold the pressure for 65-135s; then rise to 6-8.5MPa within 10-15s, hold the pressure for 50-75s; finally depressurize evenly to 0MPa within 30-45s. The hot-pressed sheet was cooled to normal temperature, tempered and sanded to obtain a fiberboard C with a thickness of 25 mm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Internal binding strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com