Wood-plastic composite floor and manufacturing method thereof
A wood-plastic composite and manufacturing method technology, applied in building structure, building, floor and other directions, can solve the problems of high density, low strength of wood-plastic floor, easy to creep and large-span floor, etc. cracking effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
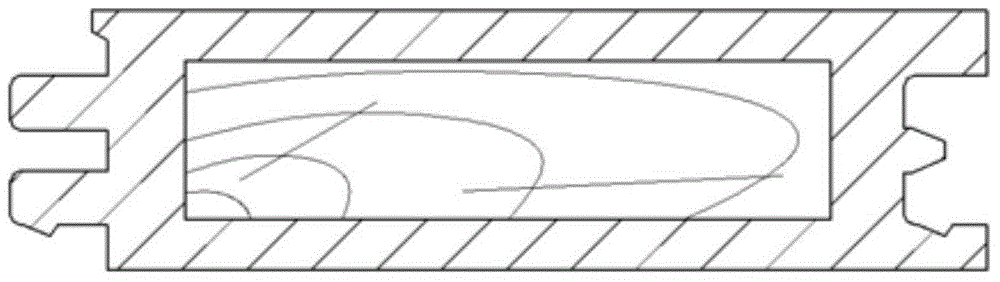
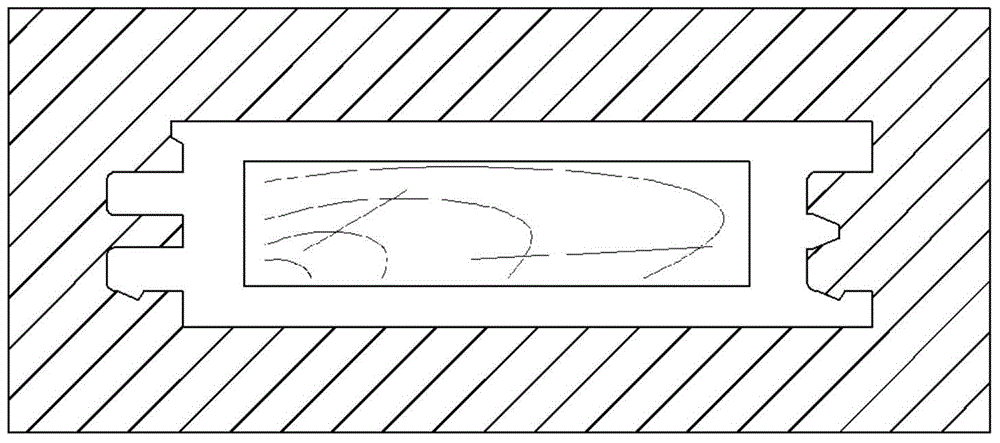
[0009] Specific embodiment 1: The manufacturing method of a wood-plastic composite floor described in this embodiment includes the step a of preparing a wood core; preparing a thermoplastic wood-plastic composite material masterbatch and feeding the wood core through co-extrusion equipment The step b of melting the wood-plastic composite material masterbatch and co-extruding the profile with the wood core; the step c of cutting the profile obtained through step b into floor boards; and the step c of The end faces of the floorboards are closed step d.
[0010] The technical effect of this embodiment is: by feeding the wood core in the co-extrusion equipment and co-extruding the wood-plastic composite material masterbatch and the wood core into a molding material, the wood core replaces a part of wood-plastic to become a structural material, and the processing The strength of the wood-plastic composite floor is improved, and it is suitable for use as a long-span floor, which sol...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0011] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the wood core processing method described in step a is first to process the two ends of the dried solid wood with a milling head to obtain mutually matched finger-jointed tenons, and then Polyvinyl acetate emulsion, acrylic resin, acrylic-polyurethane resin, isocyanate, melamine-urea-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde glue or phenolic glue to process the finger-joint tenons that match each other, and then apply opposite pressure on the two ends of the solid wood to make the solid wood Parallel or end-to-end splicing, the wood core is obtained after the adhesive is cured.
[0012] The technical effect of this embodiment is: by manufacturing mutually matching finger-joint tenons and treating said mutually matching finger-joint tenons with polyvinyl acetate emulsion, melamine-urea-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde glue or phenolic glue, the length of the wood core is not affected by t...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0013] Specific embodiment 3: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the wood core processing method described in the step a is, at first select the solid wood rotary-cut veneer, apply polyvinyl acetate emulsion, acrylic resin on the surface of the veneer , acrylic-polyurethane resin, isocyanate, melamine-urea-formaldehyde, urea-formaldehyde glue or phenolic glue, and then according to the texture of the veneer to assemble blanks cross-laminated in the warp and weft directions, and then apply pressure to the blanks and leave it still to obtain laminated boards, Finally, the laminated board is cut to obtain the wood core.
[0014] The technical effect of this embodiment is: by using the method for manufacturing laminated boards to manufacture the wood core, it is beneficial to overcome the inhomogeneity of the mechanical properties of the wood in all directions, so that the prepared wood core is not easy to deform or warp, The internal mechanic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com