Method for preparing high-purity ammonium metavanadate from spent catalyst
A waste catalyst and ammonium metavanadate technology, which is applied in the preparation of vanadium compounds, chemical instruments and methods, vanadium compounds, etc., can solve the problems of inability to prepare high-purity ammonium metavanadate, achieve low cost, solve molybdenum entrainment, The effect of short process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
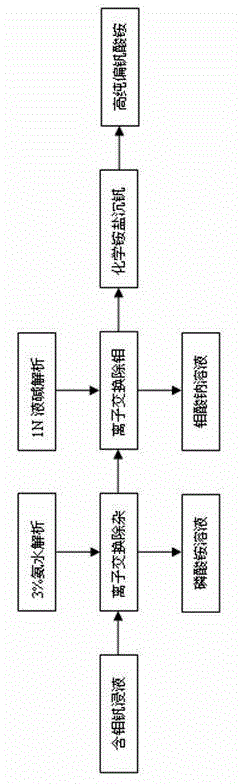
[0020] After the spent catalyst is leached and filtered, 26m 3 The leaching solution contains 0.67g / L of phosphorus, 12.73g / L of molybdenum, and 17.81g / L of vanadium.
[0021] (1) Phosphorus removal
[0022] Adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 6.5, enter the ion exchange system, pass through the ion exchange column, and use gel-type anion exchange resin to adsorb phosphorus in the leaching solution. Adjust the valve to control the feed flow rate to 0.2 times the column volume. After testing, after 270 minutes of contact between the feed liquid and the resin, the phosphorus content in the effluent is greater than 2ppm, the resin is saturated, and the adsorption is stopped immediately.
[0023] The resin is rinsed and analyzed with 4% ammonia solution, and the regeneration is completed at the same time. After the ammonium phosphate solution is concentrated and crystallized, it can be used for the production of phosphate fertilizer.
[0024] (2) Separation of molyb...
Embodiment 2
[0031] After the spent catalyst was leached and filtered, 24.6m 3 The leaching solution contains 1.34g / L of phosphorus, 12.72g / L of molybdenum, and 18.16g / L of vanadium.
[0032] (1) Phosphorus removal
[0033] Adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 7, enter the ion exchange system, pass through the ion exchange column, and use gel-type anion exchange resin to adsorb phosphorus in the leaching solution. Adjust the valve to control the feed flow rate to be 0.5 times the column volume. After testing, after 200 minutes of contact between the feed liquid and the resin, the phosphorus content in the effluent is greater than 2ppm, the resin is saturated, and the adsorption is stopped immediately.
[0034] The resin is rinsed and analyzed with 4.2% ammonia solution, and the regeneration is completed at the same time. After the ammonium phosphate solution is concentrated and crystallized, it can be used for the production of phosphate fertilizer.
[0035] (2) Separation of...
Embodiment 3
[0042] After the spent catalyst was leached and filtered, 21.3m 3 The leach solution contains 1.55g / L phosphorus, 18.97g / L molybdenum and 23.2g / L vanadium.
[0043] (1) Phosphorus removal
[0044]Adjust the pH value of the leaching solution to 7.5, enter the ion exchange system, pass through the ion exchange column, and use gel-type anion exchange resin to adsorb phosphorus in the leaching solution. Adjust the valve to control the feed flow rate to be 1 times the column volume. After testing, after 150 minutes of contact between the feed liquid and the resin, the phosphorus content in the effluent is greater than 2ppm, the resin is saturated, and the adsorption is stopped immediately.
[0045] The resin is rinsed and analyzed with 4.4% ammonia solution, and the regeneration is completed at the same time. After the ammonium phosphate solution is concentrated and crystallized, it can be used for the production of phosphate fertilizer.
[0046] (2) Separation of molybdenum and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com