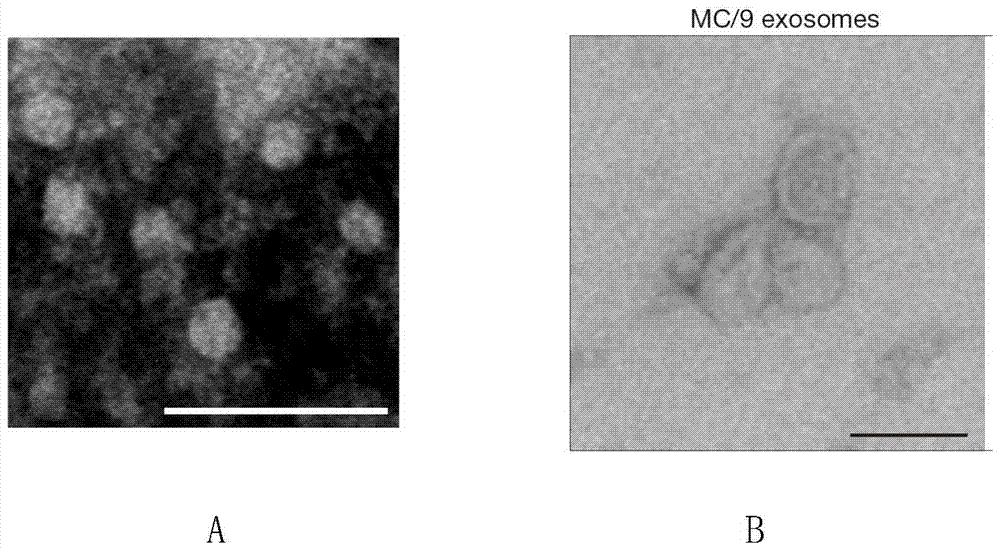
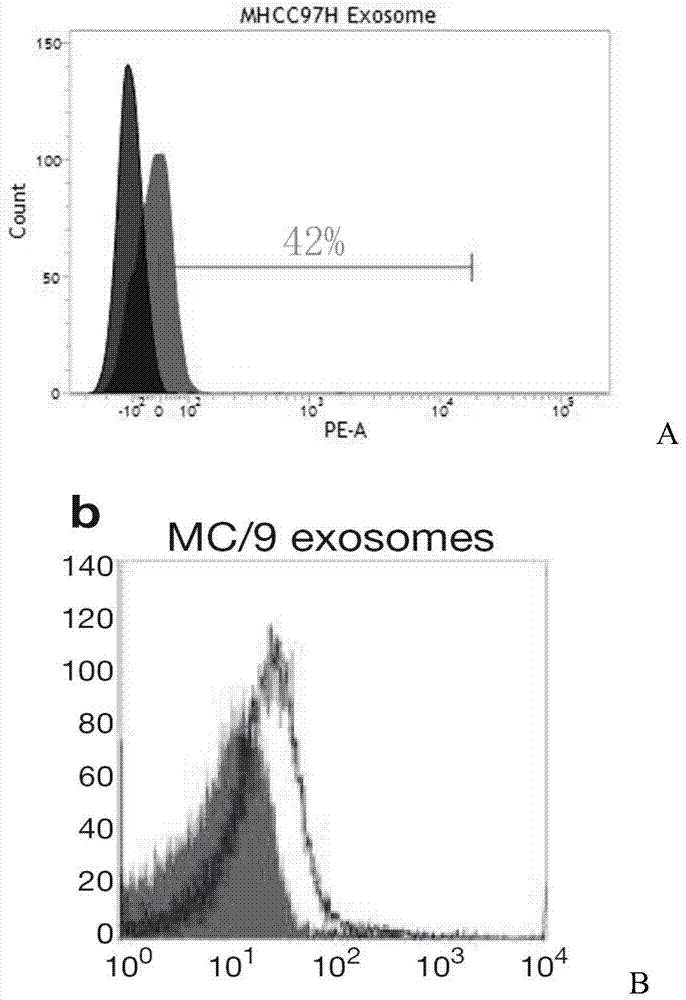
A method for rapid isolation of exosomes
A fast technology for separating cells, applied in animal cells, tumor/cancer cells, vertebrate cells, etc., can solve the problems of high cost and achieve the effects of shortening time, improving the purity of exosomes, and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1: Isolation of extracellular exosomes
[0028] Take human MHCC97H cells as an example (but the method of the present invention is not limited to MHCC97H cells):
[0029] will be 5×10 8 MHCC97H cells (Shanghai Medical College of Fudan University, Fan Jia's research group) were inoculated in T175 (Corning, USA) cell culture flasks containing 60ml of medium, and the medium composition was DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium, Life technologies, USA) plus 10 % (v / v) of fetal bovine serum (FBS, Life Technologies, USA). At 37°C with 5% CO 2 cultured in an incubator for 48 hours.
[0030] Collect 40 mL of the human liver cancer cell line MHCC97H cell culture supernatant, centrifuge at 400 g at 4°C for 5 min to remove cell debris, add RNase (Sigma, USA) at a final concentration of 1 mg / ml, 6.5% glycerol and 5.5 mM sorbitol, Then use a vacuum centrifugal concentrator (CentriVap, USA) to concentrate by centrifugation at 16° C. at 1500 g for 15 min to obtain a co...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com