Laminate, imaging element package, imaging device, and electronic device
A technology for laminates and interlayers, applied to optical components, coatings, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increased film formation time, reduced production efficiency, and dependent reflectivity, and achieve the effect of suppressing interference fringes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0050] 1. First embodiment (example of transparent laminate including a plurality of convex structures)
[0051] 1.1 Configuration of transparent laminate
[0052] 1.2 Method for producing transparent laminate
[0053] 1.3 Effect
[0054] 1.4 Variations
[0055] 2. Second Embodiment (Example in which a transparent laminate is applied to an imaging element package)
no. 3 approach
[0056] 3. Third embodiment (example in which a transparent laminate or a structural layer is applied to a camera module)
[0057] 4. Fourth Embodiment (Example in which a transparent laminate or a structural layer is applied to a digital camera)
[0058] 5. Fifth Embodiment (Example in which the transparent laminate or the structural layer is applied to a digital video camera)
[0059] 6. Sixth embodiment (example in which transparent laminate or structural layer is applied to electronic device)
[0060] 1. First Embodiment
[0061] 1.1 Configuration of transparent laminate
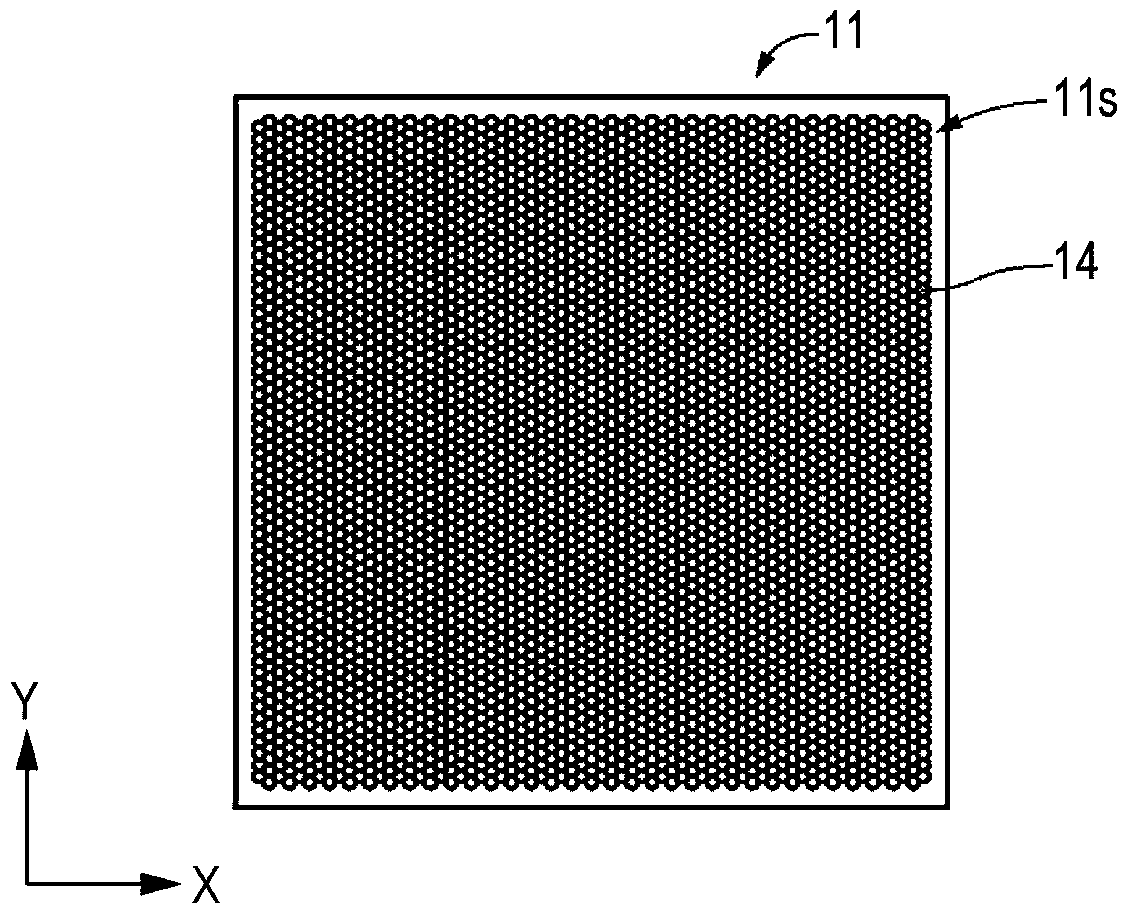
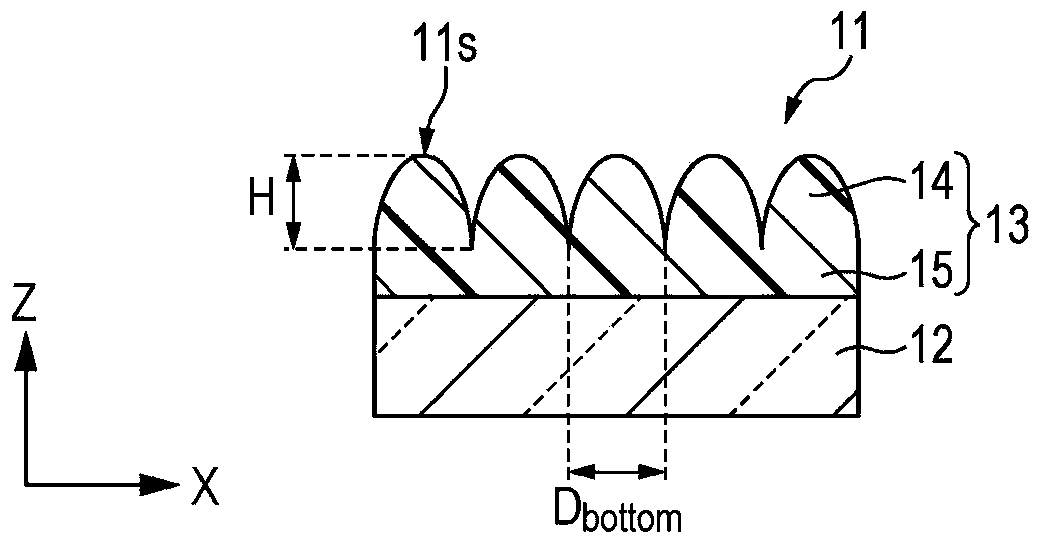
[0062] In the following, reference will be made to Figure 1A to Figure 1C A configuration example of the transparent laminate 11 is described. The transparent laminate 11 includes a surface 11s having an antireflection function. On the surface 11s, fine unevenness is provided. The transparent laminate 11 includes a substrate 12 having a surface and a structural layer 13 disposed on the surface of t...
Deformed example 1
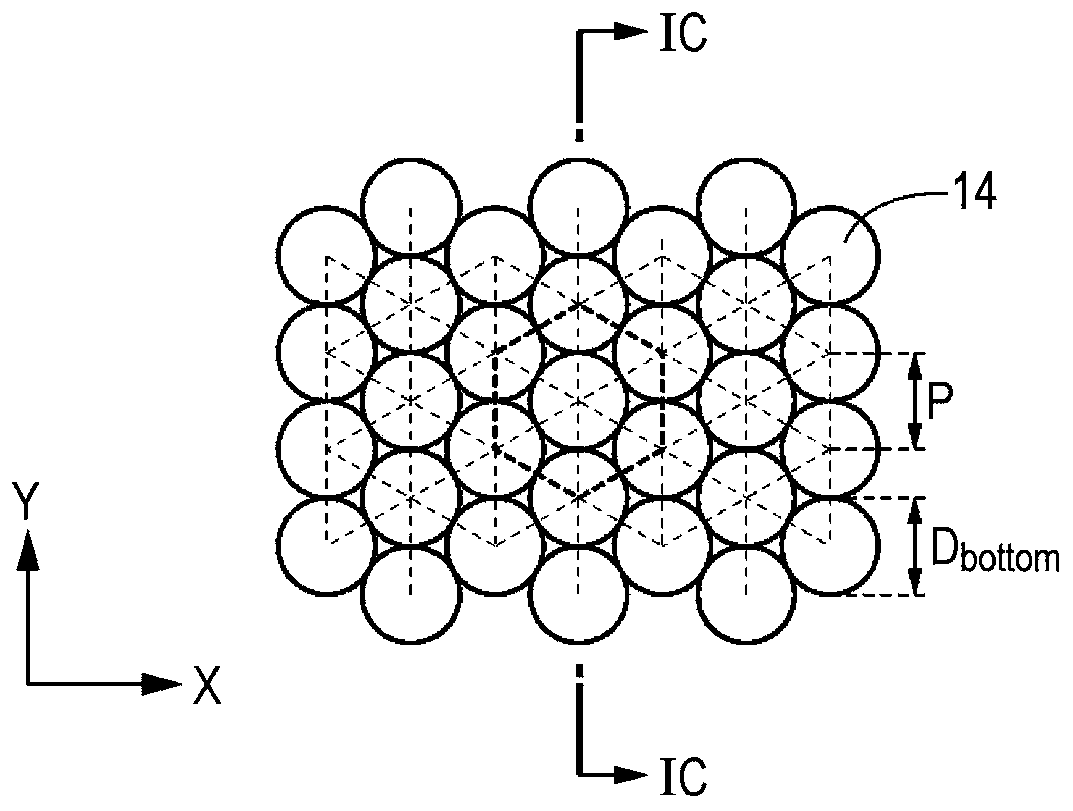
[0120] like Figure 5AAs shown, structure 14 may have a substantially flat top. For example, the plane of the top is substantially parallel to the surface of the substrate 12 . Preferably, the diameter D of the bottom of the structure 14 bottom and the distance P between the structure 14 satisfies 1.2>D bottom / P>1 relationship, and the diameter D of the top of the structure 14 top and the diameter D of the bottom of the structure bottom satisfy 0top / D bottom ≤1 / 10 relationship, and thus excellent anti-reflection performance can be obtained. For example, for the purpose of reducing reflection, the maximum reflectance of the reflective structure layer 13 itself with respect to light may be set to 0.2% or less. Here, 1.2>D bottom / P>1 means that the lower portions of adjacent structures 14 overlap each other. However, when 1.2>D is satisfied bottom / P and the overlap becomes larger, the height of the structures on the surface tends to be lower, and the antireflection p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com