Method for rapid separation of pathogen DNA from rice blast single scab
A rice blast fungus and rice blast technology, applied in the field of microbial molecular detection, can solve cumbersome problems such as grinding with liquid nitrogen, or cell wall-breaking lysis and repeated extraction, long experimental period, and high experimental cost. The effect of reducing cumbersomeness, rapid detection and monitoring, and simplification of procedures
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] It is to illustrate how the present invention is carried out by means of examples. These examples are only to illustrate how the present invention is realized, or the best implementation mode. These examples can not limit the present invention in any way. The scope of the present invention is the claims limited.
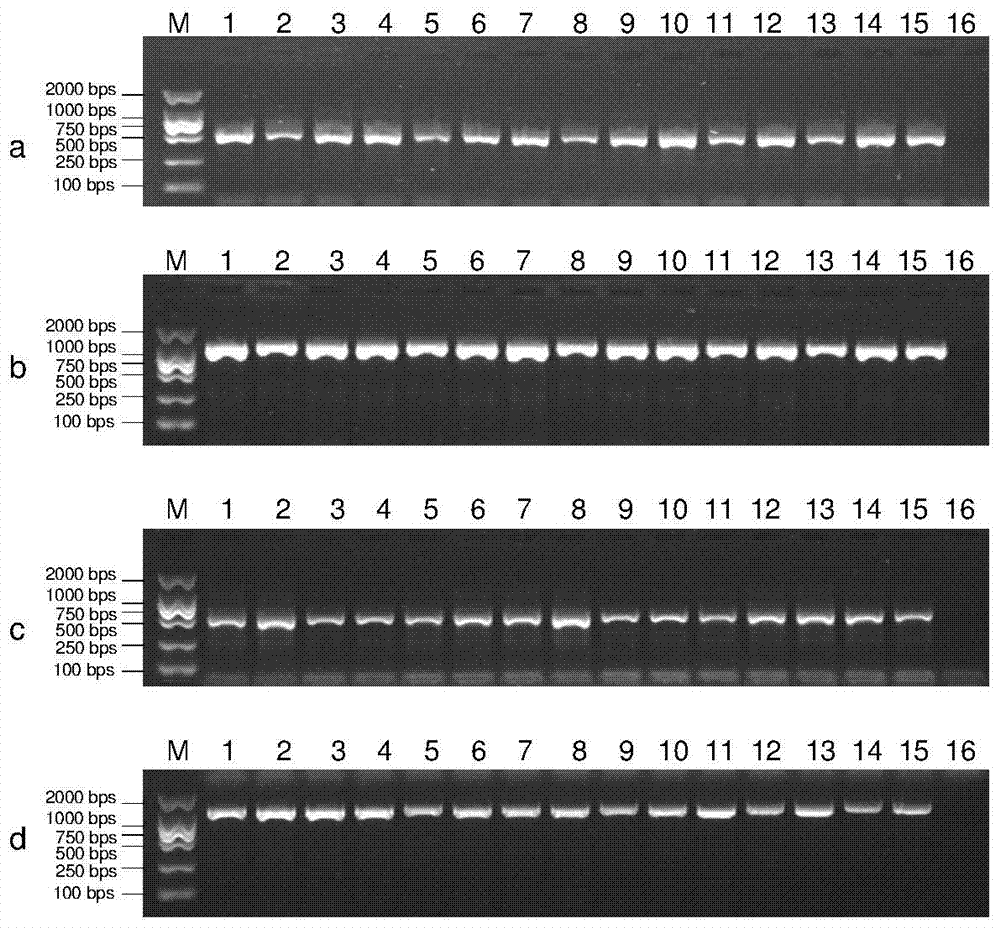
[0018] Implementation Example 1: Extraction and verification of DNA from rice leaves and Magnaporthe grisea.
[0019] The specific implementation method:
[0020] 1) Reagents: Prepare the following reagents in advance and use them after sterilization: (1), 100mM TrisHCl (pH8.7), (2), 10mM EDTA (pH 8.0), (3, )1M KCl, (4), 10% Tween 20.
[0021] 2) Sample preparation: Randomly select 15 typical diseased leaves and panicles that were collected from the field and stored in the laboratory after being dried at room temperature, and cut diseased leaves with a size of about 2 mm × 2 mm from a single lesion of the diseased rice leaf. Take 1-2mm long diseased panicle...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com