Preparation method of organic-inorganic composite separation membrane
An inorganic composite and separation membrane technology, used in semi-permeable membrane separation, chemical instruments and methods, membrane technology, etc., can solve the problems of high equipment requirements, changing proportions, and difficulty in obtaining a stable supply of raw materials in batches. The effect of increasing water flux
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022]
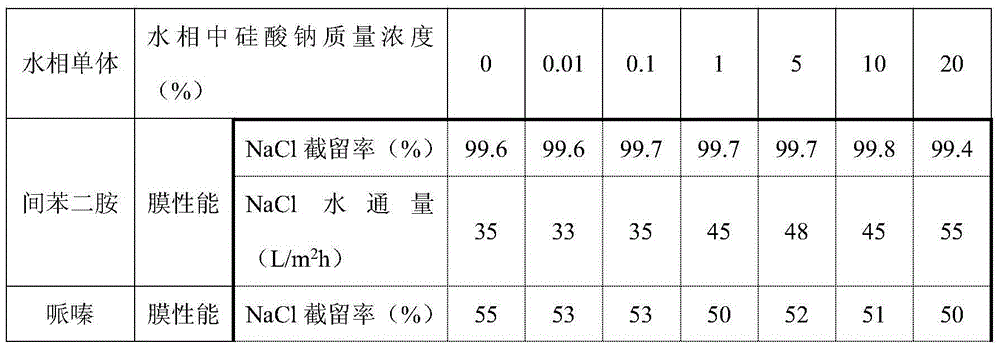
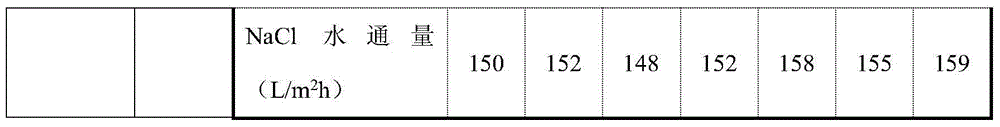
[0023]
[0024] As shown in the table above, sodium silicate is added to the water phase as a soluble inorganic precursor, and different concentrations of sodium silicate are added to the water phase during the preparation of the two composite separation membranes. The results showed that in the system of piperazine-trimesoyl chloride as the monomer, the addition of sodium silicate did not affect the rejection rate of sodium chloride by the composite membrane, and had little effect on the water flux of the composite membrane. In the system with m-phenylenediamine-trimesoyl chloride as the monomer, the addition of sodium silicate will not affect the rejection rate of sodium chloride by the composite membrane, and can effectively increase the water flux by about 10L / m 2 h.
Embodiment 2
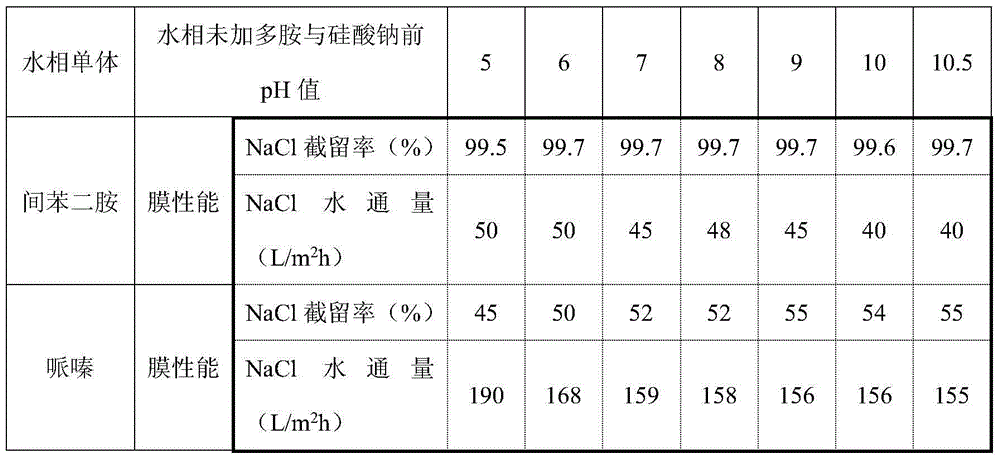
[0026]
[0027] As shown in the table above, the concentration of sodium silicate in the fixed water phase was 5%, and the pH value of the water phase was adjusted. The results showed that in the system of piperazine-trimesoyl chloride as the monomer, the change of pH value will not affect the rejection rate of sodium chloride of the composite membrane, and the influence on the water flux of the composite membrane is also small. In the system in which m-phenylenediamine-trimesic acid chloride is the monomer, the pH value should not be too high. When the pH of the water phase is less than 9 before adding polyamine and sodium silicate, the water flux can be effectively improved and the water Flux up to 50L / m 2 h. In addition, when the pH value of the aqueous phase is low, the rejection rate of the composite separation membrane has a certain attenuation.
Embodiment 3
[0029]
[0030]
[0031] As shown in the table above, ethyl orthosilicate is added to the oil phase as a soluble inorganic precursor, and different concentrations of ethyl orthosilicate are added to the oil phase during the preparation of the two composite separation membranes. The results show that in the system of piperazine-trimesic acid chloride as the monomer, the addition of tetraethyl orthosilicate will not affect the rejection rate of sodium chloride of the composite membrane, and has little effect on the water flux of the composite membrane . In the system where m-phenylenediamine-trimesyl chloride is the monomer, the addition of tetraethyl orthosilicate will not affect the rejection rate of sodium chloride in the composite membrane, and can effectively increase the water flux by about 25L / m 2 h.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com