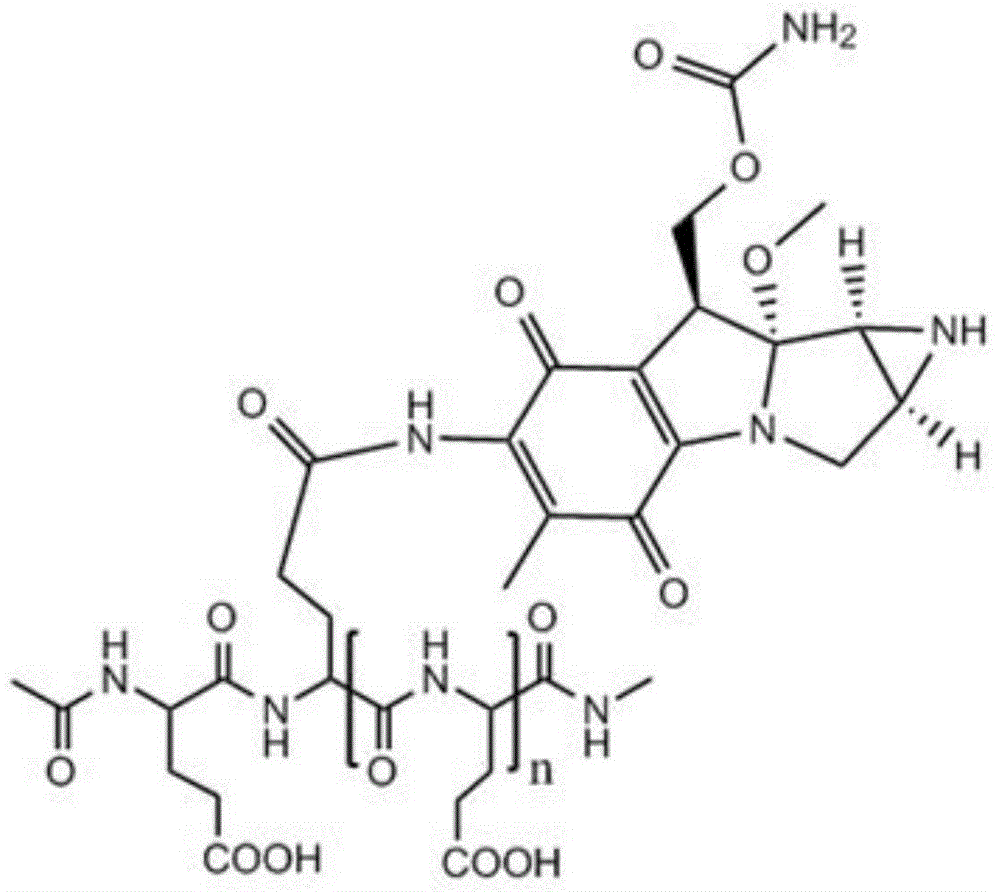
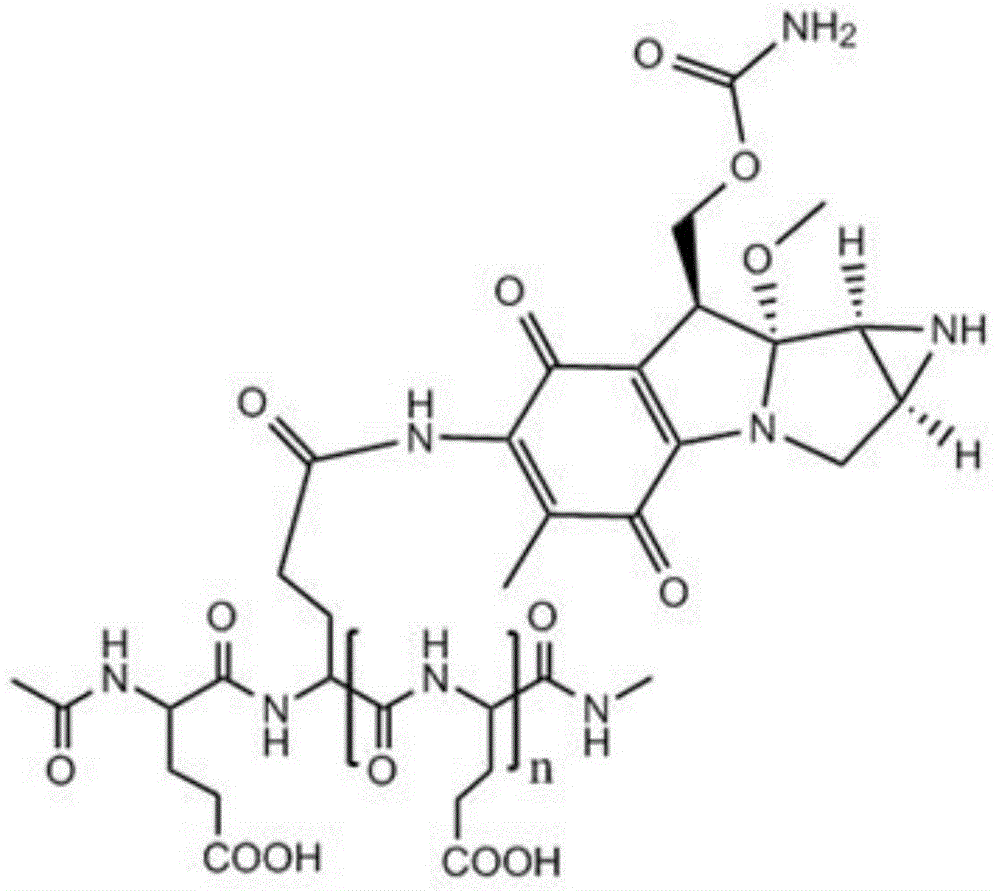
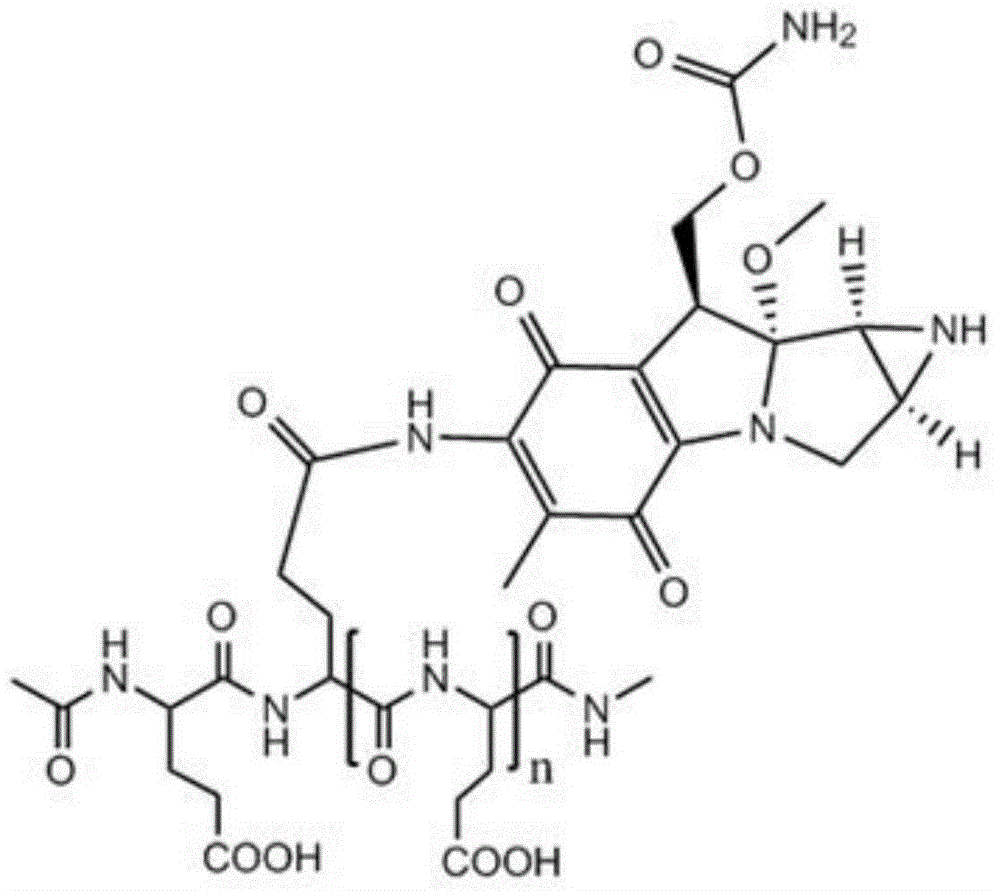
Low-molecular-weight L-polyglutamine-mitomycin C as well as synthesis method and applications thereof
A technology of polyglutamic acid and mitomycin, applied in the direction of drug combination, sensory disease, etc., can solve the problems of low molecular weight, toxic and side effects, etc., and achieve the effect of improving drug efficacy and reducing side effects of the whole eye
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0051] Take 20 g of polyglutamic acid (molecular weight of about 100,000 Daltons), dissolve it in water with pH=1, and stir it at 80°C for 8 hours; Polyglutamic acid with a molecular weight of 1500-2000, after freeze-drying, add 250ml of dioxane, 0.61g of N-hydroxysuccinimide, 1.10g of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 3ml of pyridine, and keep warm at 50°C After 10 hours, the solvent was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in 100 ml of chloroform, washed with 10 ml of dilute hydrochloric acid, and the chloroform layer was evaporated to dryness. Mycin C 3.34g, during which 0.5mol / L sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide aqueous solution was added to maintain pH 7.4; then the reaction solution was concentrated to dryness after stirring for 12 hours, and the residue was separated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent was two A mixture of methyl chloride and methanol at a volume ratio of 10:1) to obtain a yellow to white product, namely low molecular weight L-polyglutamic...
Embodiment 2
[0053] Take 22g of polyglutamic acid (molecular weight: about 100,000 Daltons), dissolve it in water with pH=1.3, and stir at 90°C for 6 hours; Polyglutamic acid with a molecular weight of 1500-6000, after freeze-drying, add 250ml of dioxane, 0.82g of N-hydroxysuccinimide, 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbon disulfide 1.08g of imide hydrochloride and 5ml of N-methylmorpholine were incubated at 40°C for 7 hours, the solvent was evaporated, and the residue was dissolved in 200ml of chloroform, washed with 20ml of dilute hydrochloric acid, and the chloroform layer was evaporated to dryness. Add to 30ml of 0.05mol / L HBS buffer (pH 7.4), add 1.67g of mitomycin C under stirring, add 0.7mol / L sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide to maintain the pH of the aqueous solution at 7.4; then stir for 12 hours After the reaction solution was concentrated to dryness, the residue was separated by silica gel column chromatography (the eluent was a mixture of dichloromethane and methanol ...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Take 24g of polyglutamic acid (molecular weight: about 100,000 Daltons), dissolve it in water with pH=2.5, and stir at 60°C for 12 hours; Polyglutamic acid with a molecular weight of 2000-3000, after freeze-drying, add 250ml of dioxane, 1.0g of N-hydroxysuccinimide, 0.51g of dicyclohexylcarbodiimide and 4ml of triethylamine, at 30°C Keep it warm for 6 hours, evaporate the solvent, dissolve the residue in 300ml chloroform, wash with 30ml of dilute hydrochloric acid, evaporate the chloroform layer to dryness, add the resultant to 40ml of 0.08mol / L HBS buffer solution (pH is 7.4), and add Mitomycin C 2.0g, during which 0.6mol / L sodium hydroxide or potassium hydroxide aqueous solution was added to maintain pH 7.4; then the reaction solution was concentrated to dryness after stirring for 12 hours, and the residue was separated by silica gel column chromatography (eluent It is a mixture of dichloromethane and methanol at a volume ratio of 10:1) to obtain a yellow to white pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com