Anhydrous arranging method for supercritical fluid textile materials
A supercritical fluid, textile material technology, applied in textile material processing, liquid/gas/steam textile material processing, and textile material processing equipment configuration, etc., can solve problems such as lack of processing, improve cleaning efficiency, shorten cleaning time and efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
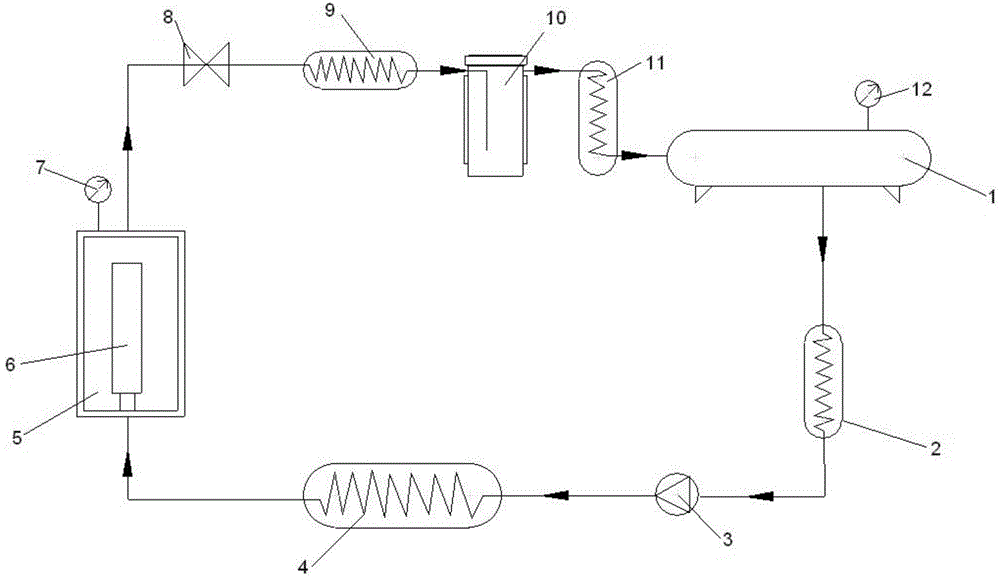
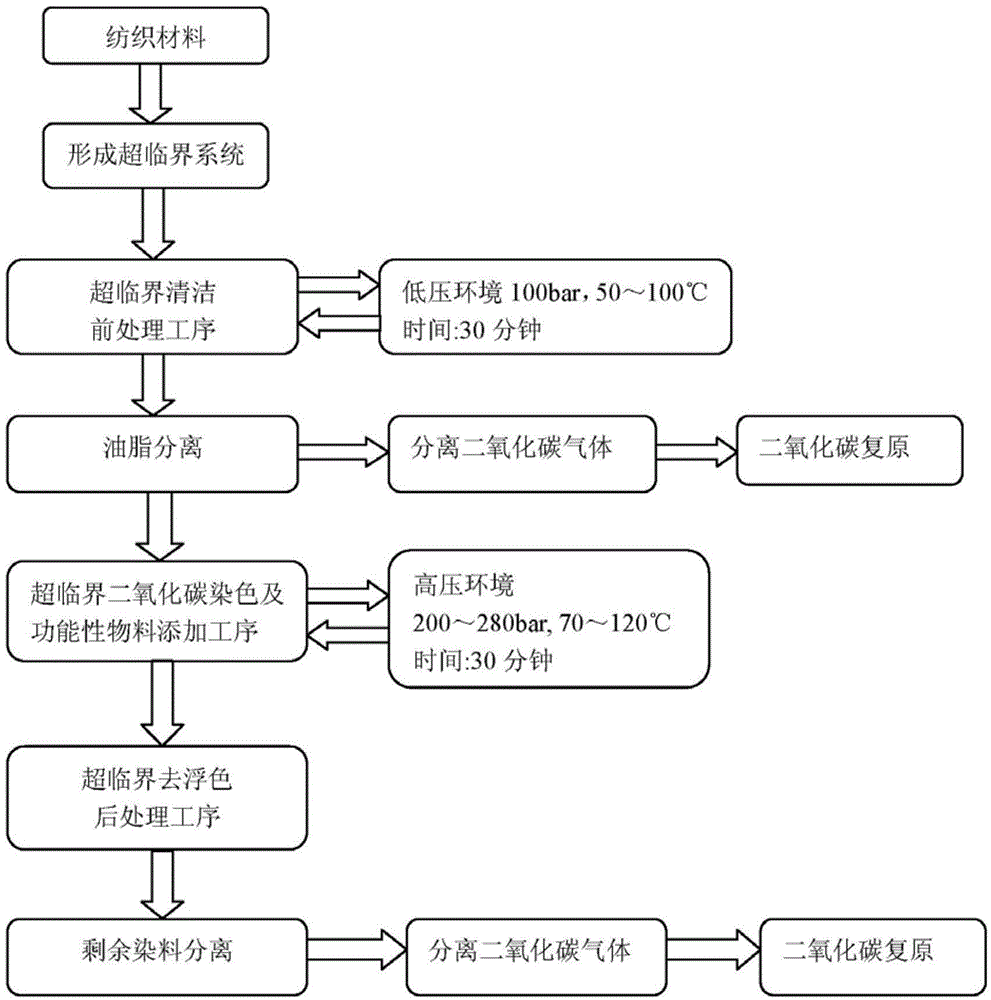
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for dyeing and finishing textile materials with supercritical fluid. Before dyeing textile materials with supercritical fluid, use supercritical fluid to clean the pretreatment process of textile materials. The specific process is as follows:
[0039] The carbon dioxide fluid is stored in the storage tank at room temperature and the pressure is about 5Mpa. The carbon dioxide enters the cooler and the temperature is controlled between 0 and 10°C (preferably 5°C), so that the carbon dioxide can fully form a liquid and the pressure is kept at About 5Mpa, the carbon dioxide is raised to a suitable pressure through a high-pressure pump, and the pressure can be controlled to about 10Mpa to reach a supercritical state, and then the temperature is raised to 50-100°C through a heat exchanger. Into the autoclave, the textile material is rinsed. The carbon dioxide containing oil is reduced to about 5Mpa by decompression. At this time, the absorbed...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Embodiment 2: Example of dyeing and functional material addition:
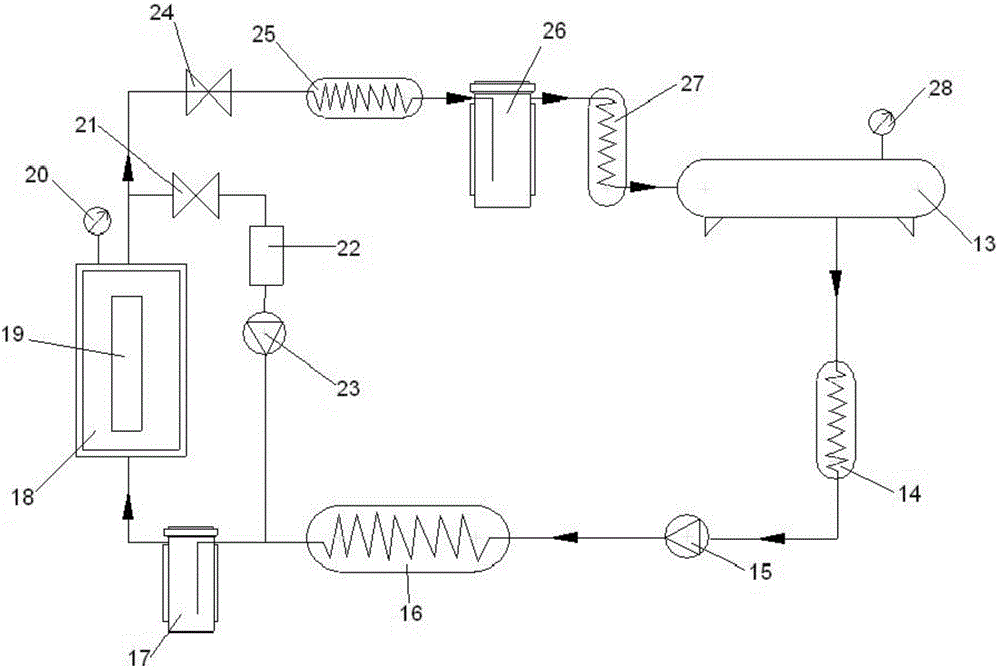
[0041] This embodiment provides a textile material dyeing and finishing method with supercritical fluid. Before dyeing the textile material with supercritical fluid, the pretreatment process of cleaning the textile material with supercritical fluid is used, and the cleaning pretreatment process and implementation Example 1 is exactly the same and will not be repeated here. The process of dyeing and adding functional materials is as follows:
[0042] The carbon dioxide fluid is stored in the storage tank at room temperature and the pressure is about 5Mpa. The carbon dioxide enters the cooler and the temperature is controlled between 0 and 10°C (preferably 5°C), so that the carbon dioxide can fully form a liquid and the pressure is kept at About 5Mpa raises the carbon dioxide to a suitable pressure through a high-pressure pump to make it reach a supercritical fluid state.
[0043] The pressure can be con...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: This embodiment provides a kind of textile material dyeing and finishing method of supercritical fluid, comprises the post-treatment process of removing floating color after dyeing is finished, specifically as follows:
[0045] The carbon dioxide fluid is stored in the storage tank at room temperature and the pressure is about 5Mpa. The carbon dioxide enters the cooler and the temperature is controlled between 0 and 10°C (preferably 5°C), so that the carbon dioxide is fully liquid and the pressure is kept at about The carbon dioxide is raised to a suitable pressure through a high-pressure pump at 5Mpa, and the pressure can be controlled to about 10Mpa to reach a supercritical fluid state, and then the temperature is raised to 50-100°C through a heat exchanger. Into the autoclave, the textile material is rinsed. The carbon dioxide containing the floating color dye is reduced to about 5Mpa through the pressure reducing valve. At this time, the absorbed heat ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com