Method for rapidly identifying disease resistance by inoculating grape powdery mildew to detached grape leaf
A technology of detached leaves and powdery mildew, applied in the field of bioengineering, to achieve the effect of fresh spores, good effect, and rich interaction theory
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Identification of disease resistance of isolated leaves of grape germplasm resources planted in the field with the powdery mildew strain NAFU1 inoculated
[0034] a. Isolation and purification of Erysiphe spp. strain NAFU1
[0035] During the onset period of grape powdery mildew, the leaves infected with grape powdery mildew were collected from serious vineyards, placed in a curler and brought back to the laboratory, and fresh diseased leaves with obvious symptoms of pathogenic bacteria were selected and placed in sealed bags until the disease occurred After it becomes particularly obvious, sweep the powdery mildew from the diseased leaves infected with powdery mildew to fresh grape leaves, and then place the inoculated grape leaves in a light incubator at a temperature of 22±1°C, light intensity of 10000LX, and relative humidity 50-75%, after 10-15 days, a monoclonal colony is obtained. When the monoclonal colony of powdery mildew grows to a diameter of 1 cm...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2: Identification of disease resistance of isolated leaves of grape hybrid progeny plants inoculated with grape powdery mildew strain NAFU1
[0050] a. Isolation and purification of Erysiphe spp. strain NAFU1
[0051] During the peak period of grape powdery mildew, the leaves seriously infected with grape powdery mildew were collected in the vineyard, and the single spore isolation method was used to isolate and purify grape powdery mildew from the picked diseased leaves, and the isolated grape powdery mildew strains were pathogenic Sexual identification, one of the strains was rapidly susceptible and highly pathogenic, meeting the identification requirements, and named the strain NAFU1;
[0052] b. Infection with Erysiphe spp. strain NAFU1
[0053] The healthy leaves of grapes were inoculated with preserved fresh powdery mildew NAFU1 by tablet inoculation method, and the infection process of NAFU1 on grapes was detected;
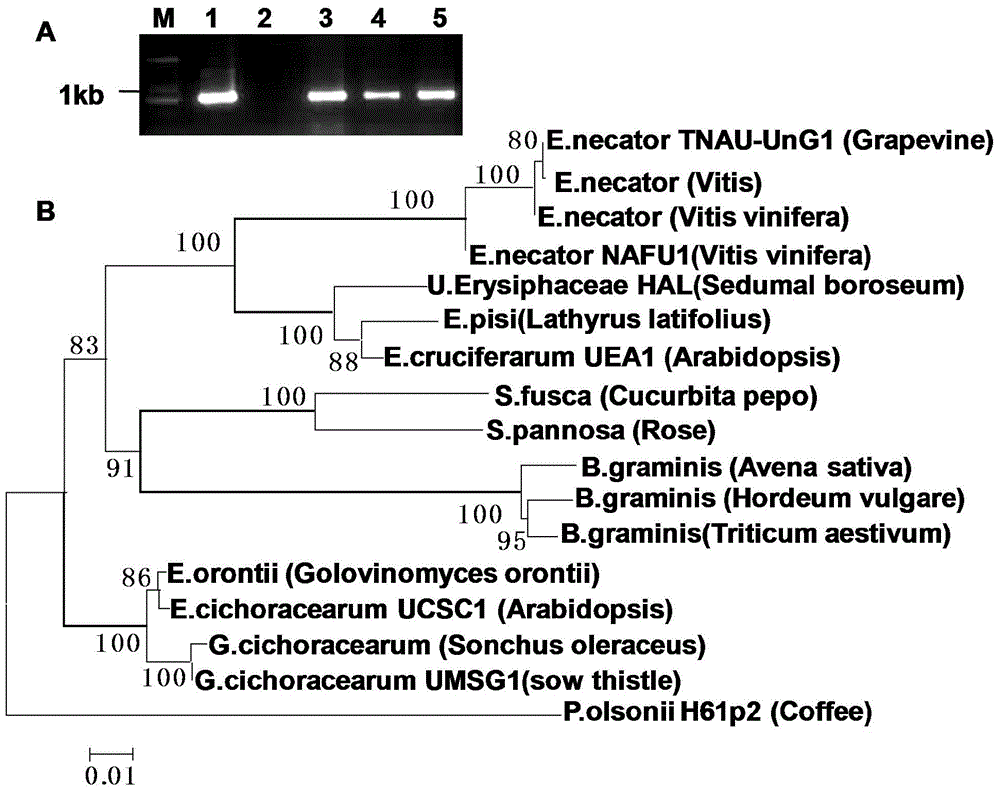
[0054] c. Sequence amplification of ...
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3: Identification of disease resistance of isolated leaves of transgenic grape plants inoculated with Vitis vinifera strain NAFU1
[0070] a. Isolation and purification of Erysiphe spp. strain NAFU1
[0071] During the peak period of grape powdery mildew, the leaves seriously infected with grape powdery mildew were collected in the vineyard, and the single spore isolation method was used to isolate and purify grape powdery mildew from the picked diseased leaves, and the isolated grape powdery mildew strains were pathogenic Sexual identification, one of the strains was rapidly susceptible and highly pathogenic, meeting the identification requirements, and named the strain NAFU1;
[0072] b. Infection with Erysiphe spp. strain NAFU1
[0073] The healthy leaves of grapes were inoculated with preserved fresh powdery mildew NAFU1 by tablet inoculation method, and the infection process of NAFU1 on grapes was detected;
[0074] c. Sequence amplification of NAFU1 rDNA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com