Trichoderma capable of preventing and treating root rot of loquat
A technology of loquat root and Trichoderma, which is applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as being difficult to achieve, and achieve the effect of strong antagonistic effect, large ecological benefit, and no environmental pollution.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Inoculate the LY1 Trichoderma strain in the center of a 90mm-diameter petri dish filled with PDA medium in advance, culture at 28°C for 5 days, and use a 5mm-diameter punch to take out the fungus cake for later use. The main phloem of the seedling is punched out, and the phloem is removed; the above-mentioned bacteria cake is placed in the loquat trunk hole from which the phloem has been removed, and sealed and kept moist with a plastic wrap. PDA nutrient cakes inoculated with the same diameter were used as a control. Routine fertilizer and water management was performed during the experiment. On the 30th day of inoculation, use a puncher with a diameter of 5 mm between the two inoculation points where the LY1 Trichoderma cake was inoculated, and take its phloem, and take 3 pieces for each plant for use. Disinfect with 74% alcohol for 1 min, 0.1% mercuric chloride for 1 min, rinse with sterile water for 3 times, blot the water with sterilized filter paper, inoculate on...
Embodiment 2
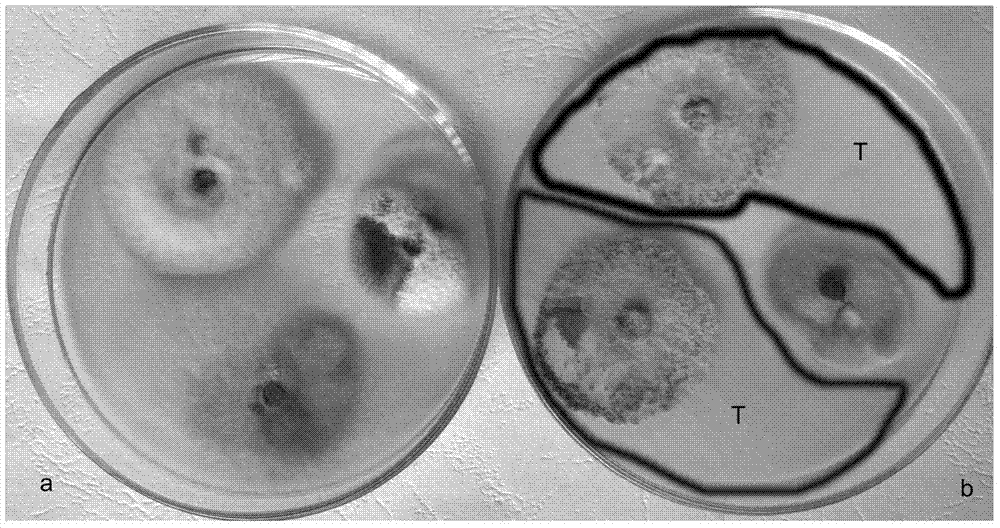
[0028] Trichoderma LY1 and loquat root rot strains (Pestalotiopsis sp.) were inoculated in the center of a 90 mm-diameter petri dish filled with PDA medium in advance, cultured at 28°C for 5 days, and then respectively Bacteria cakes with the same radius were taken and inoculated on a 90mm-diameter petri dish filled with PDA medium at the same time. The distance between the two inoculation points was 45mm. As a control, the cakes of loquat root rot fungus were inoculated separately, cultured at 28°C for 7 days, and measured. Root rot fungus colony diameter. The formula for calculating the inhibition rate is:
[0029] Inhibition rate / %=[(dCK-dB) / dCK]×100
[0030] In the formula, dCK represents the colony diameter of the control pathogenic bacteria, and dB represents the colony diameter of the treated pathogenic bacteria.
[0031]Measurement result dCK=90mm, dB=10.8mm, so inhibition rate=88%; Find that LY1 heavy parasitism on loquat root rot bacterial colony simultaneously ( ...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Example 3 The method of preventing and treating loquat root rot at the seedling stage
[0033] Inoculate the LY1 Trichoderma strain and the loquat root rot strain in the center of a 90mm-diameter petri dish filled with PDA medium in advance, culture at 28°C for 5 days, and use a 5mm-diameter punch to take out the fungus cake for later use. Punch out holes in the main phloem of loquat seedlings and remove the phloem; place the above-mentioned bacterium cake in the loquat trunk hole where the phloem was removed, and inoculate 5 bacterium cakes per plant, between two inoculation points, use the same method to inoculate 4 loquat root rot bacteria cakes, sealed with plastic wrap to keep moisture. Set only the plants inoculated with 5 loquat root rot bacteria cakes as the control, and the inoculation methods were the same. Routine fertilizer and water management was performed during the experiment. On the 12th day of inoculation, it was observed that the control leaves turn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com