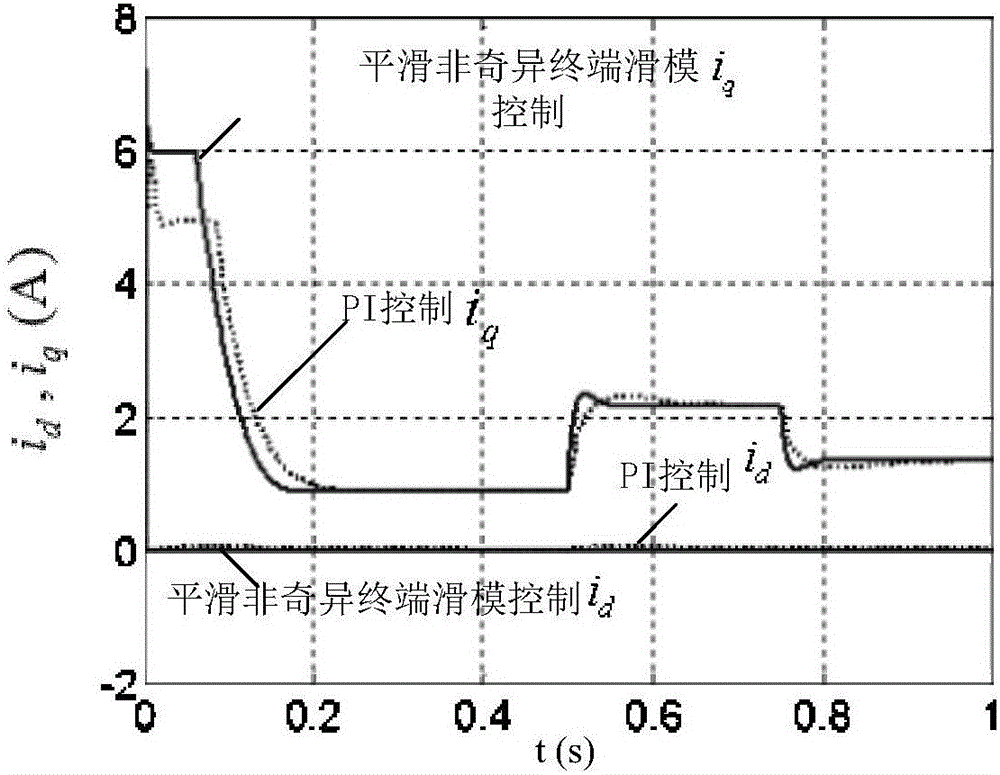
Smooth nonsingular terminal sliding mode control method for permanent magnet synchronous motor anti-reset windup based on relative order
A permanent magnet synchronous motor, non-singular terminal technology, used in motor generator control, electronic commutation motor control, control system and other directions, can solve the current and torque harmonic increase, motor heating, system speed response deterioration, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of continuous and smooth control signal, solving chattering problem, and fast response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
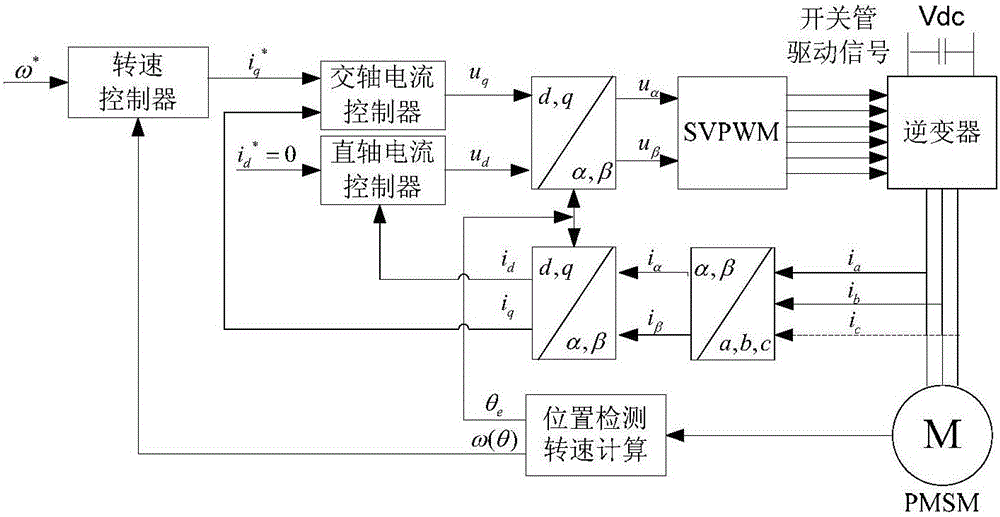
[0030] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 , the anti-resetWindup smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control method based on the relative order of the permanent magnet synchronous motor of the present embodiment, it is realized according to the following steps:
[0031] 1. Permanent magnet synchronous motor speed vector control system:
[0032] The mathematical model of the system in the dq synchronous rotating coordinate system can be expressed as:
[0033] i · d = - R s L i d + pωi ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
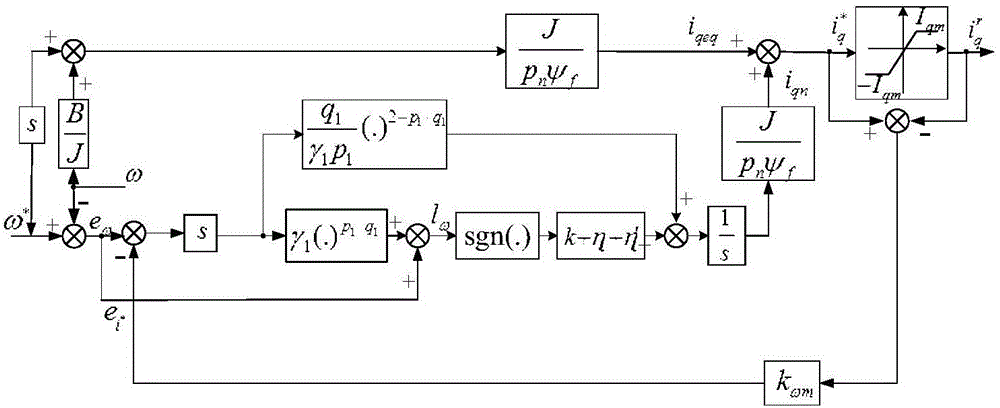
[0044] Specific implementation mode two: the difference between this implementation mode and specific implementation mode one is: combining figure 2 , it is noted that since the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode control method proposed in the present invention contains integral terms, the Windup problem described by Eq.
[0045] Learn from the integral elimination idea of the Anti-reset Windup method in PI control, introduce an adaptive anti-saturation mechanism, superimpose it into the speed tracking deviation system, and use the switching item i of the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode speed controller qn Adaptively eliminate the windup problem, specifically:
[0046] (1) Suppose the speed given signal ω * Smooth enough, speed tracking deviation e ω = ω * -ω and speed controller output signal deviation The variation is bounded, where, η 1 ′>0 is the feedback compensation coefficient. According to formula (1), the rotational speed tracking deviation s...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0084] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the smooth non-singular terminal sliding mode quadrature axis current controller in the step 3 is specifically:
[0085] Define the bias variable e q = i q * -i q , from formula (1), the quadrature axis current deviation system can be obtained as
[0086] e · q = i · q * - i · q = i · q * + pωi d + R s L i q + pψ f ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com