In-vivo drug testing system based on nanoparticle modified hollow-core optical fiber
A technology of hollow-core optical fiber and nano-particles, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting signal recording and weak spectral signals, and achieve the effect of no need for marking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
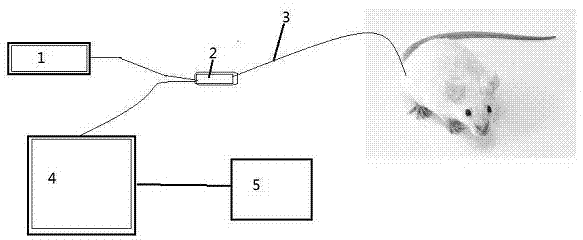
[0019] see figure 1 ~ image 3 , an in vivo drug detection system based on nanoparticle-modified hollow-core optical fiber, including a spectrometer (4), a hollow-core optical fiber (3), a laser light source (1), a lens combination optical path (2) and a computer (5), characterized in that The hollow-core optical fiber (4) is a hollow-core optical fiber modified with nanoparticles; the laser light source (1) is connected to the hollow-core optical fiber (3) through the output end of the lens combination optical path (2), and the hollow-core optical fiber (3) is modified with nanoparticles One end of the lens is inserted into the body; the other output end of the lens combination optical path (2) is connected to the spectrometer (4), and the spectrometer is connected to the computer (5); the laser excites the drug molecules in the body, and the generated optical signal information passes through the hollow-core optical fiber (3) To the lens combination optical path (2), throu...
Embodiment 2
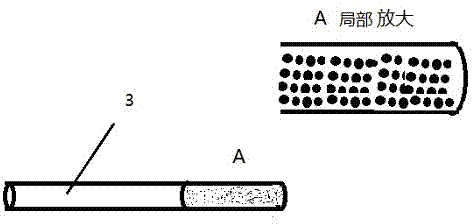
[0022] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special feature is: the inner surface of the nanoparticle-modified hollow-core optical fiber is decorated with nanoparticles, and the nanoparticles are gold, silver, copper, or gold-shell silver core or Silver core and gold shell, or nanoparticles or films whose surface is gold, silver or copper. The hollow-core fiber (3) includes a photonic crystal fiber, or a common hollow-core fiber.
Embodiment 3
[0024] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 2, and the special feature is
[0025] The spectrometer (4) uses a Renishaw Invia Confocal Raman Microscope confocal microscope system, the hollow-core fiber (3) uses an ordinary hollow-core fiber, and the nanoparticles modified at one end of the hollow-core fiber (3) are gold nanoparticles of about 50 nm The combined optical path (2) of the particles and the lens adopts an optical path with a filter, a trap and a reflective lens, and the computer (5) is an ordinary computer such as a Lenovo desktop computer. For example, the following test is done: inject ambroxol hydrochloride injection into the intraperitoneal cavity of the mouse, and half an hour later detect the Raman spectrum in the tail vein of the mouse through the hollow-core optical fiber (3). The characteristic peak of the Raman spectrum of ambroxol hydrochloride was detected, and through spectral analysis, it was shown that the mouse blood contained ambroxo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com