A kind of separation, culture method and application of testicular mesenchymal stem cells
A separation method and testicular interstitial technology, applied in the field of separation and culture of testicular interstitial stem cells, can solve the problems of unclear cell type, low amount of obtained cells, and lack of cell identification standards.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
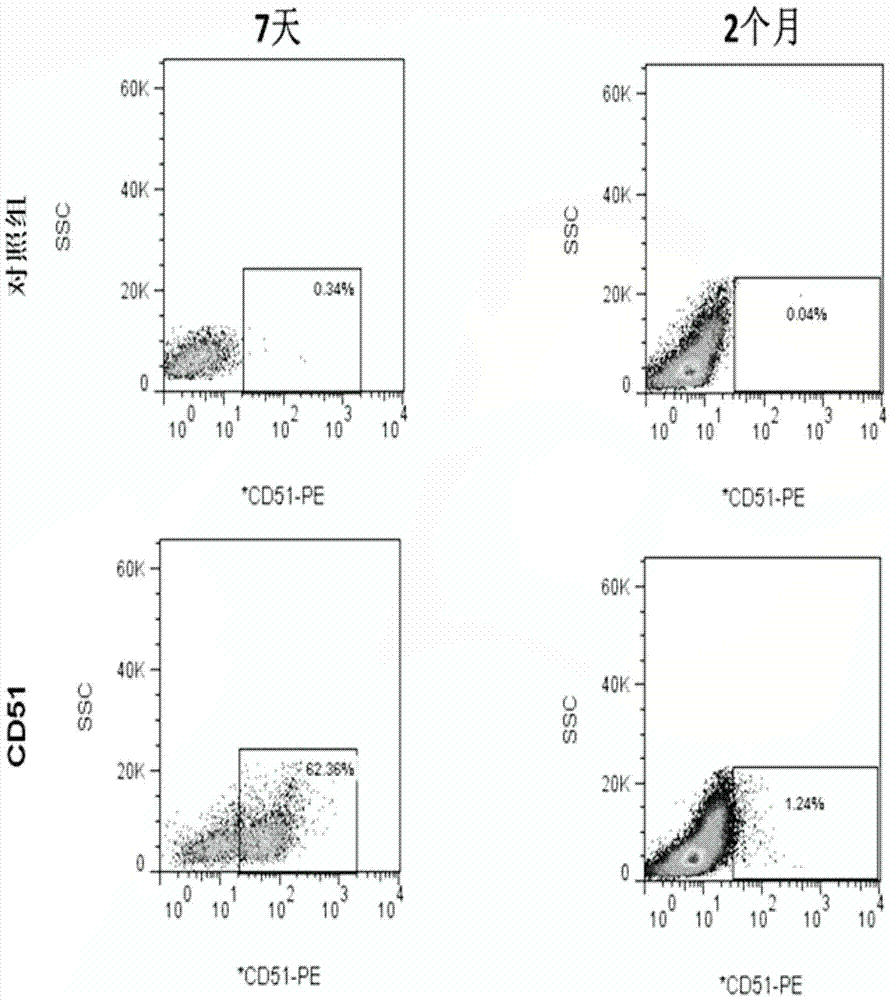
[0025] Example 1: Isolation of CD51-positive cells in the interstitium of mouse adult testis
[0026] In this example, testicular mesenchymal stem cells were isolated from mouse adult testes.
[0027] The separation method is as follows:
[0028] a. Take out the male C57BL / 6 male mice with healthy reproductive system 7 days after birth, kill them by cervical dislocation, open the scrotum under aseptic conditions, take out the bilateral testes, remove the capsule and blood vessels under a dissecting microscope, and use Wash repeatedly with 1×PBS containing 1% double antibody. Then blow gently with a straw and a gun tip to disperse the interstitial tissue and the fine tubules as much as possible, and cut the tissue part with small scissors. Then put in 1mg / ml type IV collagenase solution containing a small amount of DNase enzyme, incubate at 37°C and 5% CO2 for 15 minutes, add a large amount of 1×PBS containing 0.5% BSA to terminate the digestion of collagenase, and centrifuge...
Embodiment 2
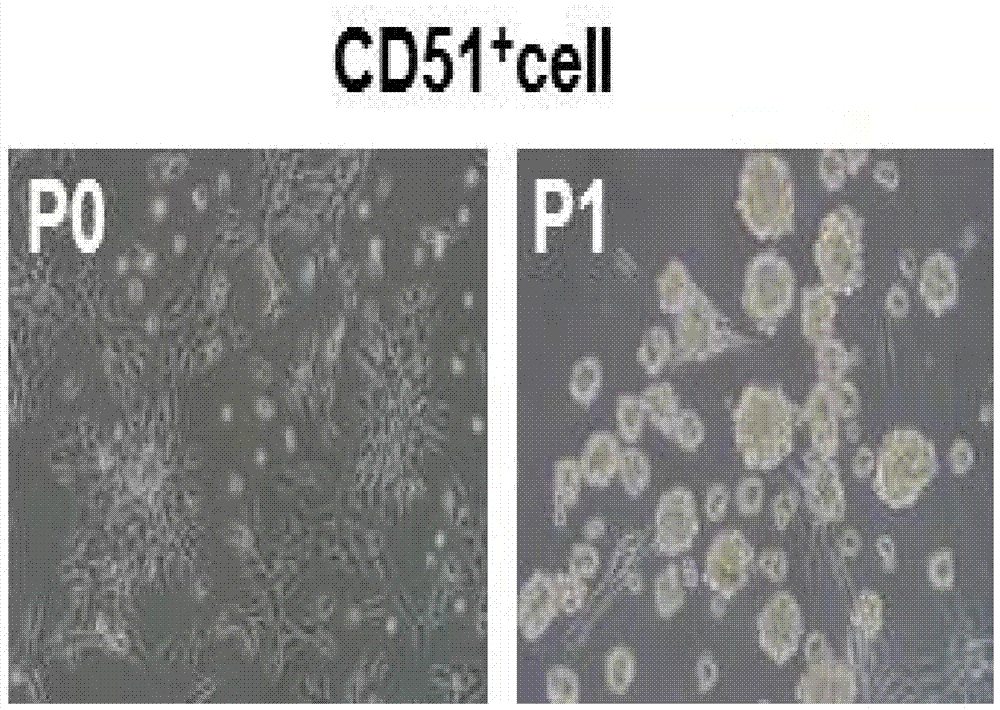
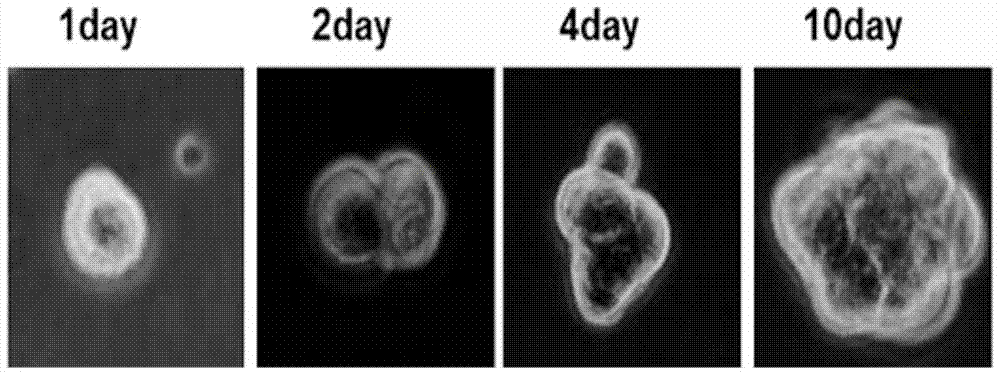
[0031] Example 2: Identification of self-renewal and proliferation abilities of CD51-positive testicular mesenchymal stem cells
[0032] In this example, on the basis of Example 1, the self-renewal and proliferation abilities of the obtained CD51-positive testicular mesenchymal stem cells were identified.
[0033] a. Identification of self-renewal ability of CD51-positive testicular stromal stem cells:
[0034] 1) Single CD51-positive cells sorted from mouse adult testes were placed in each single well of a 6-well plate for culture. The components of the culture solution include 1nM dexamethasone, 1ng / ml LIF (leukemia inhibitory factor), 5mg / liter insulin (insulin), 5mg / litertransferrin (transferrin), 5ug / litersodium selenite (selenite) added to DMEM-F12 medium ITS (insulin-transferrin-sodium selenite), 5% chicken embryo extract, 0.1mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1% non-essential amino acids, 1% N2 (N2 additive), 2% B27 (B27 serum-free additive) , 20ng / ml bFGF (basic fibroblast growt...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Example 3: Observing the role of CD51-positive testicular mesenchymal stem cells in tissue repair in vivo
[0043] Establishment of rat EDS model:
[0044] The ability of stem cells to regenerate damaged tissues in the body is an important attribute. Therefore, we investigated whether CD51-positive Leydig stem cells could promote Leydig cell recovery in a rat model of Leydig cell loss. Previous studies have shown that the cytotoxin ethane dimethylesulfonate (EDS) may deplete Leydig cells after 4 days of treatment. We selected three groups of adult rats, which were normal group, model group and cell group. Rats in model group and cell group were inoculated with EDS, 1x10 after 4 days 6 CD51-positive Leydig stem cells were injected into the cell group mice. Serum testosterone concentrations were measured on day 10 after transplantation. The result is as Figure 7 As shown, CD51-positive Leydig stem cells significantly promoted the secretion of testosterone in the te...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com