Laser noise elimination in transmission thermometry
A laser and grating technology, applied in the field of annealed substrate devices, can solve problems such as noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
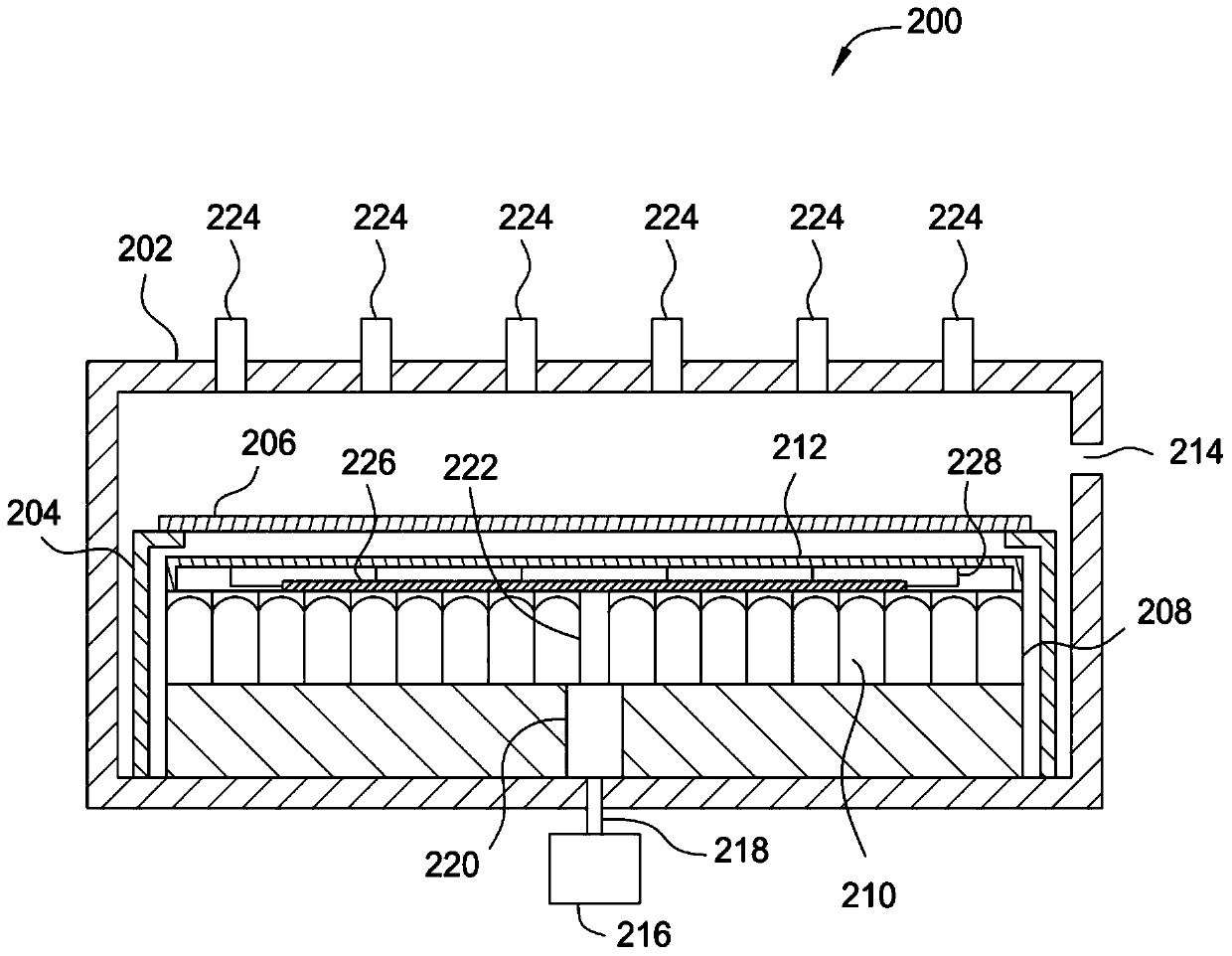
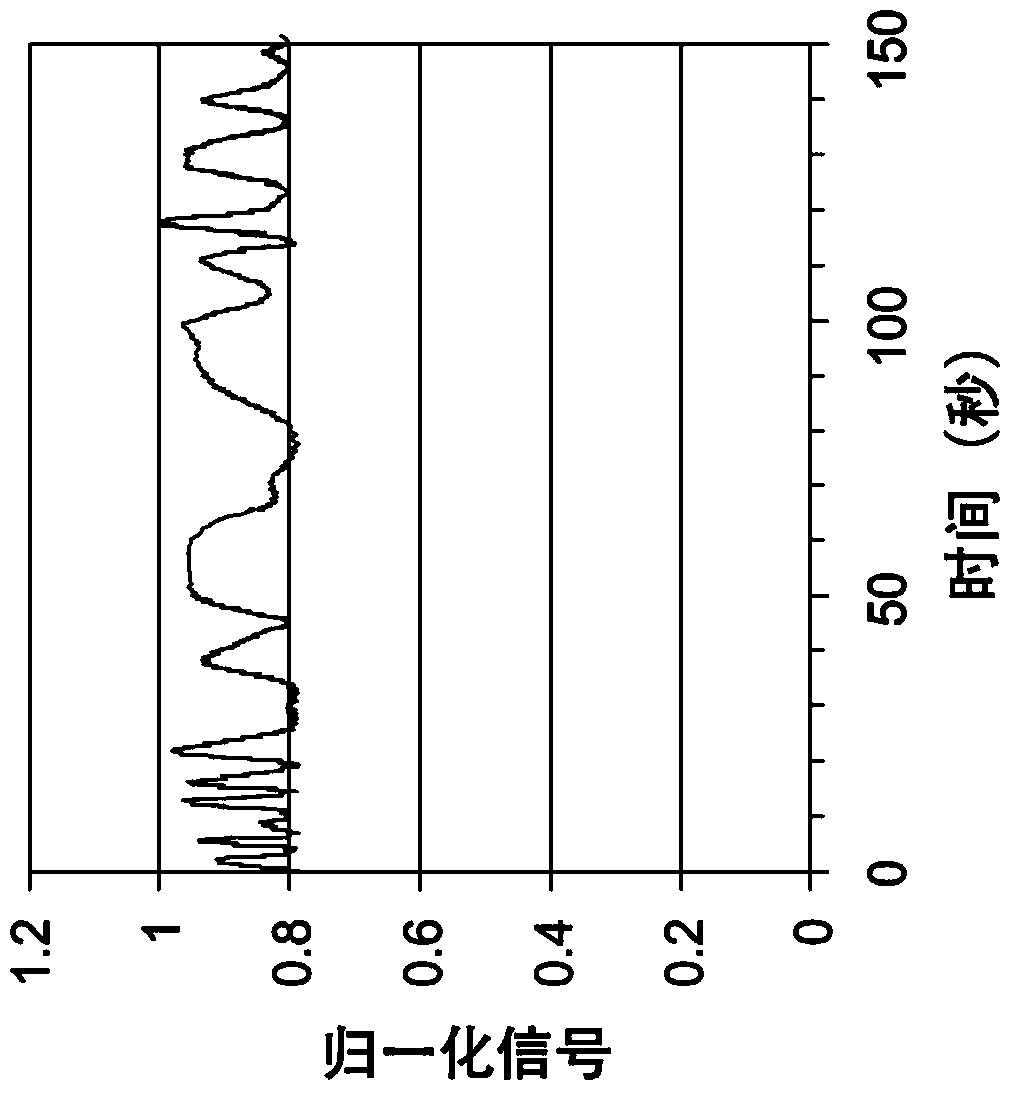
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
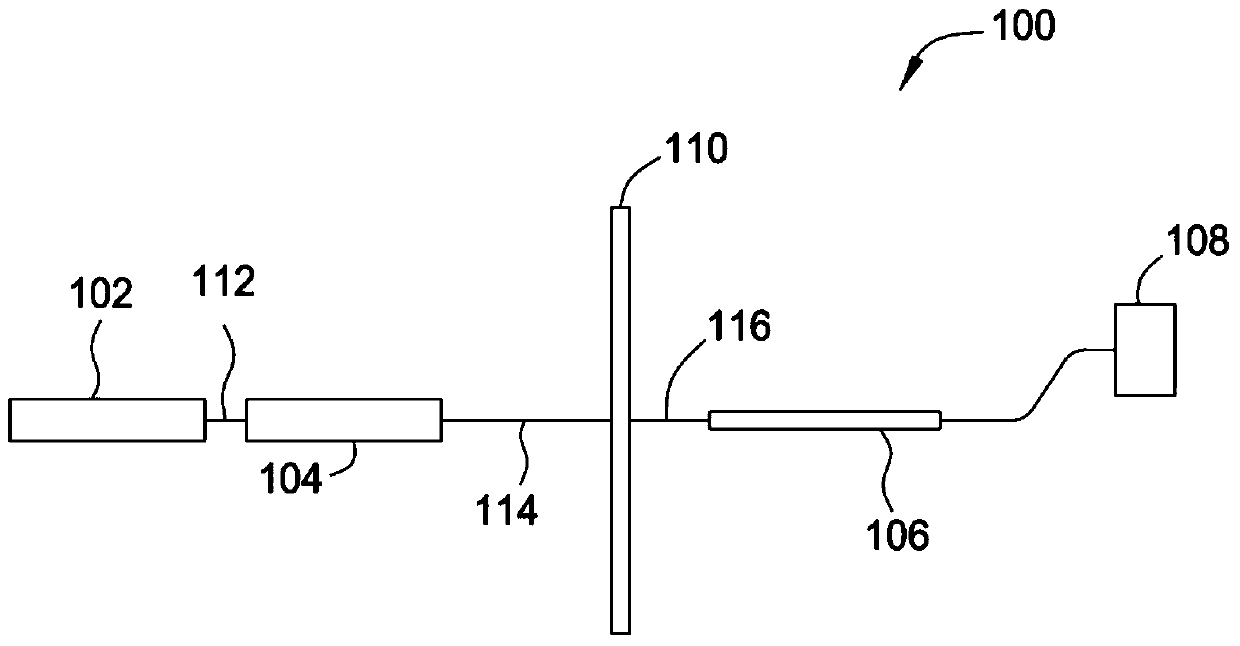
[0017] figure 1 Is a schematic illustration of an apparatus 100 for determining the thermal state of a substrate 110 according to one embodiment. The apparatus 100 comprises: a source 102 of coherent thermal radiation 112; a decorrelator 104 which converts the coherent thermal radiation 112 into decorrelated thermal radiation 114; a detector 106 which detects the transmitting radiation 116; and a data processor 108, such as a computer, for converting the signal from the detector 106 into an indication of the thermal state of the substrate 110.
[0018] Source 102 may be a laser, such as a laser diode, or source 102 may be another superluminescent source, such as a light emitting diode (LED). To accurately detect the thermal state of the substrate, source 102 is typically a source that emits a narrow spectrum of radiation such that absorption of said radiation by the substrate can be accurately determined. In most embodiments, source 102 is a laser diode. Laser diodes emitti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com