Methods and compositions for therapeutic drug monitoring and dosing by point-of-care pharmacokinetic profiling
A technology of pharmacokinetics and curve analysis, applied in the direction of analyzing materials, measuring devices, scientific instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing doctor-patient contact time, expensive, error-prone, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
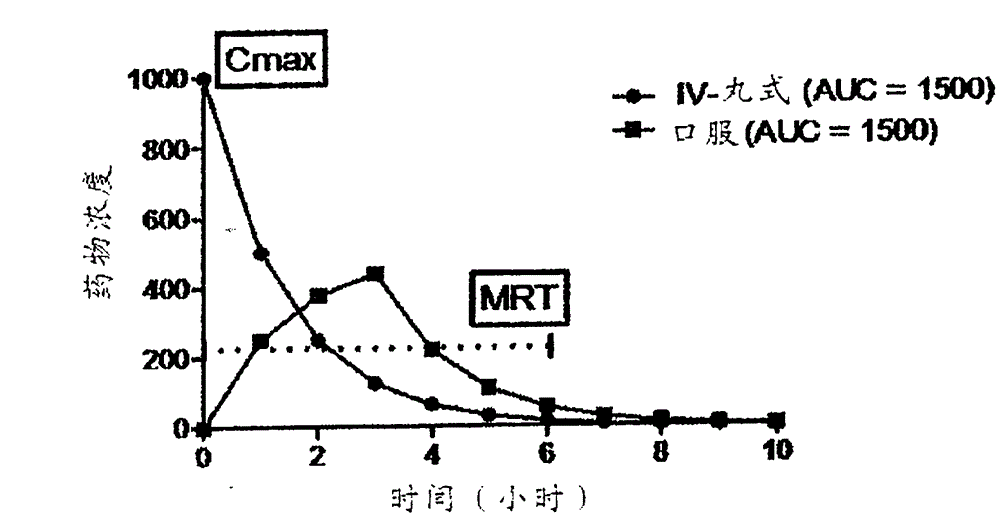
[0063] Example 1. The theoretical PK curve is shown in figure 1 middle. Such as figure 1 As shown in , the PK curve has two principal components, the absorption portion of the curve immediately after administration and the maximum blood concentration (C max ) after the attenuation / clearing portion of the curve. This topic starts with instant C in the case of pill administration max Delay C to case of oral administration max Variety. In between are intravenous infusion, intranasal, intrabuccal, intramuscular, intraperitoneal, etc. The three main features of the PK curve are: C max (maximum blood concentration), mean residence time (MRT) and AUC (area under the curve). AUC is often used to indicate blood exposure. However, two curves with the same AUC, such as figure 1 can have very different curves as depicted in . Intravenous bolus dosing exhibited higher initial blood concentrations, as indicated by C max = defined by dose / blood volume. Oral dosing exhibits longer...
Embodiment 2
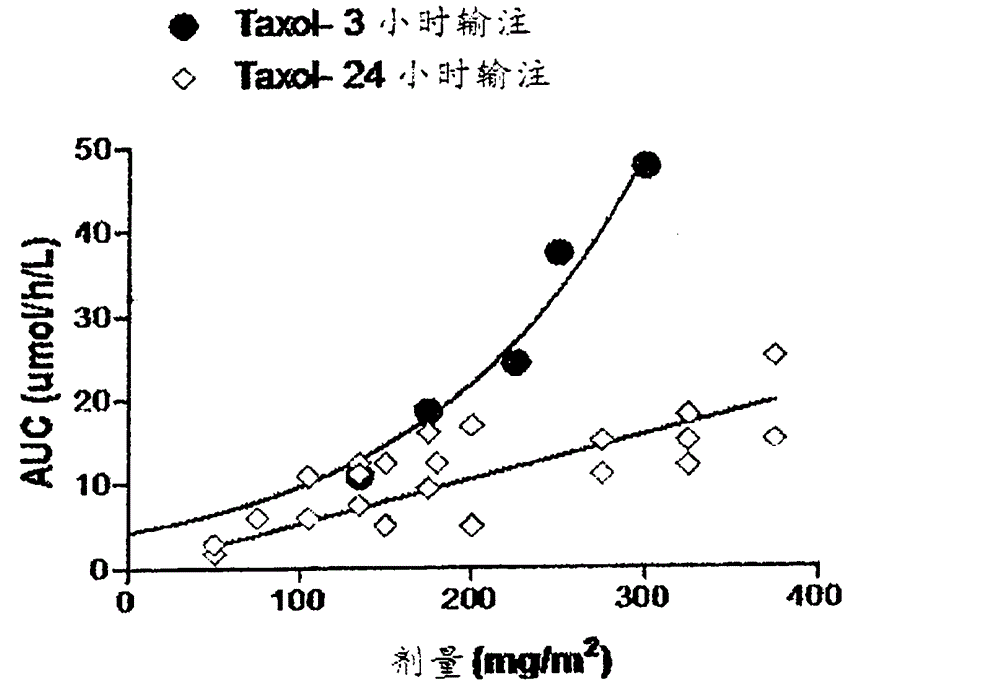
[0064] Example 2. To demonstrate that changing drug intake alone would change the PK profile, we studied the PK profile of Taxol dosed at a 3-hour infusion rate and a 24-hour slower infusion rate using Taxol's published pharmacokinetic data ( Ohtsu T, Sasaki Y, Tamura T, Miyata YNakanomyo H, Nishiwaki YSaijo N. (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of paclitaxel: a3-hour infusion versus a24-hour infusion. Clin Cancer Res. 1: 599-606.; Wiemik PH , Schwartz EL, Einzig A, Strauman JJ, Lipton RB, Dutcher JP. (1987) Phase I trial of taxol given as a24-hour infusion every21days: responses observed in metastatic melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 5: 1232-9.; Tamura T, Sasaki Y, Eguchi K, Shinkai T, Ohe Y Nishio M, Kunikane H, Arioka H, Karato A, Omatsu H, et al. (1994) Phase I and pharmacokinetic study of paclitaxel by 24-hour intravenous infusion. Jpn J Cancer Res. 85: 1057-62.; Tamura T, Sasaki Y Nishiwaki Y Saijo N. (1995) Phase I study of paclitaxel by three-hour infusion:...
Embodiment 3
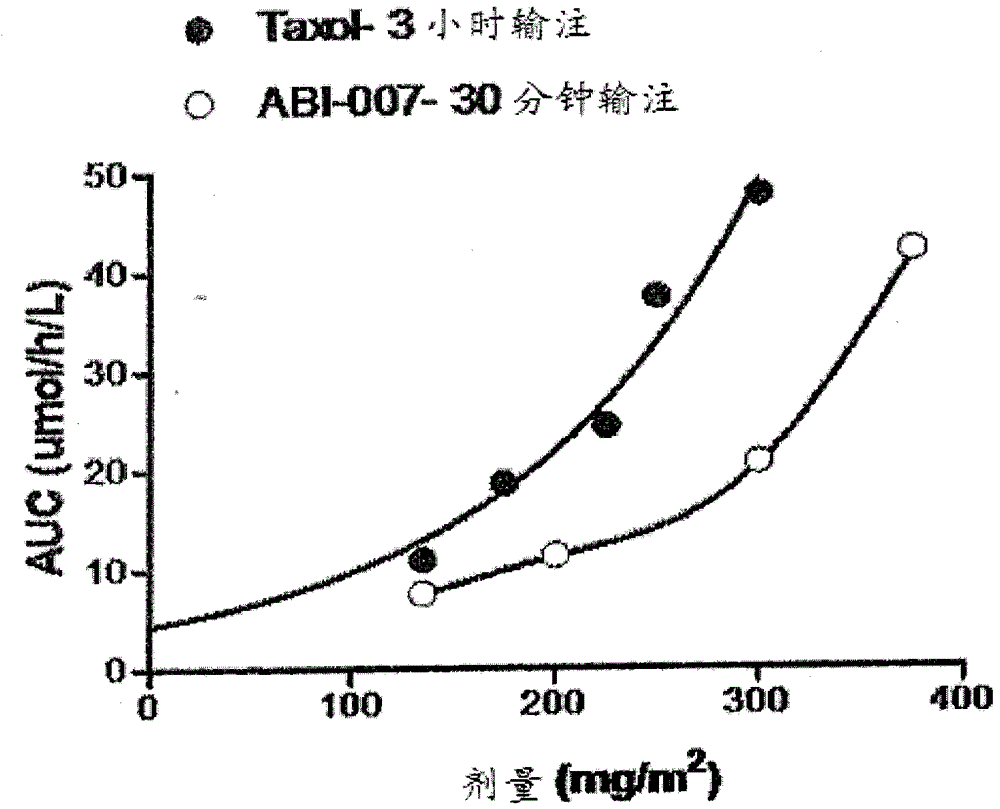
[0065] Example 3. To demonstrate that an increased rate of tissue distribution and thus a decreased rate of drug accumulation in the blood alters the PK profile, we investigated the PK profile of Abraxane versus Taxol. Such as image 3 Paclitaxel formulated as Abraxane (ABI-007) exhibited lower AUC compared to paclitaxel formulated as Taxol (Cremophor EL) as shown in . No increase in AUC was observed with faster absorption / infusion (30-minute infusion of Abraxane versus 3-hour infusion of Taxol). FDA approved Abraxane in 2005 (albumin-conjugated paclitaxel, Abraxis BioSciences) for metastatic breast cancer. Abraxane formulations are known to result in faster tissue penetration, a property known to vary among individuals, depending on their levels of paclitaxel-binding proteins, among others. This again demonstrates that PK curve analysis using global PK data is more suitable for therapeutic drug monitoring. We found that such as Genexol ( Figure 4 ) and Nanoxel ( Figu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com