A method for assisting identification of soybean mosaic virus resistance gene and its application
An auxiliary identification and leaf virus technology, applied in the field of soybean genetics, can solve the problems of long genetic distance between markers and genes and small application range, and achieve the effects of improving breeding efficiency and accuracy, efficient selection, and accelerated breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
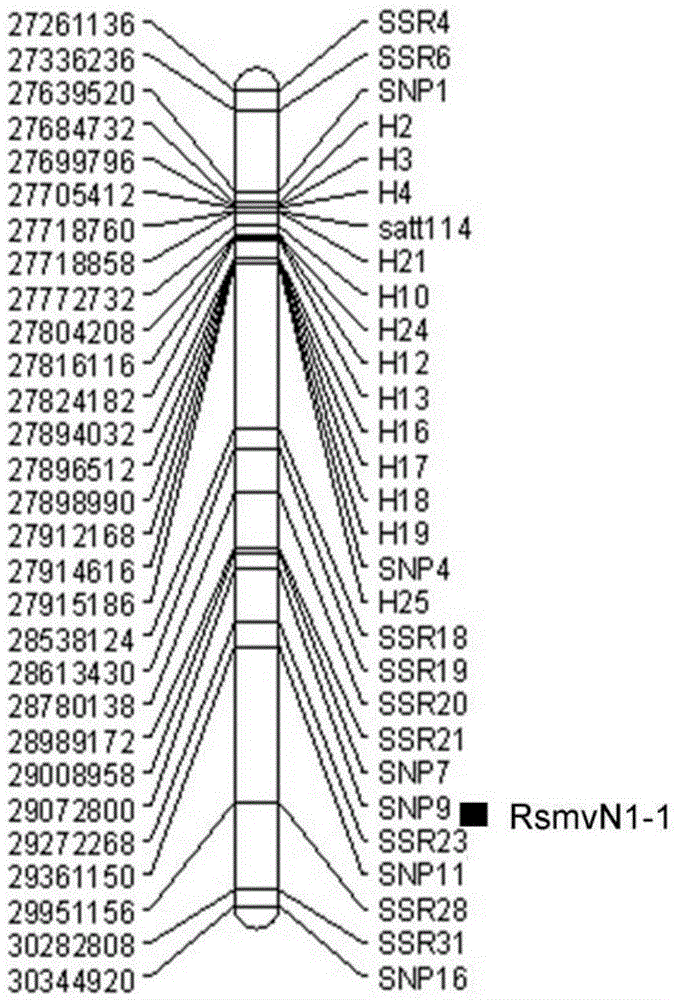
[0031] The acquisition of the gene locus RsmvN1-2 of the resistance soybean mosaic virus disease (SMV) N1 strain of embodiment 1
[0032] 1. Construction of recombinant inbred lines and F2 segregation generation populations and identification of SMVN1 strains
[0033] Hybrid F1 was obtained by crossing Chinese soybean cultivars Dongnong 93-046(♀) and Hefeng 25(♂); the offspring were obtained by self-pollination of the hybrid F1 generation, and 130 offspring were obtained by single seed propagation (SSD) F2: 6th generation recombinant inbred line; hybrid F1 was obtained by crossing the above parents, and continued selfing to obtain 2000 seeds of F2 segregation generation individuals.
[0034] In 2007, 2008, and 2009, 130 strains and their parents were inoculated with N1 race in an independent aphid-proof net room, and the inoculation was repeated three times. In 2013, in an independent aphid-proof net room, 2000 F2 generation single plants and their parents were inoculated and...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 Application of gene locus RsmvN1-2 in assisted selection in hybrid high-generation populations
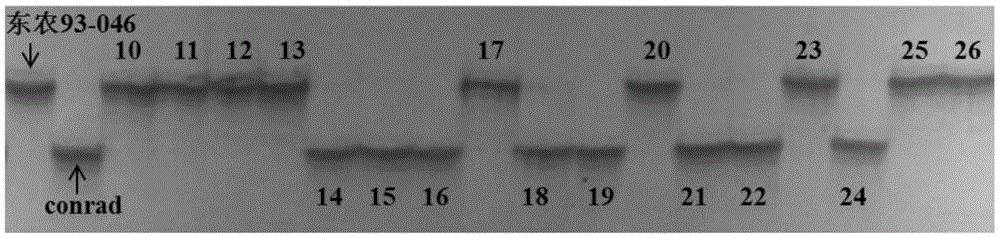
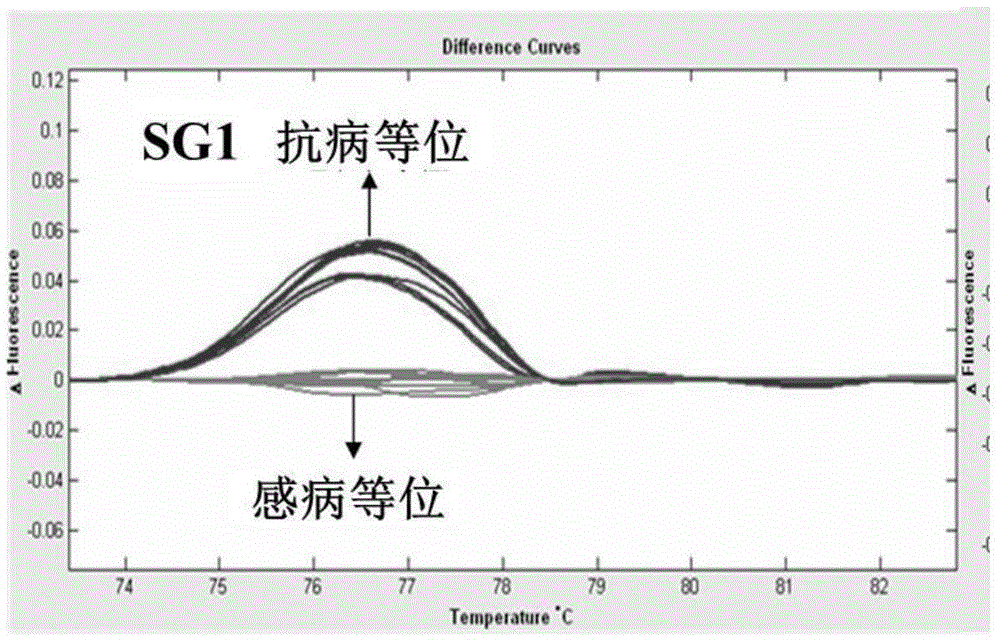
[0053] After obtaining the genetic locus RsmvN1-2 of soybean mosaic virus (SMV) N1 strains, Chinese soybean cultivars Dongnong 93-046(R) and conrad(S) were used for hybridization using the SSR64 and SG1 primer sequences ( shown in SEQ ID NO.1-NO.4) PCR amplification was performed on the obtained 150 F2:6 generation recombinant inbred lines, and the anti-sensitivity responses of these tested families to the two strains were predicted. The PCR amplification conditions, electrophoresis and genotype analysis conditions were the same as those given in Example 1. At the same time, 150 families were carried out for the identification of resistance to N1 virus strains, and the degree of agreement between the field identification results and the PCR amplification-assisted screening results of the marker sites was compared (see Table 2, figure 2 and image 3 ). figure 2...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3 Application of Gene Locus RsmvN1-2 in F2 Segregation Generation Assisted Screening of Resistant and Sensitive Individual Plants
[0057] After obtaining the gene locus RsmvN1-2 of the N1 line resistant to soybean mosaic virus (SMV), using the molecular markers SSR64 and SG1 that co-segregate with the disease resistance locus, a pair of 60 Dongnong 93-046 was used as one of the parents to derive Genotyping of the F2 individual strains (the analysis method is the same as that described in Example 1) to predict the anti-sensitivity response of these tested individual strains to the SMVN1 strain. Simultaneously, 60 F2 individual plants were tested for N1 race resistance, and the results of field identification and marker-assisted screening were compared (see Table 3). The results showed that the results of marker-assisted screening were in good agreement with the actual resistance identification performance.
[0058] Table 3 The genotyping results of molecular ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com