An Infrared Identification Method of True and False Cinnabar Root Tubers
A true and false black and infrared technology, applied in measuring devices, material analysis through optical means, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, time-consuming, complicated identification procedures of true and false roots of black medicine, and reduce machine errors , the effect of improving the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
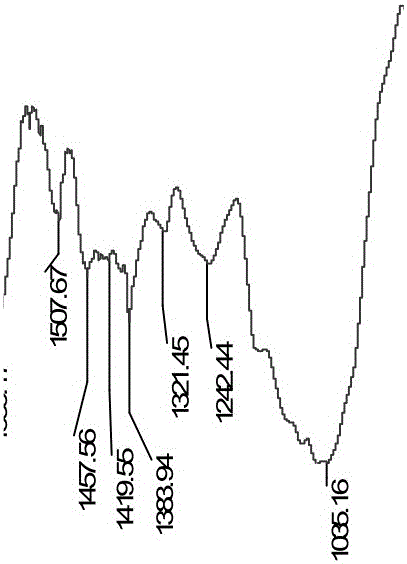
[0020] see figure 1 , In this embodiment, the infrared identification method of true and false black medicine tuber is composed of the following steps in turn.
[0021] (1) Weigh 10 g of sliced Agarwood root samples, and dry them in a 60°C oven to constant weight.
[0022] (2) pulverize the dried agarwood root sample, pass through a 100-mesh sieve, accurately weigh 0.5 g of spectrally pure potassium bromide, accurately weigh 0.005 g of agaric powder, place it under an infrared lamp, and grind it in an agate mortar Mix evenly and press to obtain a tablet sample.
[0023] (3) Put the pressed sample into the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, and set the resolution to 1cm -1 , scanning wavelength range 400-4000cm -1 Under the conditions of 32 scans, the average infrared spectrum was obtained.
[0024] (4) Observe the average infrared spectrum, such as figure 1 shown at 1450cm -1 ~1380cm -1 There are sawtooth peaks between, and the wavelength is 1080.4±1cm -1 There...
Embodiment 2
[0026] see figure 2, In this embodiment, the infrared identification method of true and false black medicine tuber is composed of the following steps in turn.
[0027] (1) Take 10 g of agarwood decoction pieces as agarwood root samples, and dry them in an oven at 60°C to constant weight.
[0028] (2) pulverize the dried agarwood root sample, pass it through a 100-mesh sieve, accurately weigh 0.5 g of spectrally pure potassium bromide, accurately weigh 0.005 g of the powdered agaric root sample, place it under an infrared lamp, and place it in an agate mortar. The internal grinding and mixing are uniform, and the tablet is pressed to obtain a tablet sample.
[0029] (3) Put the pressed sample into the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, and set the resolution to 1cm -1 , scanning wavelength range 400-4000cm -1 Under the conditions of 32 scans, the average infrared spectrum was obtained.
[0030] (4) Observe the average infrared spectrum at a wavelength of 1450cm -1 ~...
Embodiment 3
[0032] In the present embodiment, the infrared identification method of true and false black medicine tuber consists of the following steps in turn.
[0033] (1) Weigh 10 g of sliced Agarwood root as a Agaricus root sample, and dry it in an oven at 60°C to constant weight.
[0034] (2) pulverize the dried agarwood root sample, pass through a 100-mesh sieve, accurately weigh 0.5 g of spectrally pure potassium bromide, and accurately weigh 0.005 g of the powdered agaric root sample powder, place it under an infrared lamp, and place it in an agate mortar. Grind and mix evenly and press to obtain a tablet sample.
[0035] (3) Put the pressed sample into the Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, and set the resolution to 1cm -1 , scanning wavelength range 400-4000cm -1 Under the conditions of 32 scans, the average infrared spectrum was obtained.
[0036] (4) Observe the average infrared spectrum, wavelength 1450cm -1 ~1380cm -1 There are sawtooth peaks between, and the wa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com