Numerical analysis method for piping phenomenon
A numerical analysis and phenomenon technology, applied in the fields of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., which can solve the problem that the results are quite different from expectations, have no adaptability, and cannot consider the geometric and hydraulic characteristics of soil and water-soil interaction. function and other issues, to achieve the effect of less constraints and a wide range of applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] Embodiments of the present invention will be described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
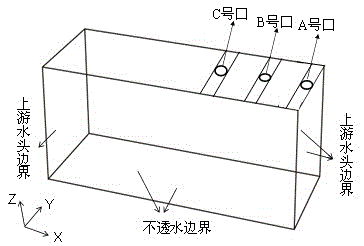
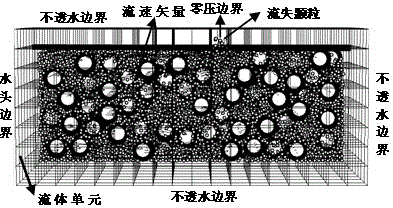
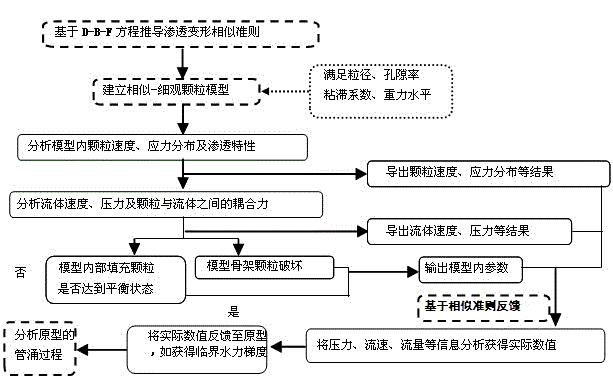
[0035] The present invention has designed a kind of numerical analysis method of piping phenomenon, and the concrete steps of implementation are as follows image 3 shown, including:
[0036] Step (1), based on the fluid dynamics similarity criterion combined with the action item of the medium on the fluid, deduce the similarity criterion followed when the sand seepage deformation occurs. details as follows:
[0037] (1.1) Based on the similarity criterion of the existing fluid dynamics of porous media, the extended D-B-F equation is introduced by considering the interphase dynamic action term of the medium on the fluid;
[0038] (1.2) Considering the Darcy-non-Darcy effect of seepage, according to the similarity of geometry, movement and dynamics, the similarity criterion followed when seepage deformation occurs in sandy soil is deduced. The specific derivatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com