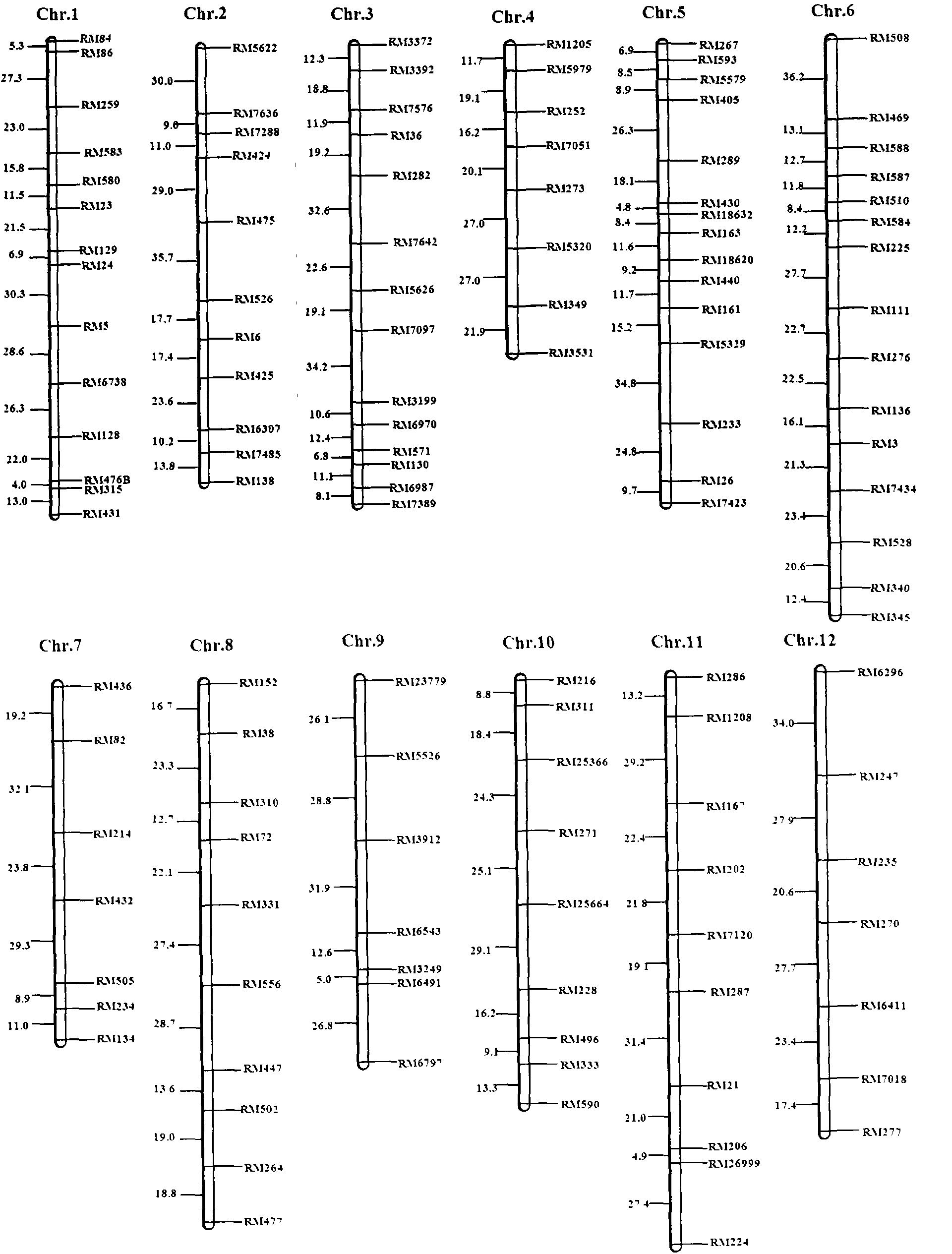
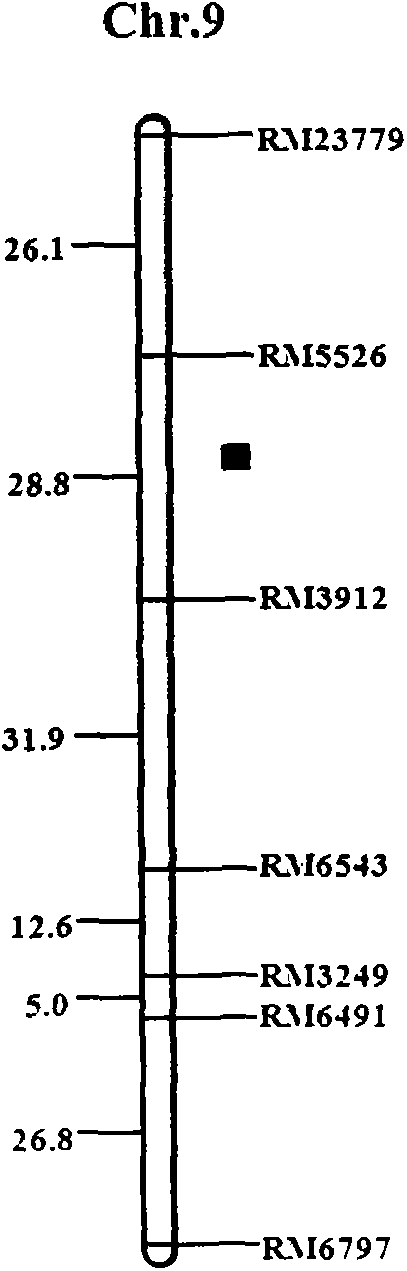
SSR (simple sequence repeat) markers, linked with Aphelenchoides besseyi Christie resistant QTL (quantitative trait locus), on chromosome 9 and application thereof
A technology for resistance to D. elegans in rice, which is applied to the determination/inspection of microorganisms, DNA/RNA fragments, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the effective utilization of resistance resources of D. elegans, and improve the breeding efficiency. , the effect of speeding up the breeding process and simplifying the selection method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Example 1, Acquisition of Molecular Markers Linked to the Resistance QTL of D.
[0020] 1. Plant material
[0021] In 2008, Huaidao 5 and Tetep were planted in the field of Jiangsu Academy of Agricultural Sciences and crossed to obtain the hybrid F 1 , next year F 1 F 2 Lizi, bred F in Hainan in 2009 2 group, as a mapping group. f 2 Individual plant number, parent and hybrid F at tillering stage 1 and F 2 Some leaves of each individual plant in the population were stored in a -70°C refrigerator for SSR analysis, F 2 Harvest the individual plants of the population for phenotypic identification.
[0022] 2. Cultivation and isolation of nematodes
[0023] Inoculate Botrytis cinerea (Botrytis cinerea) bacterium blocks on PDA (Potato Dextrose Agar) medium and cultivate at 25°C. After the Botrytis cinerea is overgrown with the medium, use 3% hydrogen peroxide to disinfect the surface of the rice dry acerbion for 10min. After washing with sterilized ultrapure water f...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2, the application of molecular markers on chromosome 9 linked to the resistance QTL of rice stem nematodes in the offspring of a cross with Huaidao 5 and Tetep as parents
[0061] The SSR marker linked to the rice stem nematode resistance QTL acquired on chromosome 9, the F 2:3 Part of the individual plants in the family were predicted for the resistance of rice stem nematode, and the DNA of each individual plant was extracted, and then PCR amplification analysis was performed with the primers of SSR markers RM5526 and RM3912, and the band type analysis was used to determine whether there were corresponding markers. The mark indicates that the line has reached the level of resistance to the rice stem nematode, and if it does not exist, it is susceptible. Subsequently, the actual resistance of the tested lines to rice A. spp. was determined by using the artificial inoculation identification method of A. sativa, and compared with resistant varieties and susceptib...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com