Dual-frequency identification sonar image sequence splicing method
A technology of image mosaic and image sequence, which is applied in image enhancement, image data processing, graphic image conversion, etc. It can solve the problems of sonar image deformation, narrow field of view of high-resolution sonar, and easy fatigue, and achieve the effect of improving contrast
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] join figure 1 , the forward scanning sonar image splicing method is characterized in that: the seamless splicing of the sonar image sequence is realized through the following steps:
[0058] 1) Sonar image preprocessing: remove the noise of the sonar image and improve the contrast;
[0059] 2) Double detection of feature points: to improve the detection accuracy of feature points in sonar images;
[0060] 3) Double verification of feature point pairs: in order to improve the accuracy of feature point pair matching;
[0061] 4) Sequence image homography matrix solution: used for splicing sonar image sequences;
[0062] 5) Image fusion: to eliminate the seams after sonar image stitching.
[0063] 2. The forward-scan sonar image mosaic method according to claim 1, characterized in that: the specific steps of the step (1) sonar image preprocessing are:
[0064] ① Use Gaussian smoothing method to remove Gaussian noise;
[0065] ②A method based on image grayscale stretch...
Embodiment 2
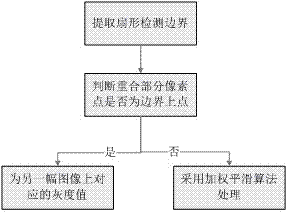
[0102] attached figure 1 It is a flowchart of a stitching method of a forward-scan sonar image sequence in an embodiment of the present invention. Such as figure 1 As shown, the operation steps of the forward-scan sonar image stitching method include the following:
[0103] (1) Sonar image preprocessing
[0104] ① Use Gaussian smoothing method to remove Gaussian noise;
[0105] ②A method based on image grayscale stretching is used to improve the contrast of the image.
[0106] (2) Double detection of feature points
[0107] ①Convert the sonar image into an integral image: for a point in the integral image , , the value of this point is Indicates that the calculation is as shown in formula (1);
[0108] (1)
[0109] ② Use the Hessian matrix to calculate the interest point of the image: calculate the local maximum value of the determinant of the Hessian matrix at different scales in the image. any point in the image , the point is at scal...
Embodiment 3
[0134] Step (5) image fusion is another preferred embodiment of the present invention. The operation steps of image fusion include the following:
[0135] ① Use the histogram normalization algorithm to adjust the brightness of the subsequent image to be consistent with the brightness of the reference image;
[0136] ②A boundary-preserving weighted smoothing algorithm is used to realize the fusion of registered images. The algorithm flow chart is as follows: image 3 shown;
[0137] Assume , is the sonar image of two adjacent frames to be spliced, and in interval Overlap, assuming Indicates the fused image, and the value of the smoothed pixel is , the specific steps of the algorithm are as follows:
[0138] 1) respectively for and The image is edge detected, and the contour of the fan-shaped area is extracted;
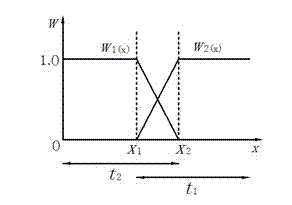
[0139] 2) set and The value of the pixel corresponding to the overlapping part and ,Such as figure 2 As shown, take
[0140] ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com