Fungus nitrilase mutants with improved catalytic activity and heat stability and construction method thereof
A technology of nitrilase and thermal stability, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve the problems of insufficient catalytic efficiency and poor thermal stability, and achieve the improvement of catalytic activity and thermal stability, enzyme activity and thermal stability, and broad market foreground effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] The present invention uses known information to conduct bioinformatics analysis on the current fungal nitrilase gene, and establishes the important functions of the 128th isoleucine Ile and the 161st asparagine Asn near the active center for catalytic characteristics. Using a recombinant plasmid carrying the fungal nitrilase gene as a template from a methylation-capable E. coli host E. coli For DH5α, the oligonucleotide sequence with the mutation site was used as a primer to carry out saturation mutation, and the mutant plasmids at positions 128 and 161 were amplified by reverse PCR technology.
[0023] The sequences of the saturation mutation primers are as follows:
[0024]
[0025] NNN represents the mutation site, and the site was mutated into other 19 amino acids to construct a saturated mutation library.
[0026] The reverse PCR reaction system is:
[0027]
[0028] The PCR program conditions were set as follows: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 min; denatu...
Embodiment 2
[0030] The linear mutant plasmid recovered from rubber tapping was used Dpn Restriction endonuclease I was used for digestion and digestion, and the digestion conditions were: warm bath at 37°C for 0.5 h. The enzyme digestion reaction system is as follows:
[0031]
[0032] The digested products were detected by agarose gel electrophoresis, and the remaining products were used in subsequent experiments.
Embodiment 3
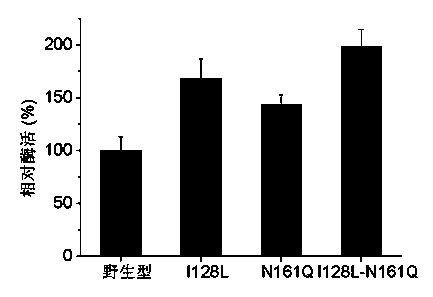
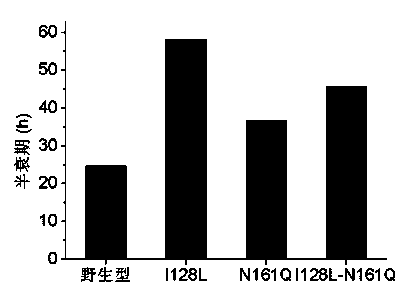
[0034] Transform the digested linear mutant plasmid directly into E. coli by heat shock at 42°C E. coli DH5α host cells were spread on LB plates containing kanamycin resistance, and cultured at 37°C for 10-12 h. Pick a single colony, insert it into LB liquid medium for culture, extract the plasmid, carry out enzyme digestion and PCR verification. The plasmids of positive clones were selected and sent to Shanghai Sangon for sequencing. Those with correct sequencing results were transformed into Escherichia coli E. coliRosetta-gami (DE3) expression host was cultured overnight at 37°C on an LB plate containing kanamycin and chloramphenicol resistance, and positive transformants were selected, which were fungal nitrilase mutants. 0.5 mM IPTG was used to induce enzyme production, and the cells were collected by centrifugation to make a bacterial suspension, and the enzyme activity of the mutant was detected, such as figure 1 shown. The mutant free cells were warmed in a wate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com