Hydrogen-supplied delayed coking method for high-acid feedstock oil
A delayed coking method and raw oil technology, applied in the treatment of hydrogen-generating compounds, etc., can solve problems such as increasing investment costs, and achieve the effects of increasing processing capacity, reducing acid value, and reducing free radical concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
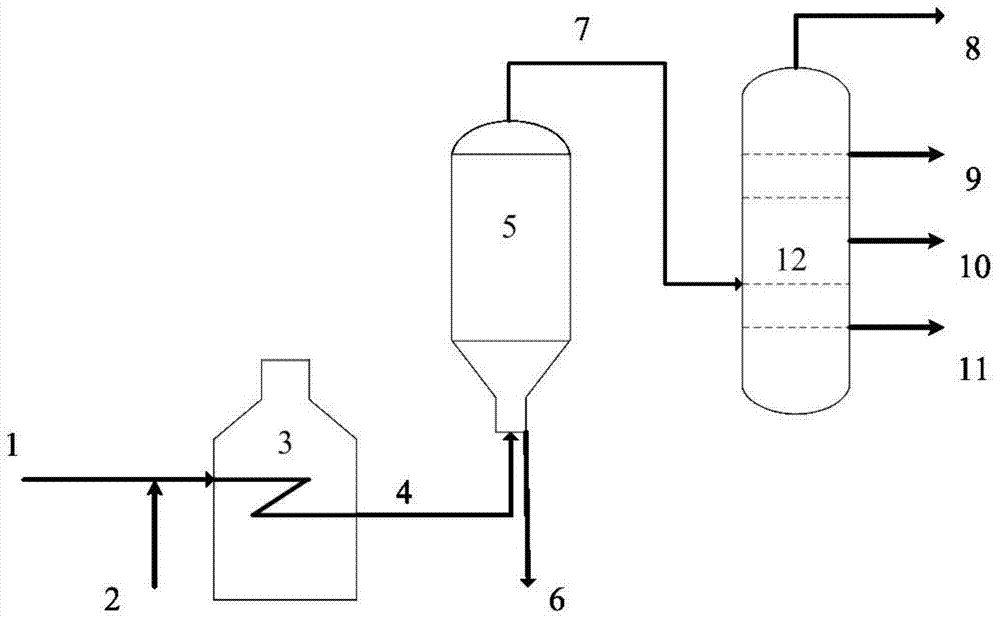
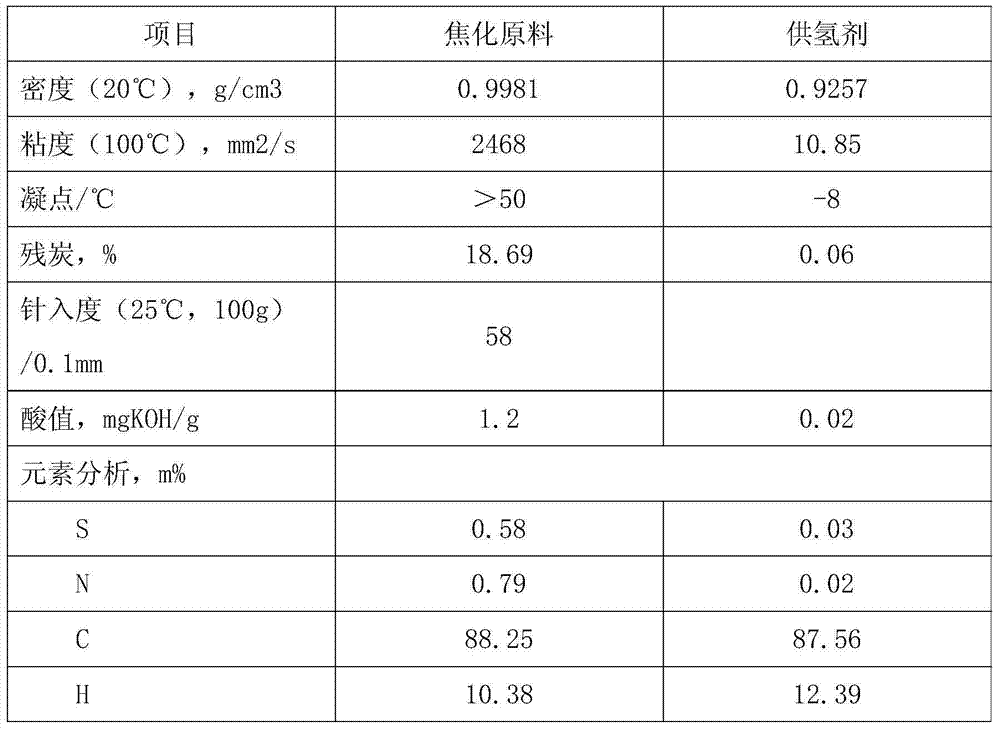
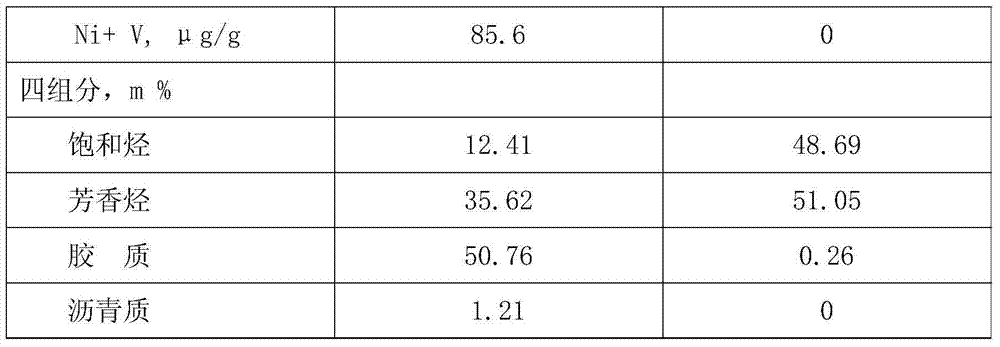
[0029]The high-acid vacuum residue is mixed with a hydrogen-donating agent for delayed coking processing. The amount of hydrogen-donating agent added is 8.0% of the weight of the vacuum residue raw material. The coking reaction conditions are: reaction temperature 510°C, coke tower The top pressure is 0.18MPa, and the circulation ratio is 0. Results The product yields obtained were: coke yield 25.71%, coking gas yield 7.21%, coking liquid yield 67.08% (including coking gasoline 20.66%, coking diesel oil 22.18%, coking wax oil 24.24%).
[0030] After one year of continuous operation of the delayed coking equipment, the corrosion amount was tested according to the method on pages 13-16, Volume 35, Phase 4, 2006 of Shandong Chemical Industry. 0.01 mm, the corrosion amount of the upper and lower parts of the coke tower is 0.01 mm and 0.02 mm respectively.
Embodiment 2
[0032] The high-acid vacuum residue is mixed with a hydrogen-donating agent for delayed coking process. The hydrogen-donating agent is added in an amount of 25.0% of the weight of the coking raw material. The coking reaction conditions are the same as in Example 1. Results The product yields obtained were: coke yield 24.95%, coking gas yield 6.23%, coking liquid yield 68.82% (of which coking gasoline 19.92%, coking diesel oil 22.05%, coking wax oil 26.85%).
[0033] After one year of continuous operation of the delayed coking equipment, the corrosion amount was tested according to the method on pages 13-16, Volume 35, Phase 4, 2006 of Shandong Chemical Industry. 0.01 mm, the corrosion amount of the upper and lower parts of the coke tower is 0.01 mm and 0.02 mm respectively.
Embodiment 3
[0035] The high-acid vacuum residue is mixed with a hydrogen donor to carry out delayed coking process. The hydrogen donor is added in an amount of 48.0% of the weight of the coking raw material. The coking reaction conditions are the same as in Example 1. Results The product yields obtained were: coke yield 24.68%, coking gas yield 5.96%, coking liquid yield 69.36% (including coking gasoline 19.71%, coking diesel oil 21.83%, coking wax oil 27.82%).
[0036] After one year of continuous operation of the delayed coking equipment, the corrosion amount was tested according to the method on pages 13-16, Volume 35, Phase 4, 2006 of Shandong Chemical Industry. 0.01 mm, the corrosion amount of the upper and lower parts of the coke drum is 0.01 mm and 0.01 mm respectively.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid value | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com