Preparation method of high molecular weight polylactic acid stereocomplex with melt stability
A technology of stereocomplex and melt stability, which is applied in the field of preparation of high-molecular-weight polylactic acid stereocomplex, can solve the problems of poor memory effect, difficult formation of sc, difficulty in forming a large amount or complete sc, etc., and achieves The effect of improving crystallization ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
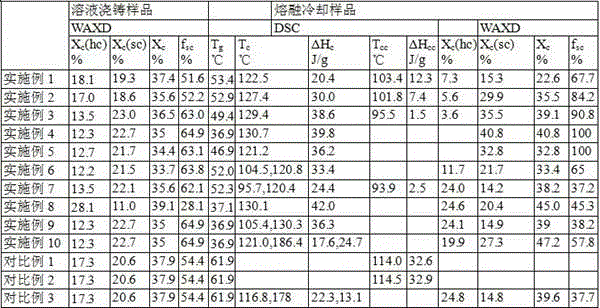
[0025] The weight average molecular weight was 2.1×10 5 g·mol -1 PLLA and 1.0 x 10 5 g·mol -1 PDLA, and a molecular weight of 1000 g·mol -1 PEG was dissolved in dichloromethane at a concentration of 1 g dl -1 . After complete dissolution, mix under vigorous stirring and solution cast at room temperature. PLLA:PDLA=1:1wt in PLLA / PDLA / PEG blend, PEG content is 3wt%. The solution-cast samples were vacuum-dried and heated rapidly at a rate of 100 °C / min under nitrogen protection using a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC), and then cooled slowly at a rate of 10 °C / min to 270 °C for 2 min. The melt-cooled sample was obtained at 0 °C, and the temperature was raised again at a rate of 10 °C / min to detect the crystallization parameters of the melt-cooled sample. The crystal structures of the solution-cast samples and the melt-cooled samples were characterized by wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD).
Embodiment 2
[0027] The weight average molecular weight was 2.1×10 5 g·mol -1 and 1.0×10 5 g·mol -1 PLLA, PDLA, and a molecular weight of 1000 g·mol -1 PEG was dissolved in dichloromethane at a concentration of 1 g dl -1 . After complete dissolution, mix under vigorous stirring and solution cast at room temperature. PLLA:PDLA=1:1wt in PLLA / PDLA / PEG blend, PEG content is 5wt%. The solution-cast samples were vacuum-dried and heated rapidly by DSC at a rate of 100 °C / min under nitrogen protection, and then cooled slowly to 0 °C at a rate of 10 °C / min after isothermally at 270 °C for 2 minutes to obtain a melt-cooled sample, and The temperature was raised again at a rate of 10 °C / min to detect the crystallization parameters of the melt-cooled sample. And by WAXD to characterize the crystal structure of the solution cast sample and the sample after melt cooling.
Embodiment 3
[0029] The weight average molecular weight was 2.1×10 5 g·mol -1 and 1.0×10 5 g·mol -1 PLLA, PDLA, and a molecular weight of 1000 g·mol -1 PEG was dissolved in dichloromethane at a concentration of 1 g dl -1 . After complete dissolution, mix under vigorous stirring and solution cast at room temperature. PLLA:PDLA=1:1wt in PLLA / PDLA / PEG blend, PEG content is 7wt%. The solution-cast samples were vacuum-dried and heated rapidly by DSC at a rate of 100 °C / min under nitrogen protection, and then cooled slowly to 0 °C at a rate of 10 °C / min after isothermally at 270 °C for 2 minutes to obtain a melt-cooled sample, and The temperature was raised again at a rate of 10 °C / min to detect the crystallization parameters of the melt-cooled sample. And by WAXD to characterize the crystal structure of the solution cast sample and the sample after melt cooling.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| optical purity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com