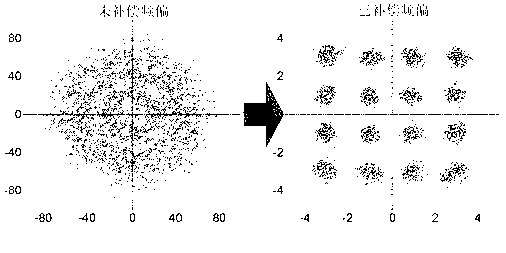
Self-adaptive damage compensation method and system for digital-related optical communication system
A technology of coherent optical communication and adaptive compensation, applied in baseband system components, optical fiber transmission, shaping network in transmitter/receiver, etc. Achieve the effect of occupying less spectrum resources, low computational complexity, and high compensation accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
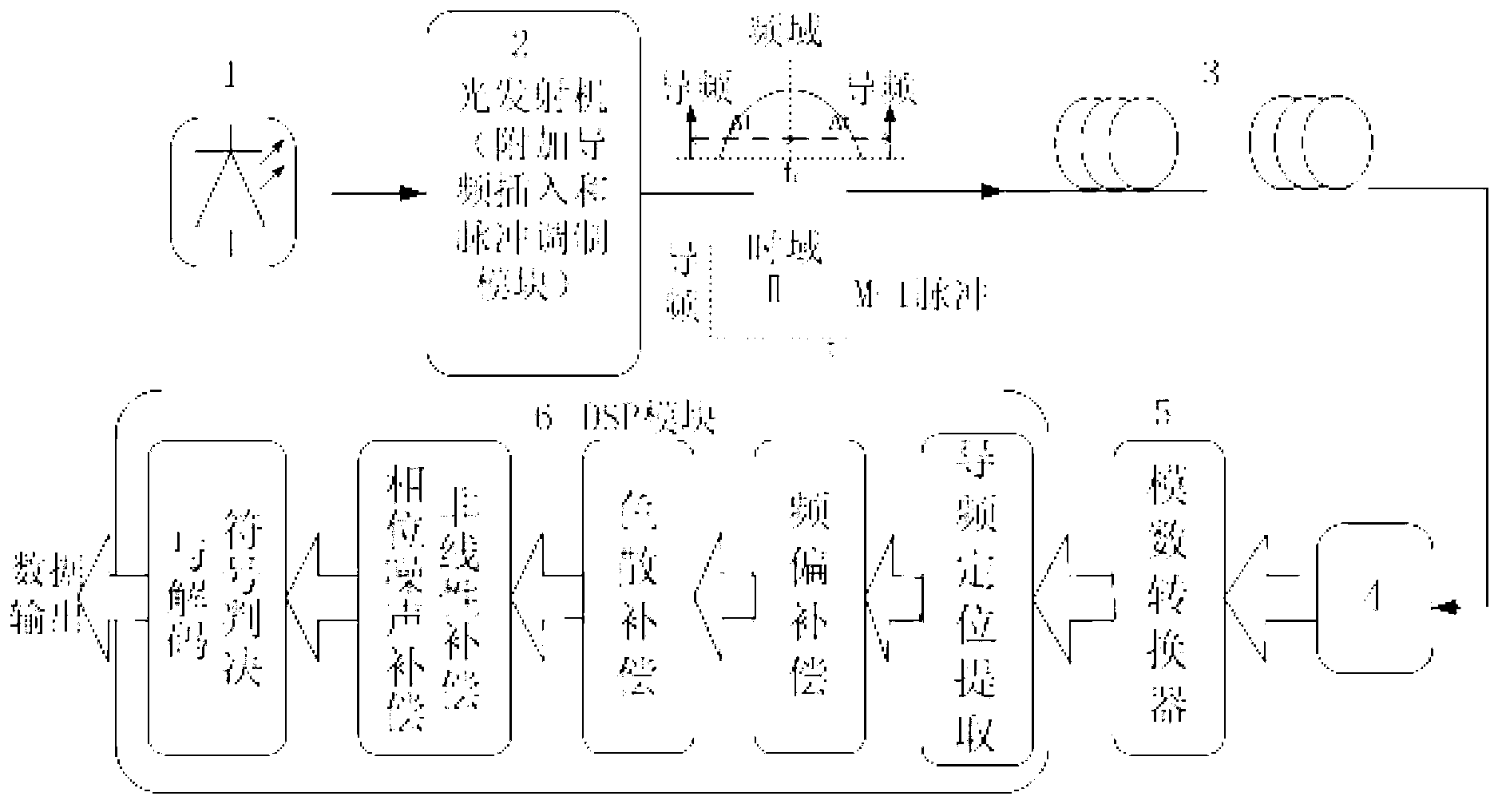
[0034] The simultaneous adaptive compensation system of CD, NLD, LFO and LPN based on the optical guide proposed by the present invention, such as figure 1 shown. It includes a pilot insertion and modulation module added to the optical transmitter 2, and an adaptive compensation module based on a digital signal processor 9 at the receiving end.
[0035] At the transmitting end: the signal light generated by the laser 1 enters the optical transmitter 2, and the optical transmitter 2 is equipped with a pilot insertion and modulation module. The pilot insertion and modulation module is used to insert two symmetrical to the signal frequency f c distributed pulse-modulated pilot signal (f c ±Δf); the optical guide and the optical signal are combined and then transmitted to the transmission optical fiber 6 .
[0036] At the receiving end: the optical receiver 7 converts the optical signal into an electrical signal output, and then enters the adaptive compensation module of the di...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com