Photovoltaic type quantum well infrared detector with high working temperature
An infrared detector and operating temperature technology, applied in the field of infrared detection, can solve the problems of low operating temperature, limit the wide use of quantum well infrared detectors, and large dark current, and achieve low heat load, reduced heat dissipation requirements, and improved sensitivity Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
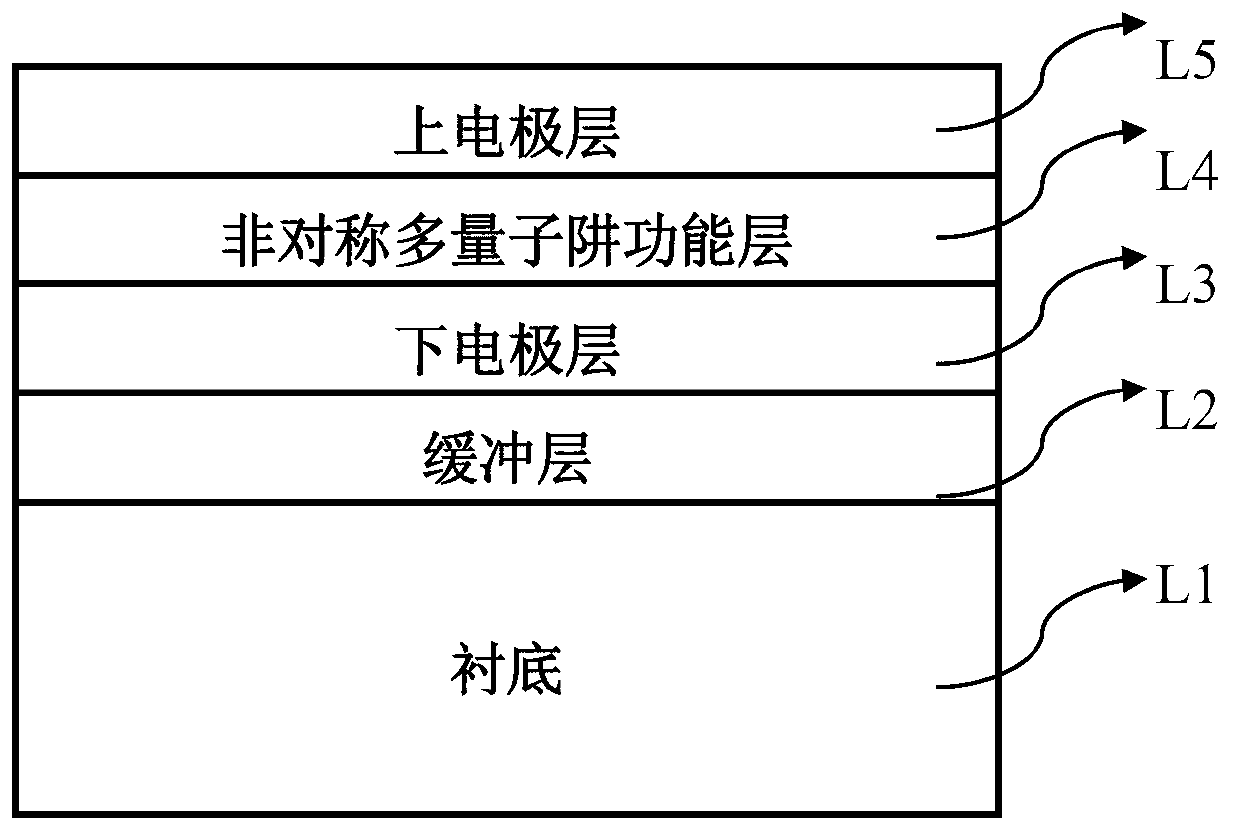
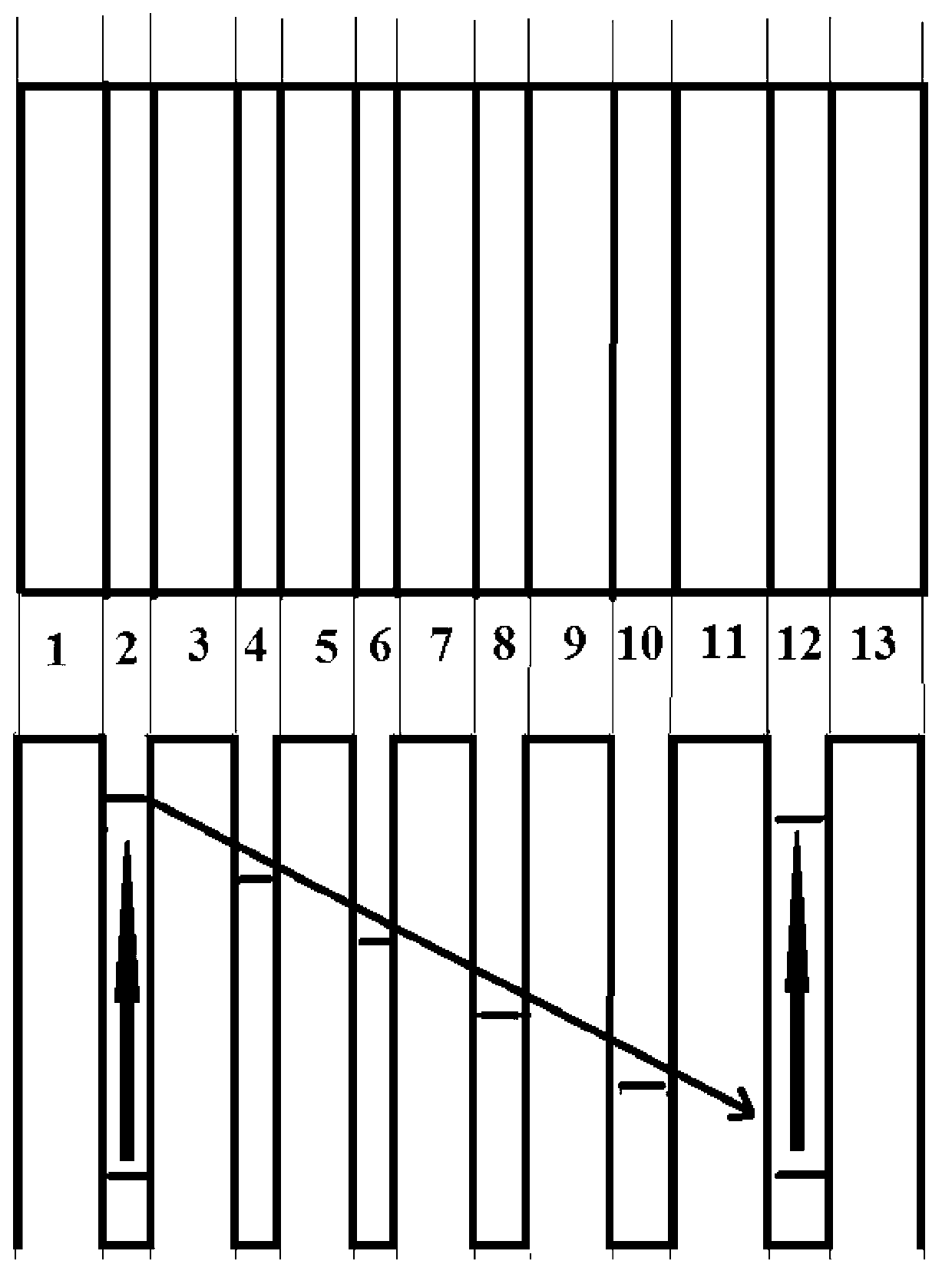
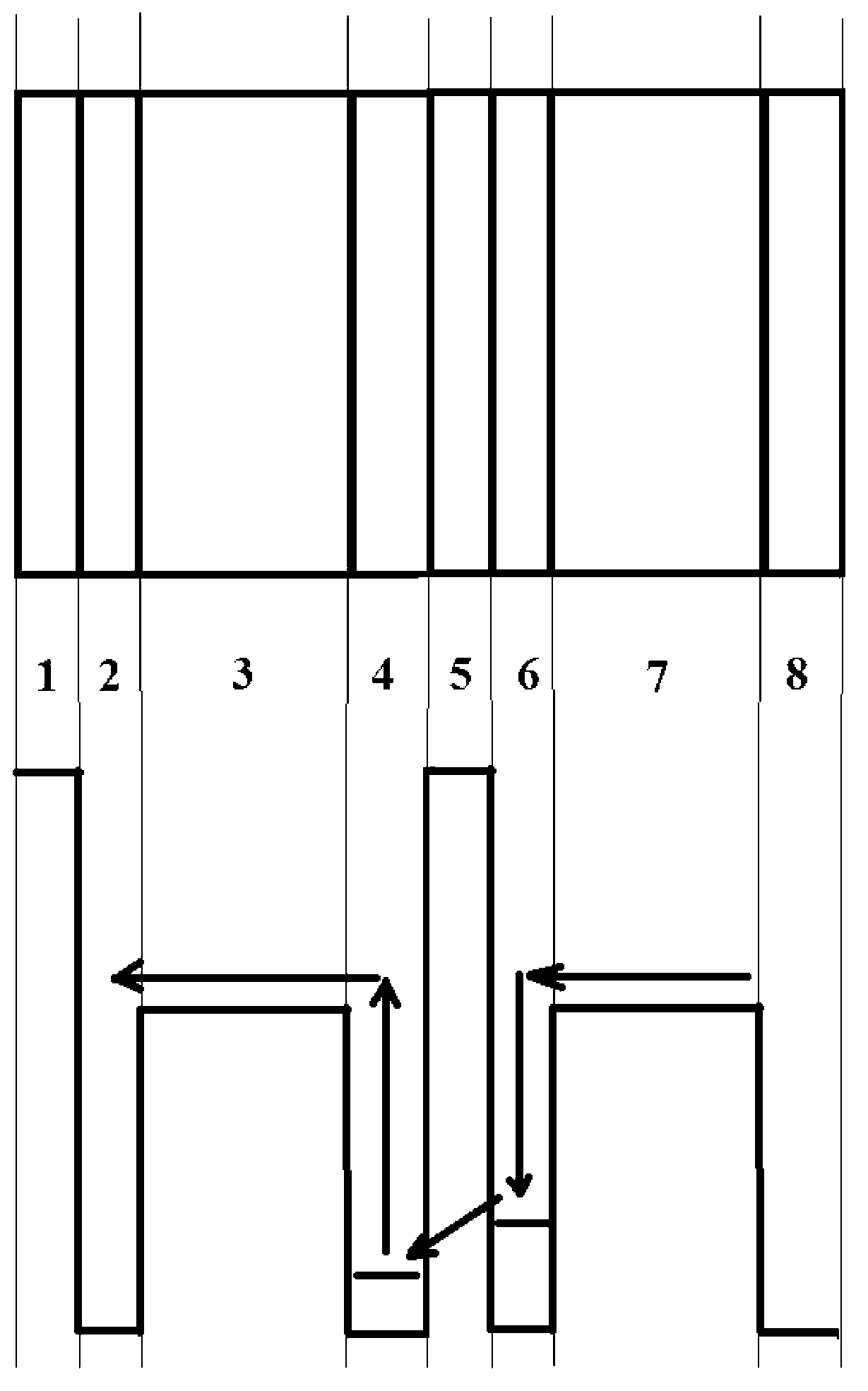
[0033]The invention proposes a photovoltaic quantum well infrared detector with high working temperature. Similar to the photoconductive QWIP, the functional layer of the photovoltaic quantum well infrared detector is composed of multiple periods of semiconductor quantum wells, and infrared light detection is realized by using the energy level transition of electrons or holes in the quantum wells. However, unlike the photoconductive QWIP, the functional layer of the photovoltaic quantum well infrared detector has an asymmetric structure. When no bias voltage is applied, the photoexcited carriers will move in one direction, thereby forming a photocurrent. The unique advantage of the photovoltaic quantum well infrared detector is that it can work with no bias voltage or very low bias voltage, and the dark current is very low or zero. Compared with the photoconductive QWIP, the dark current noise is also significantly reduced, and the operating temperature of the device is improv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com