Strongly basic amines for minimizing corrosion in systems prone to corrosive salt formation
A corrosive, volatile technology applied in the field of acid salts to solve problems such as not being able to help
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
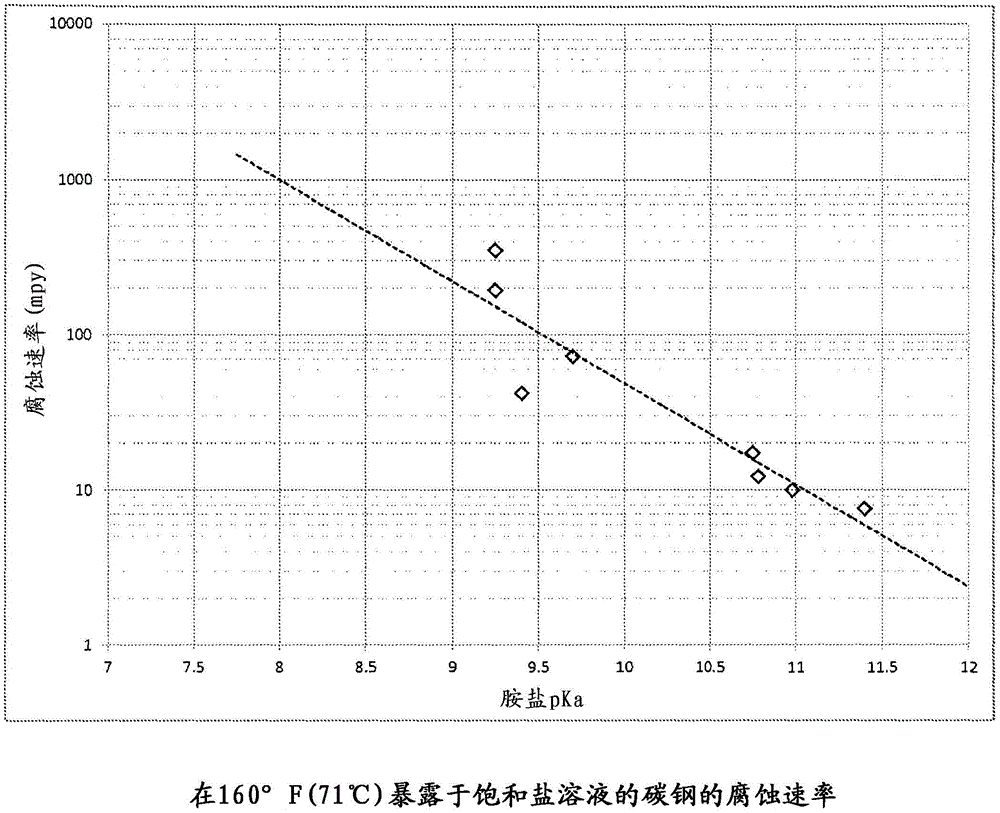
[0025] Theoretically, the hydrochloride salt of ethylamine should be less corrosive than the ammonium chloride salt. The ethylammonium ion has a pKa of 10.75, which is significantly weaker than ammonium's pKa of 9.25. The pH of ethylamine HCl salt is expected to be 0.75, which is higher than that of ammonium chloride. This means that ammonium chloride will generate 5.6 times more hydrogen ions and, theoretically, 5.6 times the corrosion rate. Table 1 shows the results for carbon steel exposed to a 5M molar solution of ammonium chloride and ethylamine HCl at 75°F (24°C) under approximately standard conditions. The difference is close to the predicted value. Corrosion rates for mpy are in mils per year.
[0026] Table 1 The effect of pKa on pH and corrosion rate
[0027]
Embodiment 2
[0029] Experiments were conducted at 160°F (71°C) on ammonium chloride, ethylamine (EA) hydrochloride and a 50 / 50 blend of the two. As mentioned, ammonia has a pKa of 9.25, while EA has a pKa of 10.75. The ammonia salt has a corrosion rate of 349 mpy (8.9 mm / yr) on carbon steel, while the EA salt only corrodes at 17 mpy (0.4 mm / yr). The mixture exhibited a corrosion rate of 146 mpy (3.7 mm / yr), demonstrating that the corrosivity of less basic HCl salts can be reduced by the addition of stronger bases.
Embodiment 3
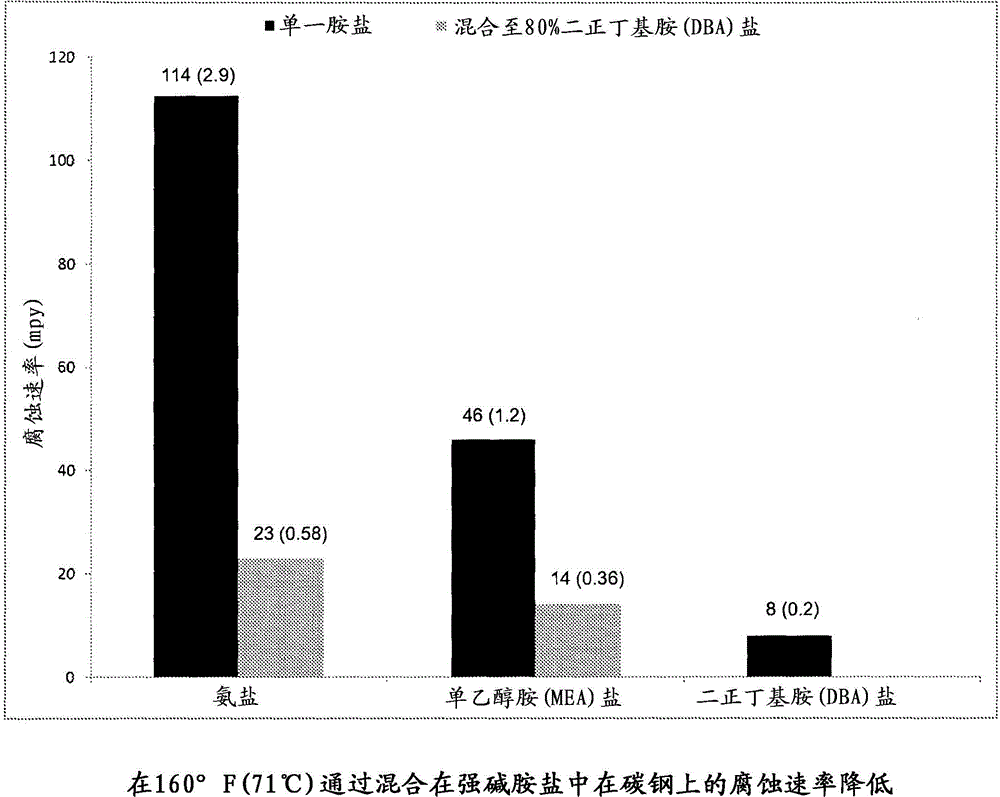
[0031] Ammonia and monoethanolamine (MEA) are two common pollutants that form salts. Carbon steel coupons were exposed to 1M solutions of the HCl salts of each amine in a degassed environment. The resulting metal loss revealed a corrosion rate of 114 mpy (2.9 mm / yr) for the ammonia salt and 46 mpy (1.2 mm / yr) for the MEA salt. The HCl salt of the strong base amine di-n-butylamine (DBA) was also tested in the same manner, and the resulting corrosion rate was only 8 mpy (0.2 mm / yr). The HCl salt of DBA was then added to the ammonia and MEA salts so that the strong base represented 80% of the total salt. The resulting corrosive effect on carbon steel coupons was significantly reduced. The coupon exposed to the mixture with the ammonia salt showed a corrosion rate of 23 mpy (0.58 mm / yr), ie a drop of 80%. The coupon exposed to the mixture with MEA salt showed a corrosion rate of 14 mpy (0.36 mm / yr), ie a 70% drop. image 3 The figure in shows the results of this experiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com