Heavy metal stabilizing method in process of preparing filler by chemical sludge burning ash
A technology of heavy metal stabilizer and incineration ash residue is applied in the field of chemical sludge recycling and mixing inorganic heavy metal stabilizer to achieve heavy metal stabilization. The effect of less pollution, short disposal cycle and low operating cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0016] In this example, chemical sludge incineration ash was used as raw material. The schematic diagram of the process flow is shown in Figure 1.
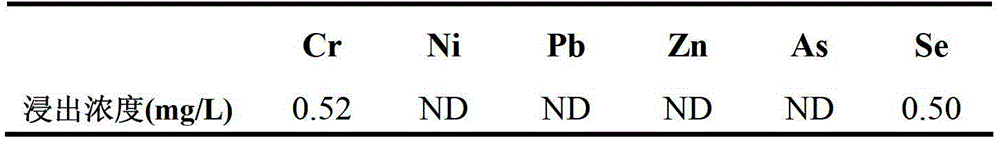
[0017] Table 1 Chemical sludge incineration ash leaching test results
[0018]
[0019] Calcium oxide and potassium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed in a certain proportion, water is added, stirred thoroughly, heated and evaporated to make potassium calcium phosphate cementing material. Then add bentonite to prepare inorganic heavy metal stabilizer. Bentonite accounts for 80% of the mass of the stabilizer, calcium oxide accounts for 15% of the mass of the stabilizer, and potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounts for 5% of the mass of the stabilizer. Chemical sludge incineration ash and clay are ground into powdery particles with uniform particle size, and passed through a 200-mesh sieve after grinding. After grinding and sieving, the sludge incineration ash and clay are mixed with inorganic heavy metal stabilizers in a certain mas...
Embodiment 2
[0025] The raw material of this example is chemical sludge incineration ash, and the heavy metal leaching concentration of chemical sludge incineration ash used in this study is shown in Table 3.
[0026] Table 3 Chemical sludge incineration ash leaching test results
[0027]
[0028] Calcium oxide and potassium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed in a certain proportion, water is added, stirred thoroughly, heated and evaporated to make potassium calcium phosphate cementing material. Then add bentonite to prepare inorganic heavy metal stabilizer. Bentonite accounts for 60% of the mass of the stabilizer, calcium oxide accounts for 30% of the mass of the stabilizer, and potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounts for 10% of the mass of the stabilizer. Chemical sludge incineration ash and clay are ground into powdery particles with uniform particle size, and passed through a 200-mesh sieve after grinding. After grinding and sieving, the sludge incineration ash and clay are mixed with ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] The raw material of this example is chemical sludge incineration ash, and the heavy metal leaching concentration of chemical sludge incineration ash used in this study is shown in Table 5.
[0036] Table 5 Leaching test results of chemical sludge incineration ash
[0037]
[0038] Calcium oxide and potassium dihydrogen phosphate are mixed in a certain proportion, water is added, stirred thoroughly, heated and evaporated to make potassium calcium phosphate cementing material. Then add bentonite to prepare inorganic heavy metal stabilizer. Bentonite accounts for 40% of the mass of the stabilizer, calcium oxide accounts for 45% of the mass of the stabilizer, and potassium dihydrogen phosphate accounts for 15% of the mass of the stabilizer. Chemical sludge incineration ash and shale are ground into powdery particles with uniform particle size, and then passed through a 200-mesh sieve. After grinding and sieving, the sludge incineration ash and shale are mixed with inorg...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com