Molecular marker interlocking with wheat stripe rust resistant gene, acquisition method and application thereof
A technology for molecular markers and stripe rust, which is applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbiological determination/inspection, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of distant target genes, few applications, and limited versatility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
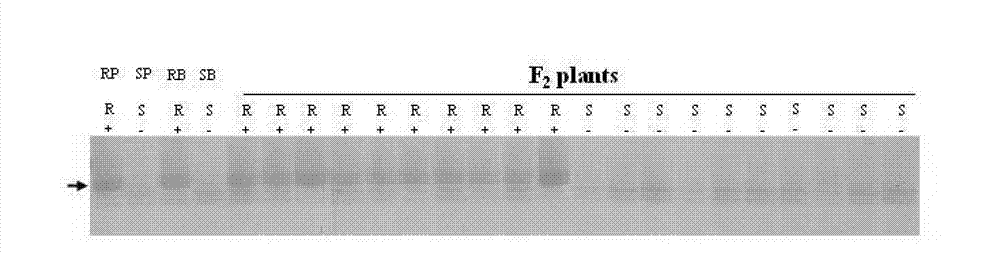
[0056] Example 1: RGAP molecular marker Xwgp linked to wheat stripe rust resistance gene -160bp the acquisition
[0057] 1. Test materials
[0058] Plant materials: The susceptible variety Taichang 29 was used as the female parent, and the new disease-resistant germplasm HRMSN-81 was used as the male parent to construct F 2 Genetic Mapping Populations. In the main season of 2010, F 2 148 individual plants of the population were planted in the disease identification nursery of Wenjiang Experimental Base, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu Campus, for resistance identification. Some leaves of each individual plant were taken at the seedling stage for RGAP analysis. When ripe, harvest F 2:3 The seeds of the family were dried and preserved, and used for resistance identification in 2011.
[0059] Mixed Physiological Races of Stripe Rust: For F 2 group and F 2:3 The mixed physiological races of stripe rust identified by family resistance consisted of equal mixtures of...
Embodiment 2
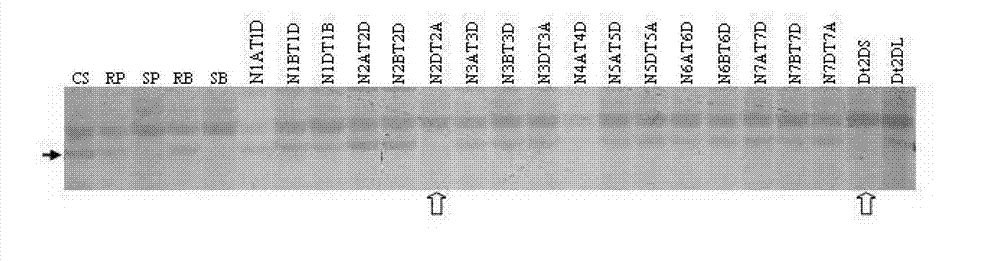
[0086] Example 2: Chromosomal location of specific RGAP molecular marker Xwgp-160bp
[0087] 1. Test materials
[0088] Chinese spring, Chinese spring deficiency-quadromic (including: N1AT1D, N1BT1D, N1DT1B, N2AT2D, N2BT2D, N2DT2A, N3AT3D, N3BT3D, N3DT3A, N4AT4D, N5AT5D, N5DT5A, N6AT6D, N6BT6D, N7AT7D, N7BT7D, N7DT7A) and 2D chromosome Diendosomal (Dt2DS and Dt2DL) genetic material.
[0089] 2. Genomic DNA extraction is the same as in Example 1.
[0090] 3. Specific molecular marker Xwgp -160bp RGAP analysis
[0091] Screening a Molecular Marker Xwgp Linked to Wheat Stripe Rust Resistance Gene -160bp , obtained by amplifying the similar sequences of disease-resistant genes with degenerate primers (upstream primer: 5'-AAGTGGAACAAGGTTACG-3'; downstream primer: 5'-GGIGGIGTIGGIAAIACIAC-3'). Using this pair of degenerate primers, RGAP analysis was performed on the above-mentioned Chinese spring, Chinese spring deletion-tetrasomy and 2D chromosome double-telosome genetic materi...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Example 3: Molecular-assisted selection of wheat stripe rust resistance gene
[0095] 1. Test materials
[0096] Plant materials: the susceptible variety Taichang 29, the new disease-resistant germplasm HRMSN-81, the advanced generation (F 5 ) 5 wheat lines (L1-L5), 11 wheat varieties that have no genetic relationship with the disease-resistant variety HRMSN-81, including: Neimai 8, Neimai 9, Kechengmai 2, Chuanmai 47 , Chuanmai 42, Chuannong 16, Mianmai 4, Mianyang 3, Mianyang 26, Mianyang 29, and Chuanfu 5. In the first season of 2011, the above materials were planted in the disease identification nursery of Wenjiang Experimental Base, Sichuan Agricultural University, Chengdu Campus, for resistance identification. Some leaves of each individual plant were taken at the seedling stage for RGAP analysis.
[0097] Mixed physiological race of stripe rust: The mixed physiological race of stripe rust used for resistance identification is composed of three races 31, 32 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com