Method for removing chlorine from chlorine-containing zinc sulfate solution
A zinc sulfate solution, a technology for removing chlorine, applied in the improvement of process efficiency, instruments, optics, etc., can solve the problems of large economic burden, low chlorine removal efficiency, and large water consumption for resin regeneration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
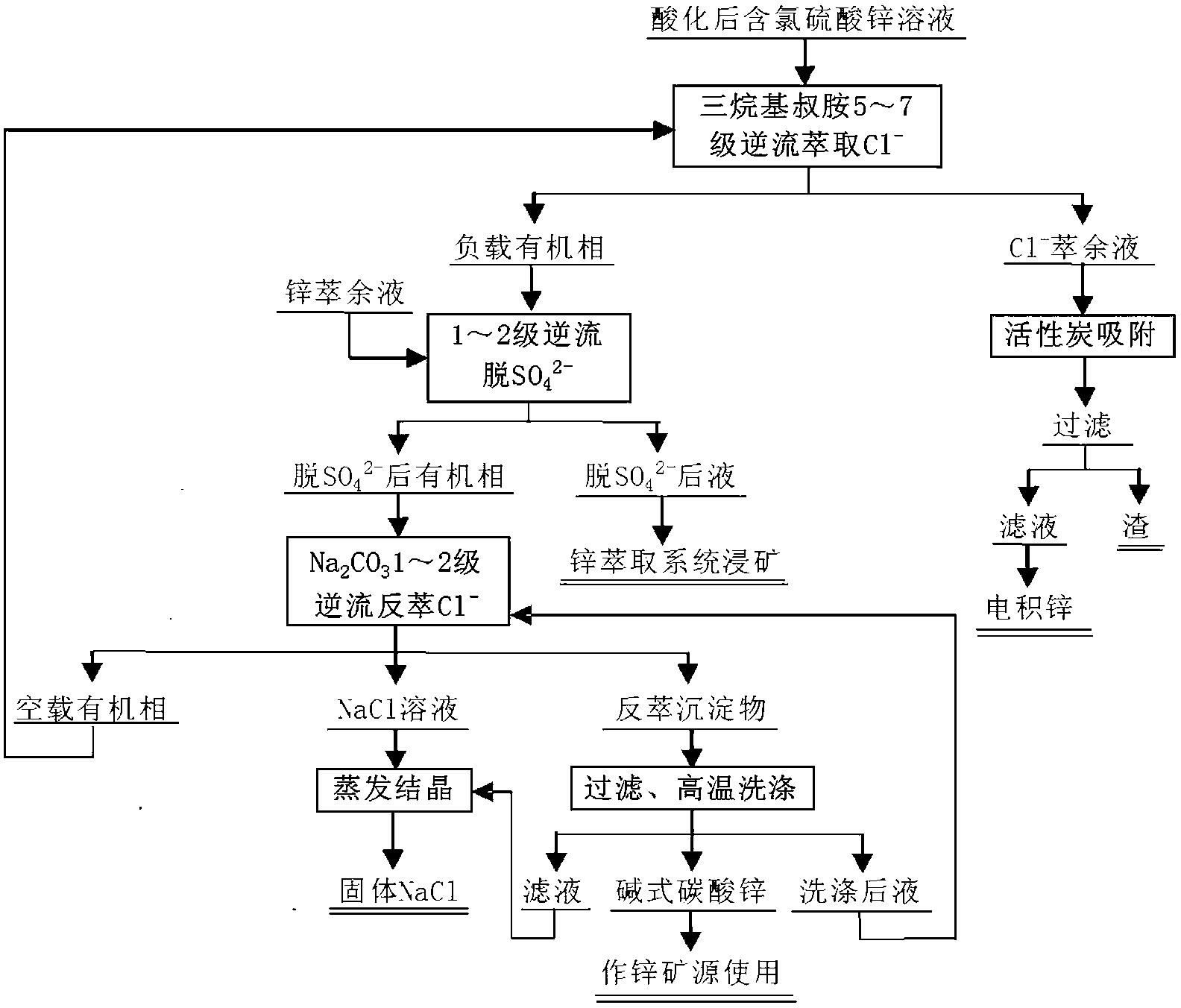
[0027] 1. Chlorine extraction: the prepared organic phase [11lv% trialkyl tertiary amine + 5lv% n-octanol + 260 # Kerosene (volume to volume)] and zinc electrolyte solution after acidification (chemical composition Zn of zinc electrolysis solution after acidification: 113.32g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 91.64g / L, Cl - : 2.55g / L) The flow rate of the organic phase is 110mL / min, the flow rate of the zinc electrolyte is 220mL / min, pumped into the self-made extraction tank with a constant flow pump for 5-stage countercurrent series extraction of Cl - ,Phase. The extraction mixing time was 1 min, the phase separation time was 3 min, and the phase ratio was 2 / 1 (water to organic phase). Analyze raffinate and negative chlorine organic phase (raffinate Zn: 112.45g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 85.73g / L, Cl - : 285.30mg / L. Negative chlorine organic phase Zn: 1.82g / L, Cl - : 4.62g / L, SO 4 2- : 10.62g / L), Cl - The extraction removal rate of 88.84wt%. After the raffinate is adsorbed by activated carbon, it...
Embodiment 2
[0032] 1. Chlorine extraction: Combine the returned empty organic phase and the acidified zinc electrolytic solution (the chemical composition of the zinc electrolytic solution after acidification is Zn: 117.16g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 73.29g / L, Cl - : 3.00g / L) The flow rate of the organic phase is 110mL / min, the flow rate of the zinc electrolyte is 220mL / min, and pumped into the self-made extraction tank with a constant flow pump for 5-stage countercurrent series extraction and phase separation. The extraction mixing time was 1 min, the phase separation time was 3 min, and the phase ratio was 2 / 1 (water to organic phase). Analyze raffinate and negative chlorine organic phase (raffinate Zn: 116.24g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 67.18g / L, Cl - : 273.51mg / L. Negative chlorine organic phase Zn: 1.31g / L, Cl - : 5.04g / L, SO 4 2- : 15.15g / L), Cl - The extraction removal rate of 90.88wt%. After the raffinate is adsorbed by activated carbon, it is sent to deposit zinc.
[0033] 2. Negative chlor...
Embodiment 3
[0037] 1. Chlorine extraction: The prepared organic phase [8lv% trialkyl tertiary amine + 5lv% n-octanol + 260 # Kerosene (volume to volume)] and acidified zinc electrolysis solution (chemical composition of zinc electrolysis solution after acidification Zn: 99.89g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 5.82g / L, Cl - : 2.57g / L) The flow rate of the organic phase is 50mL / min, the flow rate of the zinc electrolyte is 300mL / min, pumped into the self-made extraction tank with a constant flow pump for 7-stage countercurrent series extraction of Cl - ,Phase. The extraction mixing time was 1 min, the phase separation time was 3 min, and the phase ratio was 5 / 1 (water to organic phase). Analyze raffinate and negative chlorine organic phase (raffinate Zn: 98.78g / L, H 2 SO 4 : 1.14g / L, Cl - : 192.34mg / L. Negative chlorine organic phase Zn: 4.11g / L, Cl - : 11.51g / L, SO 4 2- : 2.76g / L), Cl - The extraction removal rate of 92.53wt%. After the raffinate is adsorbed by activated carbon, it is sent to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com