Method for fast estimation of lithographic binding patterns in an integrated circuit layout
A technology for determining integrated circuits and layouts, applied in the field of lithography binding patterns for rapid estimation of integrated circuit layouts, and can solve problems such as inapplicability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
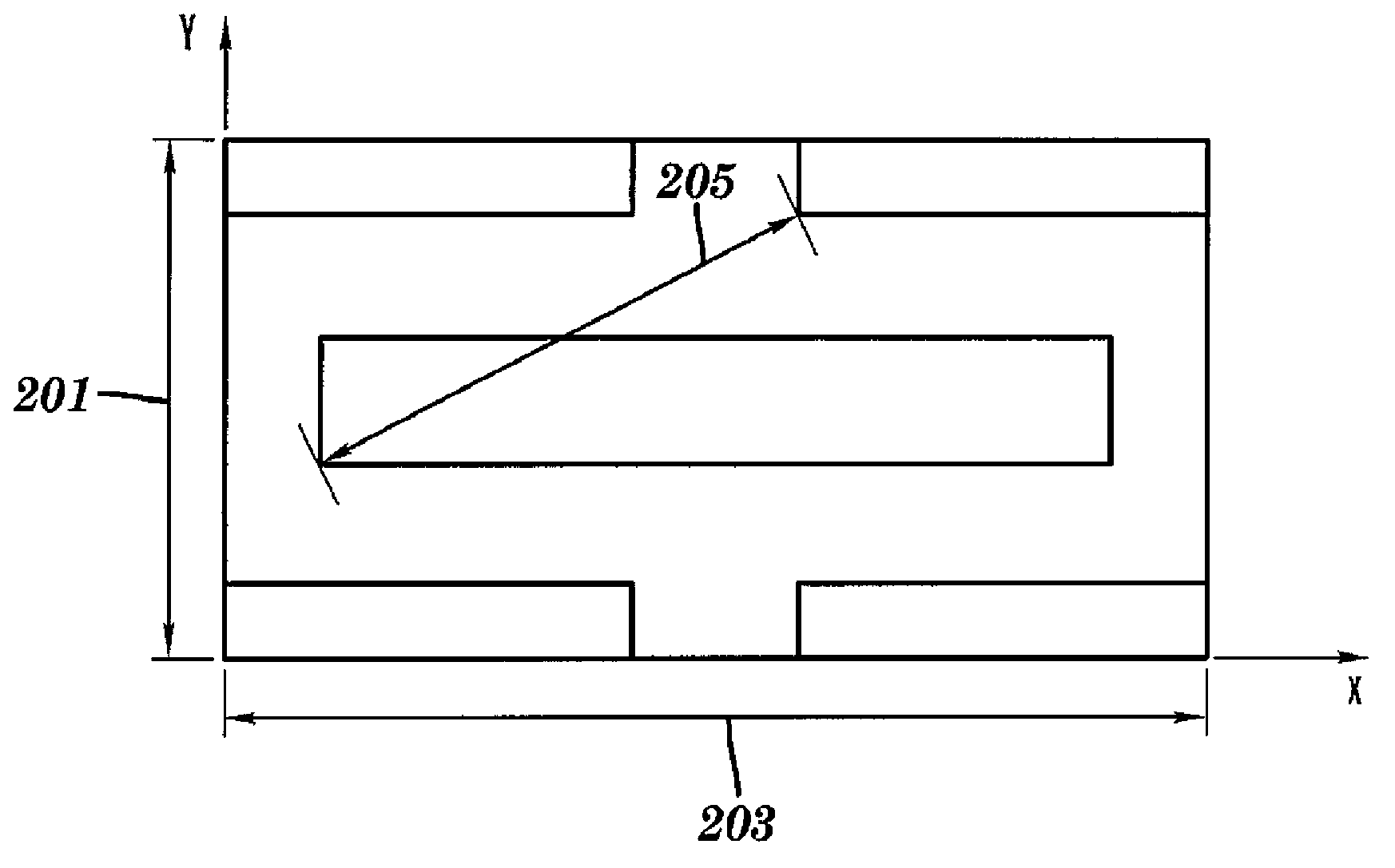
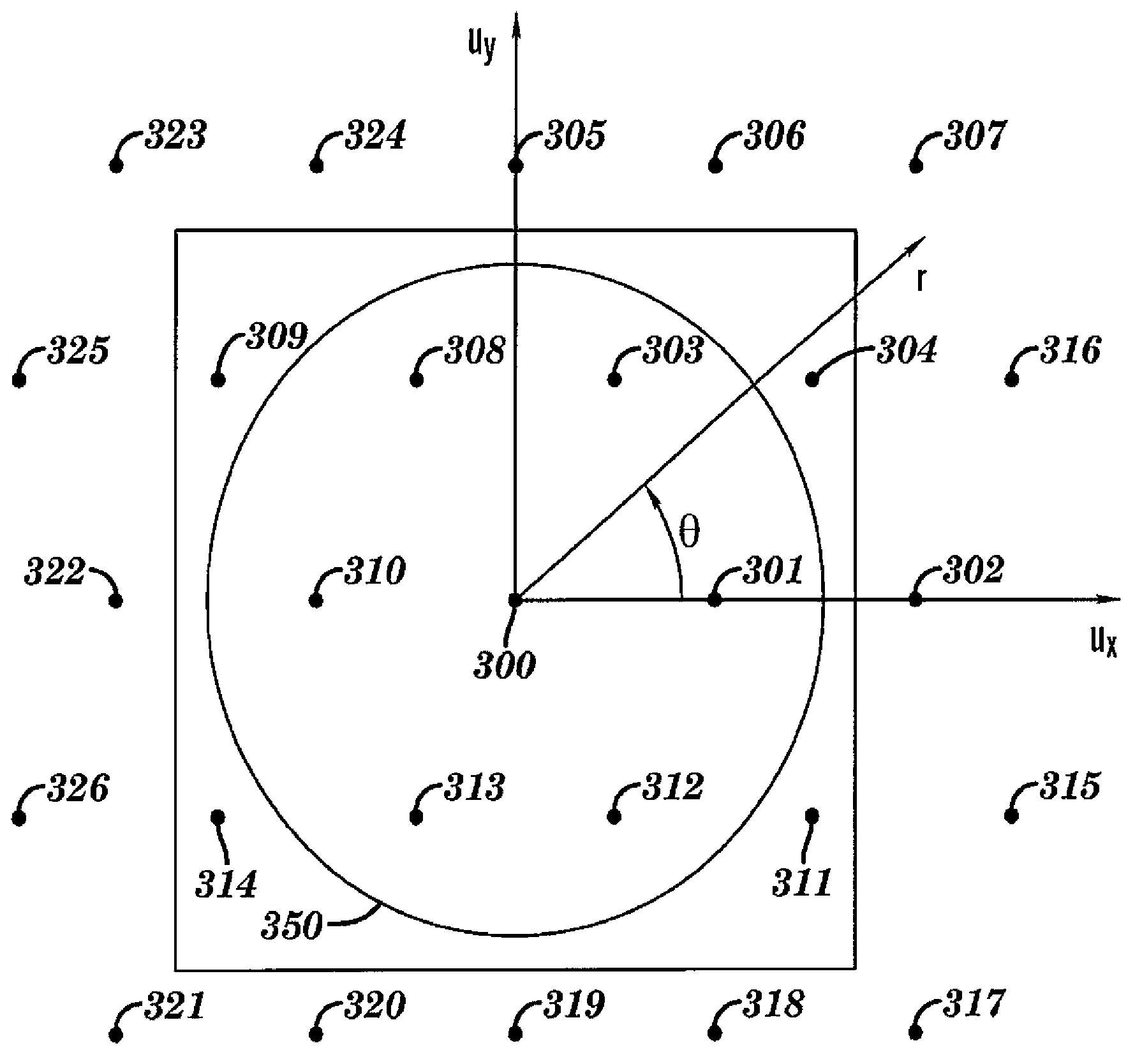
[0037] The present invention provides a method and apparatus for designing and optimizing a layout for use in the manufacture of integrated circuits, and more particularly for identifying and prioritizing portions of the layout for which a full optimization method is to be performed.
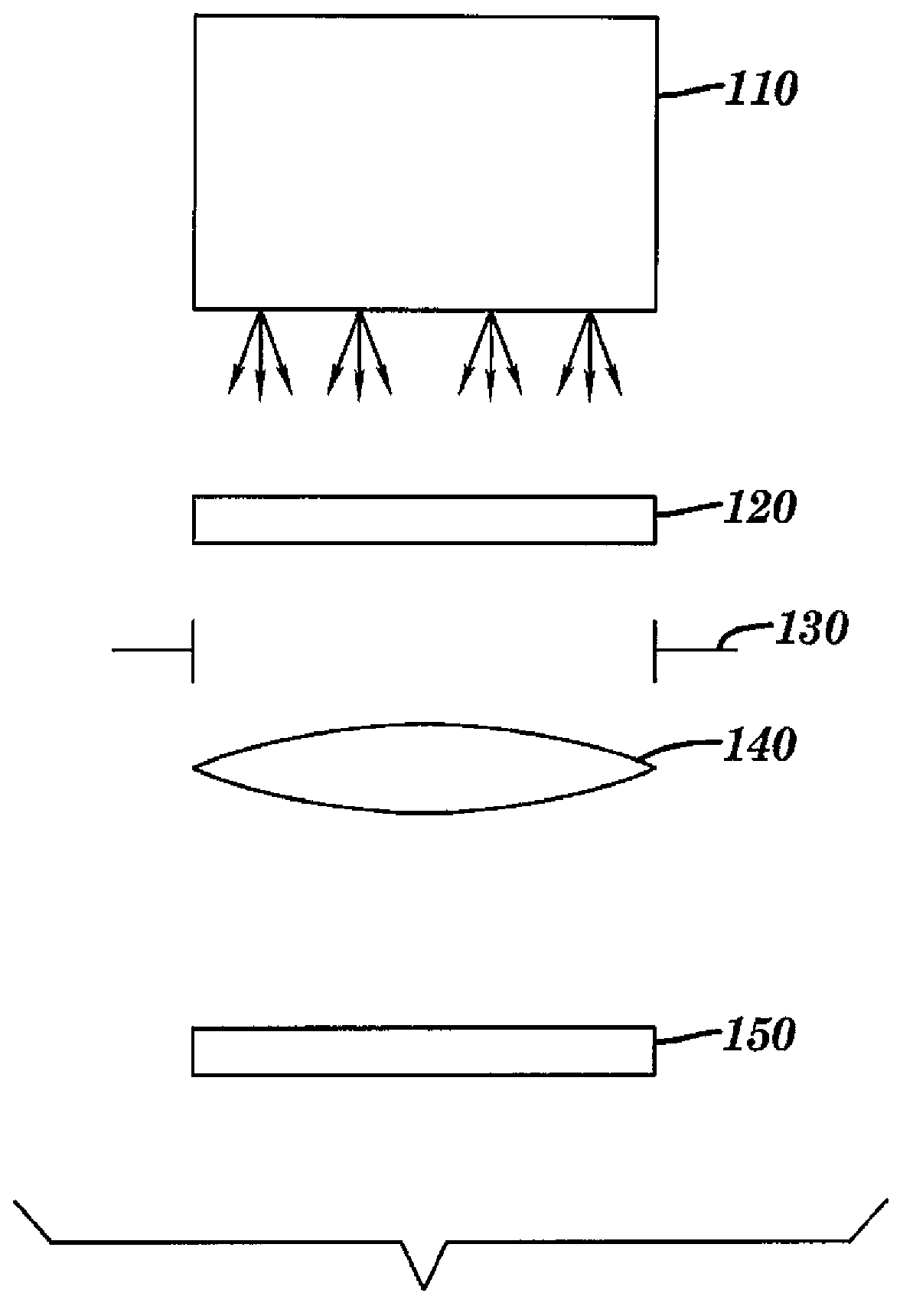
[0038] The basic components of a projection lithography system are illustrated in FIG. 1 . An illumination source 110 provides radiation that illuminates a mask 120, also called a reticle; the terms mask and reticle may be used interchangeably. Reticle 120 includes features that act to diffract illuminating radiation through lens 140 that projects an image onto an image plane, eg, semiconductor wafer 150 . The amount of radiation transmitted from reticle 120 to lens 140 may be controlled by pupil 130 . The illumination source 110 may be capable of controlling various source parameters such as direction and intensity. Wafer 150 typically includes a photosensitive material (referred to as resist...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com