Bacillus subtilis for preventing and controlling plant fungal disease and application of bacillus subtilis
A technology for bacillus subtilis and plant fungal diseases, applied in the field of microorganisms and biological fertilizers, can solve the problems of single action object, poor effect, limited competitive survival ability, etc., and achieve the effect of broad antibacterial spectrum and good genetic stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
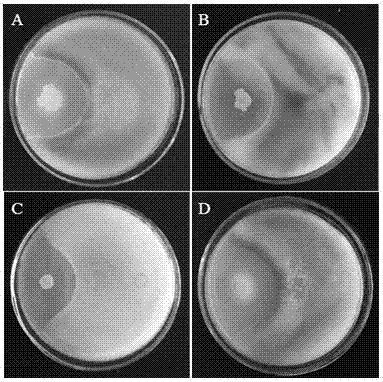
[0029] Example 2 Screening of antagonistic strains
[0030] Screening of antagonistic bacteria for the prevention and treatment of plant fungal diseases: evenly add 100 μL to a sterilized Petri dish with a concentration of 1X10 7 cfu / mL Pythium cucumber suspension, pour 20 mL of molten LB medium cooled to about 50 °C and mix well. After the culture medium is completely solidified, use an inoculation loop to inoculate the antagonistic bacteria to be tested, spot 8-10 bacterial strains to be tested in each plate, and culture them in an incubator at 28°C for 48 hours to detect the presence and size of the inhibition zone. After the initial test, the strains with antagonistic effect were purified and repeated tests were carried out. The basic method was the same as above, and 3 strains were spotted on each plate, and each plate was repeated 3 times. The degree of antagonism was determined according to the width of the antagonism zone (distance between the edge of the inhibition...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Example 3 Sequence Determination and Analysis of 16S rDNA of Bacterial Strains and Identification of Physiological and Biochemical Tests
[0032] Bacillus subtilis DNA was extracted using the conventional phenol method, and the 16S rDNA sequence was amplified with bacterial universal primers. The primer sequences were 27F (AGAGTTTGATCCTGGCTCAG) and 1492R (GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT). The PCR reaction system (50 μL) was: 5 μL of 10X PCR buffer, 4 μL of dNTP, 1 μL of each primer, 2.5 μL of DNA template, 0.25 μL of Takara Taq enzyme, and 36 μL of ultrapure water. The PCR amplification program was 94 °C for 3 min; 94 °C for 1 min, 52 °C for 1 min, 72 °C for 1.5 min, 30 cycles; 72 °C for 10 min. The amplified products were sent to Shanghai Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd. for sequencing.
Embodiment 3
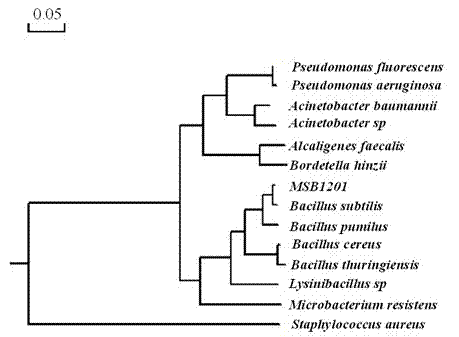
[0033] The measured 16S rDNA sequence was input into GenBank, and BLAST software was used for homology search. The 16S rDNA sequences of different strains were selected and compared with the known 16S rDNA sequences in GenBank.
[0034] Homology comparison results are as follows:
[0035] The results of the blast comparison of the PCR amplification product in GenBank showed that the bacterial strain MSB1201 of the present invention and its 50 highly homologous strains all belong to the genus Bacillus, and their homology is more than 98%. figure 2 The 16S rDNA sequence of MSB1201 is the same as Bacillus subtilis, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Acinetobacter baumannii, Acinetobacter sp, Alcaligenes faecalis, Bordetella hinzii, Bacillus pumilus, Bacillus cereus, Bacillus thuringiensis, Lysinibacillus sp, Microbacterium locophyresistens, Staples 16S rDNA cluster analysis of 15 species of bacteria. Bacillus subtilis described in the present invention and Bac...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com