Method and device for purifying cadmium in waste water through nano zero-valent iron
A nano-zero-valent iron and wastewater technology is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
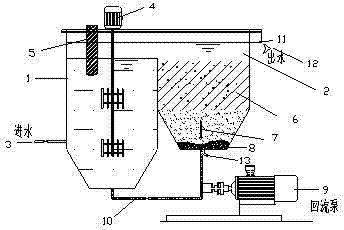
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown, the device is a two-stage reaction device, which is composed of a reaction chamber 1 and a separation chamber 2, and the reaction chamber 1 and the separation chamber 2 are semi-connected. A water inlet 3 is provided at the left bottom of the reaction chamber 1, and a nano-zero-valent iron return port is provided at the bottom, which is used to connect the nano-zero-valent iron return pipe 10. At the same time, a stirrer 4 is configured to fully and uniformly mix the wastewater and nano-zero-valent iron particles. reaction. The separation chamber 2 is divided into upper, middle and lower parts. The upper part is the water flowing out from the weir. After the water is discharged to the water outlet, it is discharged through the water outlet 12. The water outlet is covered with a layer of filter membrane 11 to intercept a small amount of nanometer zero-valent iron particles flowing out with the water. , the middle part is equipped with a slant ...
Embodiment 2
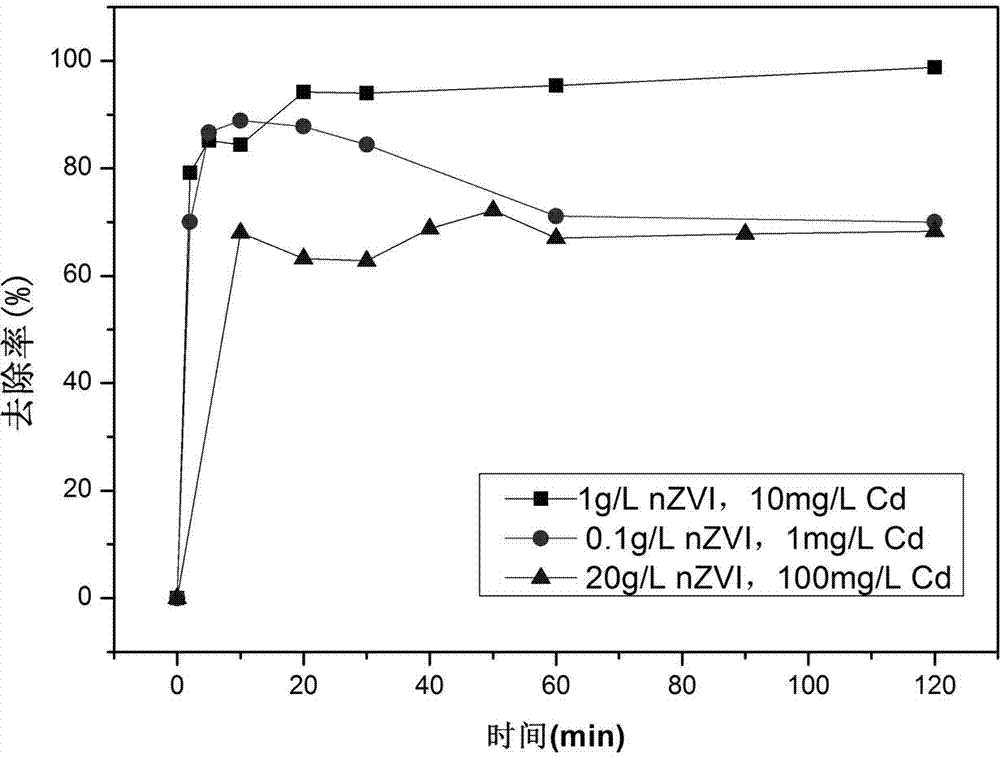
[0038]Using the device described in Example 1, the waste water is taken from river water with a certain metal cadmium content exceeding the standard, the cadmium concentration is 0.1 mg / L, and the pH of the water quality is in the range of 6.8-7.0. In this study, the volume ratio of the reaction chamber and the separation chamber of the secondary reaction device is designed to be 1.1:1, the hydraulic retention time is 60 min, the wastewater flow rate is 2-4 L / h, and the nano-zero-valent iron is added from the dosing well. 0.05-0.1 g / L, the reflux flow rate of nanometer zero-valent iron is twice that of the influent flow rate, and the dosing interval is 8 h. The cadmium-contaminated wastewater is fed from the water inlet of the reaction chamber, fully contacted with the nanometer zero-valent iron particles under the agitation of the agitator, and the pH and Eh of the mixed solution in the reaction chamber are monitored in real time. After sedimentation and separation of nanomet...
Embodiment 3
[0040] Using the device described in Example 1, in order to make the research effect more obvious, high-concentration cadmium-containing wastewater was prepared by adding standards, the influent cadmium concentration was 100 mg / L, and the pH was between 6.5-6.8. The volume ratio of the reaction chamber and the separation chamber of the secondary reaction device is designed to be 1.1:1, the hydraulic retention time is 60 min, the wastewater flow rate is 2-4 L / h, the nano-zero-valent iron is added from the dosing well, and the nano-zero-valent iron is refluxed The flow rate is 1-3 times of the water flow rate. This technological process studies the removal effect of several nanometer zero-valent iron dosages (10 g / L-20 g / L), and the dosage interval is 8 h. The cadmium-contaminated wastewater is fed from the water inlet of the reaction chamber, fully contacted with the nanometer zero-valent iron particles under the agitation of the agitator, and the pH and Eh of the mixed solutio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com