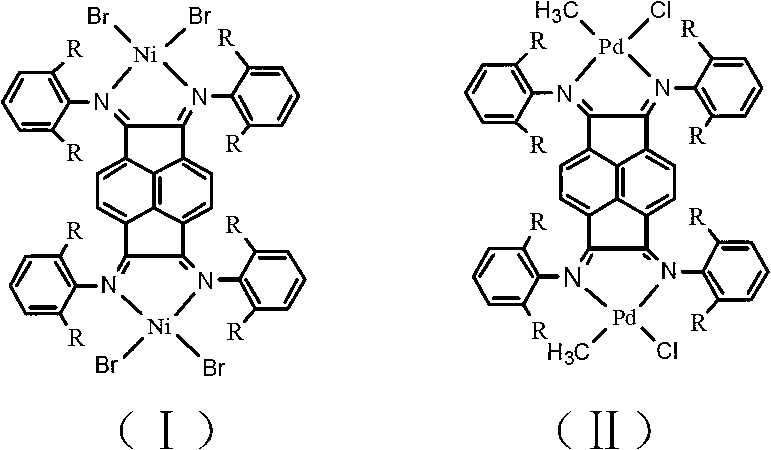
Binuclear acenaphthene (alpha-diimine) nickel/palladium catalysts for olefins, and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of olefin catalyst and diimine, which is applied in the field of dibinuclear acenaphthene (α-diimine) nickel/palladium olefin catalyst and its preparation, which can solve the problems of restricting industrial application, low molecular weight of polymerization products, and restricting the scope of industrial application, etc. , to achieve the effects of low cost, simple preparation process and high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
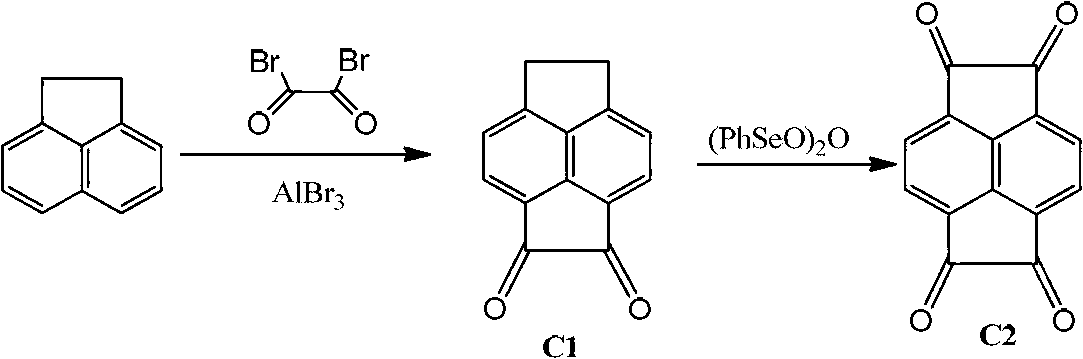
[0027] The preparation method of described dinuclear acenaphthylene (α-diimine) nickel / palladium olefin catalyst, the steps are as follows:
[0028] 1) Acenaphthene quinone undergoes a double acylation reaction to obtain compound C1, and C1 is then oxidized by benzene selenite anhydride to obtain compound C2:
[0029]
[0030] Using acenaphthylquinone as raw material, carbon disulfide as solvent, adding anhydrous aluminum bromide, under the condition of oxalyl bromide as oxidant, yellow solid C1 is obtained. Compound C2 was obtained through oxidation of benzene selenite anhydride.
[0031] 2) Compound C2 undergoes ketoamine condensation reaction with symmetrical aniline to obtain ligand C3 or C4: the raw material of acenaphthyldione obtained in the above reaction, acetonitrile as solvent, acetic acid as catalyst, α-diimine ligand is obtained through ketoneamine condensation reaction body.
[0032]
[0033] Under the condition of anhydrous and oxygen-free, C3 or C4 and ...
Embodiment 1
[0042] Synthesis of Ligand C3
[0043] Under nitrogen atmosphere and 85°C, after constant temperature for half an hour, add C2 (0.534g, 2.26mmol) into 70mL of acetonitrile, after half an hour, add 15mL of acetic acid, after two hours, add 2.08mL (9.94mmol) 2,6 - Diisopropylaniline, the solution turns reddish brown. After 24 hours, stop the reaction, stand still, and cool naturally. The upper layer is a dark red solution, and the lower layer is a bright red precipitate. The precipitate was washed with 5 × 50 mL of n-heptane, and then dried under vacuum at 70 °C for 48 h. 1.37 g of the product was obtained with a yield of 69.5%.
[0044] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 , δin ppm): 7.23 (s, 12H, Ar-H), 6.45 (s, 4H, Py-H), 2.91 (sept, 8H, CH (CH 3 ) 2 ),0.86-1.26(dd,48H,CH(CH 3 ) 2 ).
[0045] Elem.Anal.Calcd.For C 62 h 72 N 4 :C,85.27%;H,8.31%;N,6.42%.Found:C,83.40%;H,8.17%;N,6.08%.
[0046] ESI-MS: m / z 873.76 ([M+H] + .
Embodiment 2
[0048] Synthesis of Ligand C4
[0049]Add 0.310g (1.31mmol) of C2 into a 100mL single-neck round bottom flask, add 35mL of acetonitrile and 8mL of acetic acid, and reflux at 90°C for two hours. Then 0.66mL (5.24mmol) of 2,6-dimethylaniline was added and reacted for 24 hours. After the reaction, the solvent was drained, and the crude product was separated by column chromatography (dichloromethane, 1% triethylamine, silica gel) to obtain 0.598 g of the product with a yield of 70.5%.
[0050] 1 H-NMR (400MHz, CDCl 3 , δin ppm):7.11-7.16(d,6H,Ar-Hm),7.04-7.09(t,4H,Ar-Hp),6.66(s,4H,Py-H),2.06-2.12(s,24H, CH 3 ).
[0051] Elem.Anal.Calcd.For C 46 h 40 N 4 :C,85.15%;H,6.21%;N,8.63%.Found:C,85.22%;H,6.22%;N,8.23%.
[0052] ESI-MS: m / z 649.07 ([M+H] + ),671.11([M+Na] + ).
[0053] 2. Preparation of dinuclear acenaphthylene (α-diimine) palladium complex
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com