Adhesive composition, and surface protection film using it
A technology of surface protective film and composition, applied in the field of adhesive composition and surface protective film, can solve the problems of uncomfortable surface protective film, reduce the pollution resistance or transparency of the adherend, and achieve the effect of excellent pollution resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
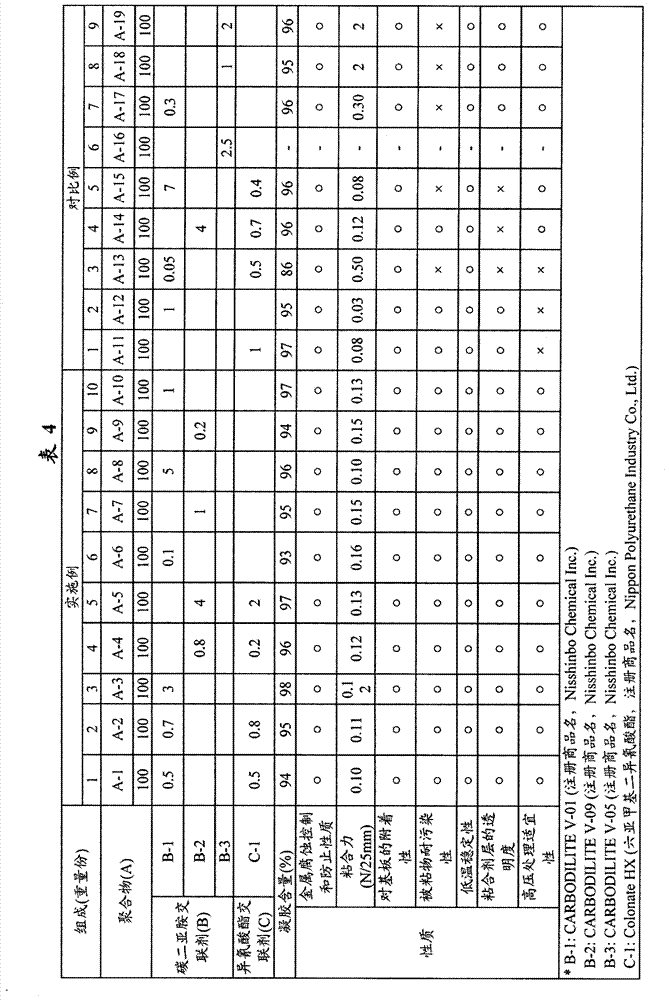
[0079] The effects of the present invention will be described with reference to the following Examples and Comparative Examples. However, it is to be understood that the present invention is not limited to the illustrated embodiments and may be implemented in various ways.
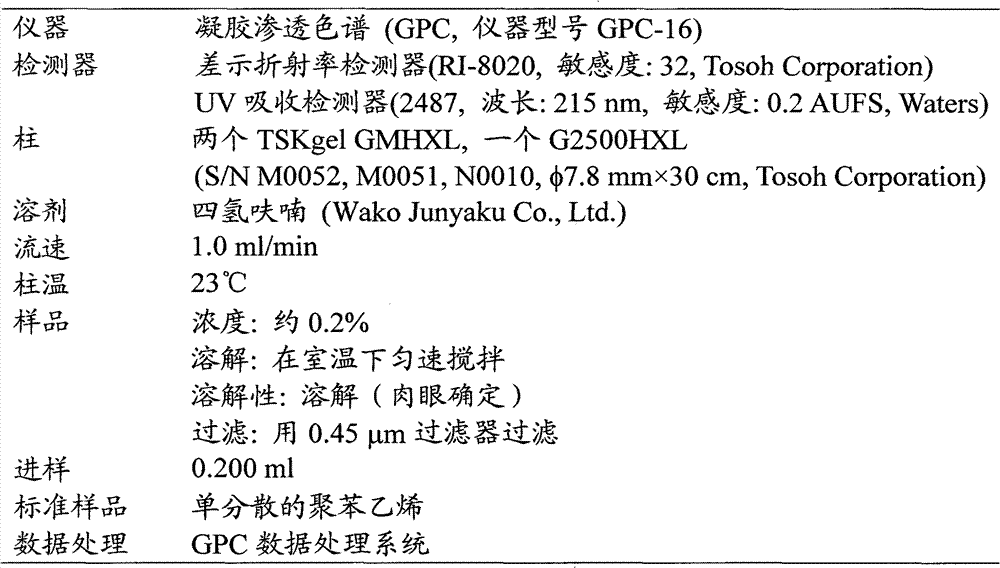
[0080] The solid content and viscosity of the solution in which the adhesive composition was dissolved and the weight average molecular weight of the acrylic polymer (A) were measured by the following methods.
[0081]
[0082] Measure approximately 1 g of polymer solution on a precisely weighed glass plate. The solution was dried at 105° C. for 1 hour and cooled to room temperature, after which the total weight and residual solids content of the glass plate were accurately measured. The mass of the glass plate is defined as X, the total weight of the glass plate and the polymer solution before drying is defined as Y, the total weight of the glass plate and the remaining solid content is defined as Z, a...
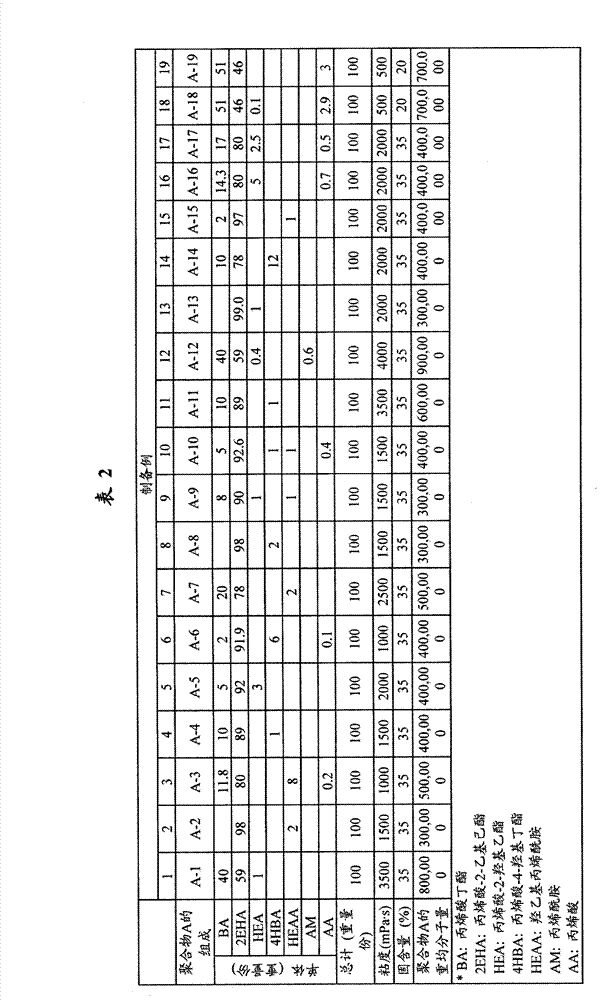
preparation example 1
[0092] 40 parts by weight of n-butyl acrylate (Nihon Shokubai, Co., Ltd.), 59 parts by weight of 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, 1 part by weight of 2-hydroxyethyl acrylate and 150 parts by weight of acetic acid The ethyl ester was placed in a flask fitted with a reflux condenser and a stirrer, and heated to 65°C under a nitrogen atmosphere. 0.1 part by weight of azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) was added, and 0.05 part by weight of AIBN was further added after 1 hour, followed by polymerization for 6 hours, and the mixture was kept at 65°C. After the polymerization was completed, 36 parts by weight of ethyl acetate was added, and the product was cooled to room temperature, thereby obtaining a solution of the copolymer (A-1). The solution of the copolymer (A-1) had a solid content of 35% and a viscosity of 3,500 mPa·s. In addition, the copolymer (A-1) had a weight average molecular weight of 800,000 g / mol. Measure the solid content, viscosity and weight-average molecular weight of copol...
preparation example 2 to 19
[0094] Solutions of polymers (A-2) to (A-19) were prepared by the same method as Preparation Example 1, except that each monomer was mixed according to the composition listed in Table 2. Subsequently, the solid content, viscosity and weight average molecular weight of the solutions of polymers (A-2) to (A-19) were measured, and the results are shown in Table 2. In Table 2, "BA", "2EHA", "HEA", "4HBA", "HEAA", "AM" and "AA" refer to butyl acrylate, 2-ethylhexyl acrylate, 2- Hydroxyethyl ester, 4-hydroxybutyl acrylate, hydroxyethyl acrylamide, acrylamide and acrylic acid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com