Biological sensitive detecting method for heavy metal cadmium in seawater
A heavy metal, cadmium pollution technology, applied in recombinant DNA technology, DNA/RNA fragment, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problem of no technical report
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
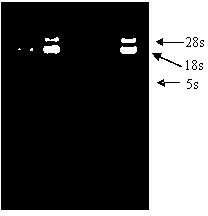
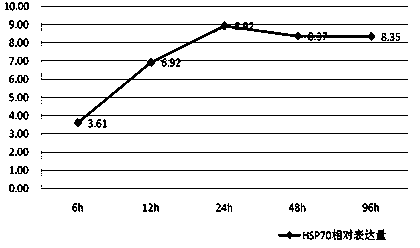
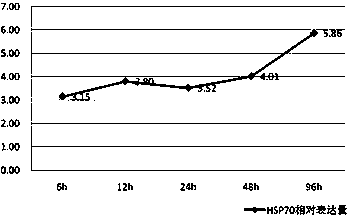
[0077] Cadmium ions (Cd 2+ ) Determination of the expression of HSP70 gene under the safe concentration of green clam
[0078] 1. Safe Concentration Experiment of Heavy Metal Cadmium Stress
[0079] The safe concentration refers to the highest concentration of toxic substances that can survive, grow and reproduce normally under the continuous action of pollutants. The currently widely used formula for calculating the safe concentration is:
[0080] Safe concentration = half-lethal concentration × application coefficient, namely SC = LC50 × f (Zhou Yongxin et al., 1983).
[0081] The selection of the application factor f is based on the toxicity of the poison, whether the physical and chemical properties are stable, whether it can accumulate in the organism, etc., and is generally selected in the range of 0.01~0.1. Under this concentration, the experimental organisms can survive normally under the stress of accepting toxic substances to the maximum, without affecting the vi...
Embodiment 2
[0144] Comparative test: The detection of metal ions in conventional water bodies is often done by spectroscopic techniques, such as ICP inductively coupled plasma emission spectroscopy. Although these analytical techniques can carry out more accurate quantitative determination of element content, there are disadvantages such as large initial investment and high operating cost. More importantly, these methods only measure the content of the total elements in the sample, and cannot measure indicators such as their valence state, existing form, and damage to organisms. For metal elements, the form that causes harm to organisms is often dissolved in the water body, and conventional quantitative analysis methods are difficult to analyze this data, which is not conducive to the degree of impact of water pollution on organisms. Effective analysis and evaluation. In addition, if the content of some heavy metal elements in the water body is low, the sample needs to be concentrated or...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com